
Teacher Association Rates Brombeer Projects Positively
Thuringian Teachers Advocate for Faster Education Reform Implementation Erfurt, Germany — The thuringian Teachers’ Association (TLV) has voiced its support for the initial steps taken

Thuringian Teachers Advocate for Faster Education Reform Implementation Erfurt, Germany — The thuringian Teachers’ Association (TLV) has voiced its support for the initial steps taken

Amy Winehouse: A Genius Lost Too Soon, Her Enduring Impact on American Music May 1, 2025 A Soulful Voice Silenced: Remembering Amy Winehouse Amy Winehouse,

Adidas AE1 Low Basketball Shoes Gain Traction in online Marketplaces [CITY,STATE] – The Adidas AE1 Low,the low-cut version of Minnesota Timberwolves star Anthony Edwards’ signature
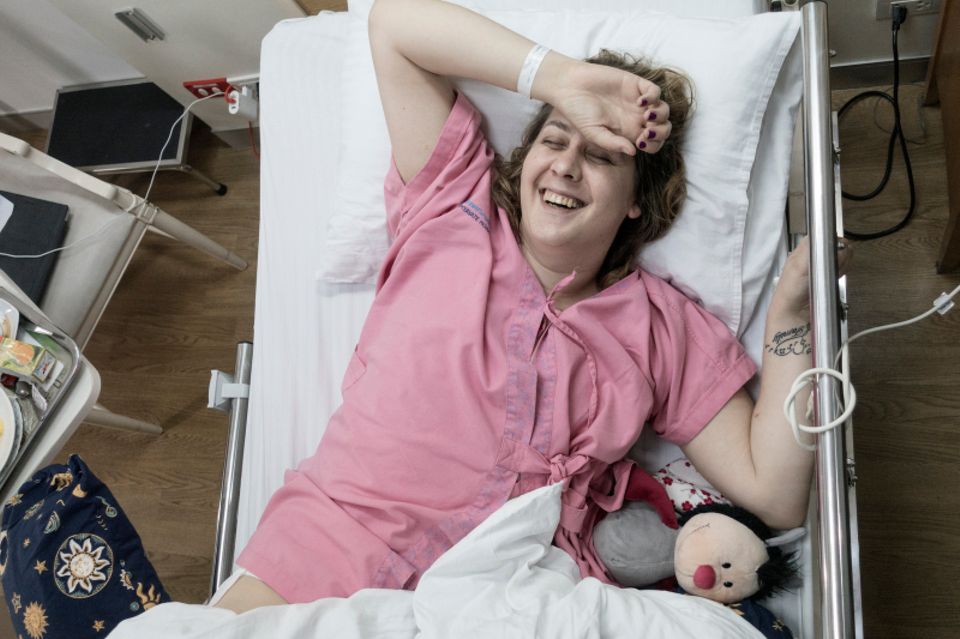
Transgender Youth treatment guidelines Released in Germany, Sparking Debate and Hope BERLIN – In a move hailed as a “milestone” for transgender youth care, a

Thuringian Teachers Advocate for Faster Education Reform Implementation Erfurt, Germany — The thuringian Teachers’ Association (TLV) has voiced its support for the initial steps taken

Amy Winehouse: A Genius Lost Too Soon, Her Enduring Impact on American Music May 1, 2025 A Soulful Voice Silenced: Remembering Amy Winehouse Amy Winehouse,

Adidas AE1 Low Basketball Shoes Gain Traction in online Marketplaces [CITY,STATE] – The Adidas AE1 Low,the low-cut version of Minnesota Timberwolves star Anthony Edwards’ signature

Transgender Youth treatment guidelines Released in Germany, Sparking Debate and Hope BERLIN – In a move hailed as a “milestone” for transgender youth care, a

© 2025 All rights reserved