99% of the world’s Internet traffic goes through undersea fiber optic cable system. As of the beginning of 2023, there are regarding 550 routes in the world Marine fiber optic cable is and is regarding to be put into operation with a total length of 1.4 million km, according to statistics of the telecom market research company Telegeography.
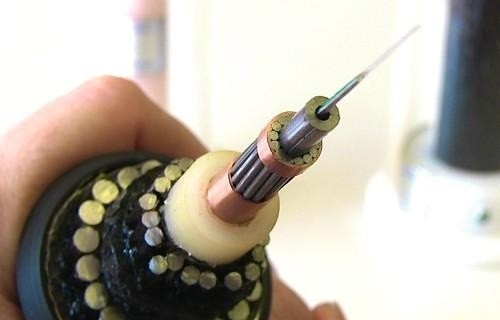
Modern underground cables use fiber optic technology. The lasers at one end follow thin glass fibers to the other end of the cable. These fiberglass are encased in protective layers of plastic and steel.
Over most of the cable’s length, the thickness is regarding 25 mm, weighing regarding 1.4 tons per km of length. Cables near shore are reinforced, thicker and heavier, because this is an area with a lot of human activity that can affect the cable.
|
|
|
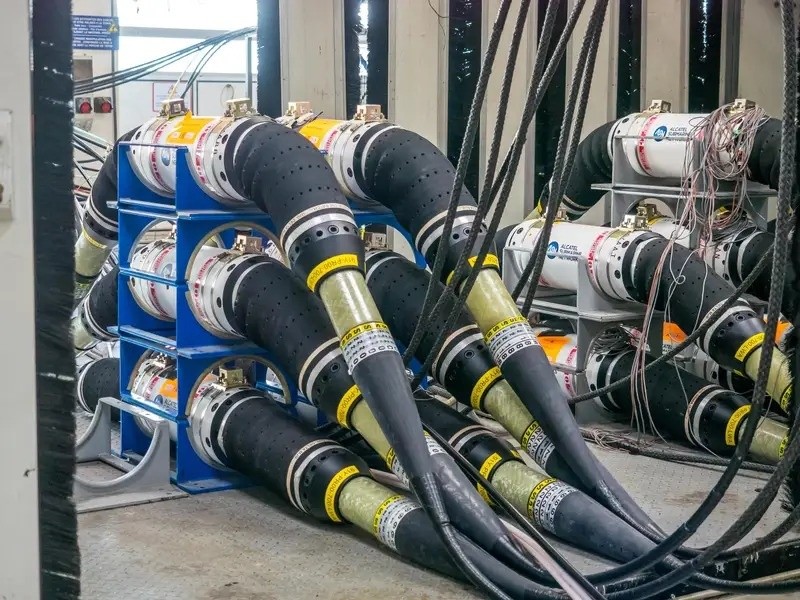
Inside the manufacturing process of undersea fiber optic cables, the infrastructure provides nearly all of the global Internet traffic. Photo: Business Insider. |
Much of the cable’s thickness and weight comes from the insulation and protection layers, and the glass fiber that carries the light signal is extremely thin, barely regarding the diameter of a human hair.
Why is the undersea fiber optic cable easy to break?
Although well-fortified, when the anchor of a ship as large as thousands of tons was hooked and dragged away, optical fiber Just like a thread, easily broken, a representative of Viettel Networks explained.
On average, there are more than 100 broken submarine cables each year. “Two-thirds of cable failures are caused by human activities, such as fishing nets and ship anchors getting caught in cables. The next cause is a natural disaster, earthquake or undersea landslide,” said Tim Stronge, vice president of research at TeleGeography.
There are also other rare incidents, such as in 2007, Vietnamese fishermen cut an underground cable to get composite materials to sell, losing 90% of the country’s Internet traffic at that time.
|
|
|
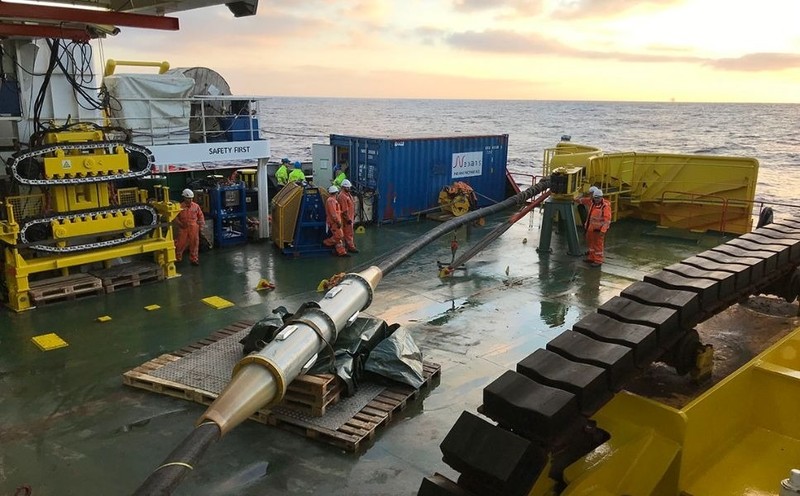
Internet fiber optic cable has multiple layers of core protection material, but it’s still easy to crash. Photo: IDG. |
However, Stronge also noted that these problems are not outside the calculations of telecommunications companies, they will use many different undersea cable routes to have a plan to compensate for traffic when one route has problems.
Up to now, undersea fiber optic cable is still an irreplaceable infrastructure for the global Internet. “Satellites can connect areas that aren’t already fiber-optic, but for most of the world, cable carries more data at a much lower cost than satellites,” according to TeleGeography.
How to fix fiber optic cable?
Fiber optic lines span many countries, even continents, and can lie at depths greater than Mount Everest, making repairs time-consuming. The first step is to find the location of the damage.
Normally, a pulse of light sent through the cable goes all the way to the other side. When the cable breaks, the fault will reflect the light pulse back, and engineers can measure the time it takes for the pulse to return to figure out where the break is. After the break location is determined, a cable ship will be sent to repair.
|
|
|
The damaged cable segments must be towed onto the boat for repair for several days. Photo: Nexans. |
The vessel pulled the damaged cable up from the seabed, removed the damaged part and connected the new cable. The cable is then tested and lowered back to the seabed. It sounds simple, but each step is time consuming. Depending on the extent of the damage, the cabling process can take tens of hours or even days.
Previously, repair ships took regarding 3-5 days to reach the cable, not to mention the waiting time for the license to be able to pass through many different seas. Weather conditions at sea are not always favorable, while cable repair requires the ship to remain in the same position on the sea surface throughout the repair period.
According to reports of fiber optic cable repairs, the repair time can last from a few weeks to several months, depending on factors such as cable location and extent of damage.