A thrombus, often called a blood clot, refers to a lump of blood that has hardened in a blood vessel. When a disease is caused by a blood clot, it is called thrombosis.
Thrombosis is largely divided into arterial thrombosis and venous thrombosis. A wide variety of symptoms can occur depending on whether a blood clot is formed in an artery that carries oxygen from the heart to the rest of the body or a blood clot in a vein that carries blood back to the heart.
“Arterial thrombosis”
Arteries with relatively high blood flow do not easily stagnate, making clots difficult to form, but once they do occur, they often have serious consequences. Since most arterial thrombosis is an emergency that can lead to death if not treated promptly, it is important to visit a hospital as soon as possible if suspicious symptoms appear.
When blood clots form in the arteries, the symptoms of ischemia occur mainly when there is insufficient peripheral blood flow due to insufficient blood supply to body tissues.

1. Acute myocardial infarction
‘Acute myocardial infarction’ is a disease in which a blood clot suddenly blocks the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart, and the blood is not supplied to the heart muscle, causing the muscle to die. Myocardial infarction can lead to death if not treated promptly. Therefore, it is good to know the symptoms of acute myocardial infarction.
2. Stroke
A ‘stroke’ can occur when a blood clot blocks a blood vessel that supplies blood to the brain. Brain cells are damaged even if there is no blood supply for a few minutes, and once dead brain cells cannot be revived. Therefore, when a stroke occurs, it is necessary to quickly read the signals sent by the body and seek medical attention immediately. The main symptoms of stroke include headache, loss of consciousness, motor abnormalities, sensory abnormalities, personality changes, vision loss, and epileptic seizures.
3. Pulmonary Thrombosis
‘Pulmonary thrombosis’ is mainly caused by a blood clot that occurs in a deep vein in the arm or leg that blocks the pulmonary artery. When the blood supply to the lungs decreases, oxygen and carbon dioxide cannot exchange smoothly in the lungs, which can lead to hypoxia. Since the lungs are an organ for oxygen exchange, pulmonary thrombosis usually causes shortness of breath. In addition, chest pain and loss of consciousness appear.
4. Acute Peripheral Artery Occlusion
A disease that occurs when a blood clot blocks the peripheral arteries going to the extremities of the body, such as arms and legs, is called ‘acute peripheral arterial occlusion’. When peripheral arteries are occluded, limb necrosis can occur, leading to amputation. If you experience symptoms such as pain, paleness, or cold in your arms or legs, you may have this disease.
“Venous thrombosis”
The possibility of thrombosis of veins is relatively high because the blood easily stagnates due to aging, improper lifestyle, varicose veins, and occupations that take one position for a long time. Venous thrombosis is often not an emergency compared to arterial thrombosis.
When a thrombosis occurs in a vein, the blood reaches the periphery but does not return to the heart, resulting in congestion or congestion.
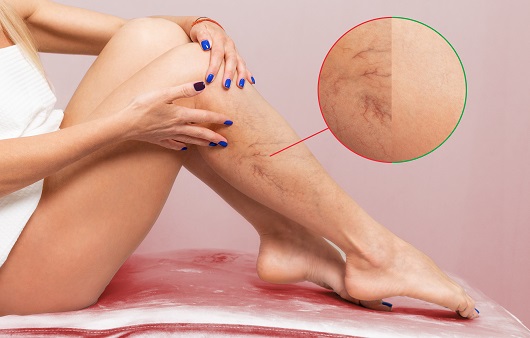
1. Deep vein thrombosis
Blood from the arteries enters the heart through a deep vein. Deep vein thrombosis is a disease in which the blood that is supposed to return to the heart cannot return due to blockage of a deep vein due to a blood clot. This disease can occur in any vein in the body, but it occurs most often in the veins in the legs that are furthest from the heart. Leg swelling and leg pain are the main symptoms of deep vein thrombosis. In the case of deep vein thrombosis, it can be a cause of pulmonary thrombosis, and when both diseases are present, the risk of death is very high.
2. Portal vein thrombosis
‘Portal portal vein thrombosis’ is a disease that causes problems due to the formation of blood clots in the portal vein, the blood circulation path of the liver and internal organs. Most of the symptoms are asymptomatic, but in some patients, ascites, which accumulates fluid in the abdomen, symptoms such as swelling of the body may appear.
“How is the treatment?”
There are various methods of treating thrombosis, but antithrombotic drugs such as antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants are the representative treatments. These antithrombotic agents play a role in inhibiting platelets and blood clotting factors, which are requirements for the formation of blood clots. Professor Lee Young-bae of Neurology (Gachon University Gil Hospital)explained in an interview with Hidak, “Antithrombotic drugs are drugs that dissolve or prevent blood clots from forming in blood vessels.” He advised, “If you take antithrombotic drugs, you need to be careful not to injure them because they inhibit hemostasis.”
(See Hidak YouTube: Antithrombotic, a lifelong drug?)
Help = Professor Youngbae Lee (Gil Hospital, Gachon University)
