Mr. Huang came to the clinic with the main complaint of frequent falls recently; he suffered from poliomyelitis when he was a child, and his lower limbs were atrophied; After assessment it was clear that he was ‘post-polio’ and he was advised to use a long leg brace and a wheelchair for mobility.
He smiled wryly and said that he had actually heard these suggestions a long time ago, and he wanted to ask if there was any way to prolong the time of not using a wheelchair; Is that what you feel in your heart?” Later, on the advice of using full-body hydrotherapy training to enhance his physical fitness, he accepted the use of low-weight long-leg braces, leaving wheelchair considerations for later.
Polio is a viral infection. The scientific name is “poliomyelitis” (poliomyelitis). ; However, sporadic cases were discovered in 2022, and it seems that the curtain has not yet ended.
Some patients will experience permanent impairment of motor function following infection, affecting their mobility and daily life functions, which are collectively referred to as sequelae of polio. The above-mentioned patients will develop some new symptoms following regarding 20 to 30 years of adulthood; the common ones are easy fatigue and progressive muscle weakness; the medical community has also noticed this phenomenon and defined it as “post-polio syndrome” (Post-polio syndrome); in addition to frequent fatigue and movement disorders are prominent features, other factors such as sleep disruption, decreased endurance, neuropsychological deficits, sensory symptoms, and chronic pain are important factors that cause a decline in quality of life.
Balance of protection and training
Protection – assistive devices and supports
The loss of muscle strength will always face a time when medical technology cannot be reversed. At this time, the use of compensatory functions should be accepted; including assistive devices and braces, to maintain and improve the quality of life.
The key point in this regard is to maintain and prolong the patient’s ability to stand upright and walk; therefore, the considerations are like replacing the visible stent with a small-scale stent; using a lightweight or smaller assistive device to replace Large accessories. For example, the author has used orthopedic shoes, short leg braces, or knee braces to replace long leg braces for patients and meet the needs of patients. The advantage of this is that it is easy to wear, and the appearance is not easy to see under the cover of clothing; however, this method is not suitable for every patient; it must be evaluated individually. Examples of the use of brackets are as follows:
(Photo provided / Taiwan Rehabilitation Medicine Association)
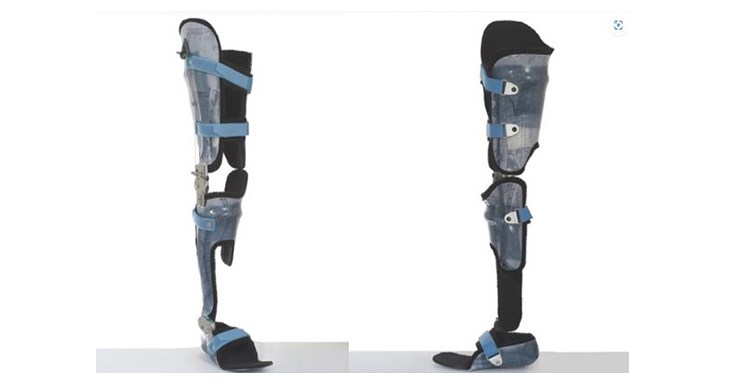
figure 1
It is a standard long leg brace commonly used by polio patients. It is designed to span two joints (knee, ankle) and three limbs (thigh, calf, and foot); the advantage is that it provides sufficient support, but the disadvantage is that it is a bit bulky and difficult to put on and take off. convenient.
(Photo provided / Taiwan Rehabilitation Medicine Association)
Figure 2 Advanced long leg support
Provide customization, tailor-made, and use lightweight materials, which can improve the above shortcomings.
(Photo provided / Taiwan Rehabilitation Medicine Association)
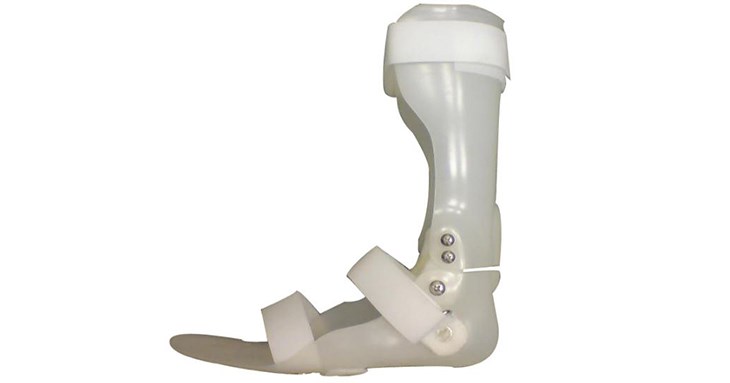
Figure 3 Knee joint support frame – knee bend support
For example, the knee bend caused by weakness of the thigh is one of the common polio lower extremity deformations; if the affected limb still retains some muscle strength, then the use of this type of knee brace may replace the long leg brace.
(Photo provided / Taiwan Rehabilitation Medicine Association)
Figure 4 Auxiliary wood of the ankle
For problems such as ankle joint instability, deformation, or combined unequal lengths of the legs, sometimes the combined use of ankle joints and corrective shoes, together with the use of inner and outer insoles, can also achieve improvement.
(The above pictures are used with the consent of the original author)
train
In general sports medicine, if muscle atrophy and muscle strength are insufficient, muscle strength training will be emphasized; but for post-poliomyelitis patients, muscle strength is no longer an inexhaustible “resource”, so Patients should use their muscle strength sparingly and efficiently. Because excessive use of muscles will increase the severity of post-poliomyelitis, patients will be advised at the beginning to keep their physical strength on necessary movements; in addition, make good use of assistive devices, such as crutches and wheelchairs as energy-saving measures; such as long-distance walking For strenuous activities, consider using a wheelchair instead.
The intent of these guidelines is to preserve the muscular ability to perform necessary activities and avoid excessive deterioration over time. However, every action in daily life depends on the use of muscles; if there is no exercise, it will cause a decline in physical fitness, and on the contrary, the function of life will decline even more. Therefore, for polio patients, it is still necessary to arrange appropriate exercise, which can increase endurance, increase confidence, and increase the range of daily activities. The following describes how patients can exercise themselves:
Introduction to Exercise for Post-Polio Patients
Exercise prescription is one of the standard post-polio treatments, along with rest, diet, energy conservation, and acclimatization. Among them, how to carry out proper exercise, maintain physical fitness, and at the same time not damage the weakened muscle groups is the most concerned and difficult thing for patients.
It is common for patients to get adverse effects due to their eagerness for good, excessive seriousness and exertion, causing sports injuries or overuse; therefore, it is recommended to exercise with an appropriate rhythm and a normal mind. For example, a horizontal stepper can start from 40 steps per minute, and following several days or weeks of adjustments, slowly increase to 110 steps per minute, instead of rushing to achieve more than 150 steps per minute for ordinary people at the beginning Level; and every time you exercise, there will also be warm-up and cool-down periods, with the gradual increase in speed, and then reach the set exercise intensity, and then gradually reach medium intensity (a little breathless but still able to complete a complete sentence) aerobic Exercise for 30 minutes.
In addition, no matter what kind of sports training, it is recommended to train every other day. The muscles and nerves of a post-polio patient need rest. Exercise should be moderate and not strenuous. Try not to sweat excessively, have shortness of breath, or experience excessive muscle pain at the end of your workout. The main training method is exhaustion, which is not suitable for post-poliomyelitis patients; however, many sports trainings on the market are aimed at exhaustion (overloading), so patients are reminded to pay more attention. Expert guidance and supervision familiar with post-polio is recommended at the outset.
The exercise prescription for post-polio syndrome also conforms to the 333 rule of exercise prescription promoted by the National Health Bureau, “exercise time is 30 minutes, exercise 3 times a week, and maintain a heart rate at regarding 130 beats.” But what is different from general exercise prescriptions is the choice of exercise types! Since polio patients are not suitable for aerobic exercise that bears weight on the lower limbs, such as jogging, brisk walking, going out to ride a bicycle, etc.; therefore, in the selection of exercise types, they will be biased towards the mode of lower limbs that do not resist gravity . Common aerobic exercises that can be used are listed below:
1. Horizontal stepper.
2. Hand flywheel machine (hand bicycle).
3. Swimming or water aerobics.
4. Walking training with proper support and protection.
The above-mentioned sports are biased towards endurance and cardiopulmonary function training; as for flexibility, you can do stretching exercises, stretching exercises or similar yoga at home, but it must be properly corrected. Pay attention to the degree of joint deformation of your limbs, and don’t force it. As for muscle strength training, since polio patients generally have overuse syndrome in their upper limbs, there are relatively few direct arrangements and suggestions for weight-bearing training.
In short, post-polio patients must find a way to strike a balance between rest and continuous exercise, avoid muscle fatigue and must continue to exercise to maintain physical fitness. If patients encounter difficulties and obstacles during exercise, professional rehabilitation department A physician can assist. Please cooperate with the diagnosis and treatment with peace of mind and maintain an independent and dignified life!
This article is provided by Taiwan Rehabilitation Medicine Association
Author of this article: Physician Chen Jiancheng (Director of Sports Rehabilitation Department of Zhenxing Hospital, Assistant Professor of Chang Gung University of Science and Technology, Director of Teacher Training Center of Zhenxing Hospital)
Article link https://www.top1health.com/Article/22/91084