[VoiceofHopeFebruary192023](Editor: Guo Qiang) The handsome gourmet Chen Hong recently appeared on the program and mentioned that in 2019, he found that the floaters were getting worse, but he didn’t seek medical treatment immediately. Then the retina of his left eye was detached, and he was rushed to the hospital for surgery and almost lost his sight. What exactly is retinal detachment? What are the precursors? Who are the high-risk groups?
Where is the retina?
Yahoo news reports that the retina is attached to the inner surface of the back wall of the eyeball and is composed of 10 layers of thin and slender photoreceptor cells and nerve fibers. play an indispensable role. And below it is the choroid, which is responsible for supplying oxygen and nutrients to the retina.
Retinal detachment is a condition in which the sensory retina of the retina separates from the underlying pigment epithelium. This situation is similar to wallpaper peeling off from the wall from top to bottom, and the range will gradually expand. After the retina is detached, because the nutrients delivered by the pigment epithelium cannot be obtained, the visual function will gradually degenerate, eventually leading to blindness, which is one of the few emergencies in eye diseases.
In the United States, the incidence of retinal detachment is approximately 1 in 10,000 per year. However, Taiwan has 16.4 retinal detachments per 100,000 people, the highest in the world; and 18.7 people between the ages of 20 and 29, which is 13 times that of the same age group in the Netherlands. The high rate of retinal detachment in Taiwan is closely related to the high rate of myopia.

What causes retinal detachment? Which categories can be divided into?
According to the cause of retinal detachment, it can be divided into three types: tear, traction and exudation.
Rhegmatogeneous retinal detachment: A hole appears in the retina, allowing the vitreous body in the eyeball to pour into it, resulting in detachment of the retina and pigment epithelium. It is the most common clinically and is closely related to high myopia and eyeball aging. A small number of people are genetically inherited.
Traction retinal detachment: Abnormal proliferation of fibrous tissue on the surface of the retina causes contraction, triggering traction forces that separate the retina from the pigment epithelium. The most common cause is proliferative diabetic retinopathy, or pulling on the vitreous from trauma to the eyeball, and is the most difficult to treat.
Exudative retinal detachment: When the inside of the eyeball is inflamed (such as uveitis, retinitis, intraocular tumor, etc.), a large amount of fluid will leak out from the blood vessels and accumulate under the retina, causing retinal detachment, which is relatively rare in clinical practice.
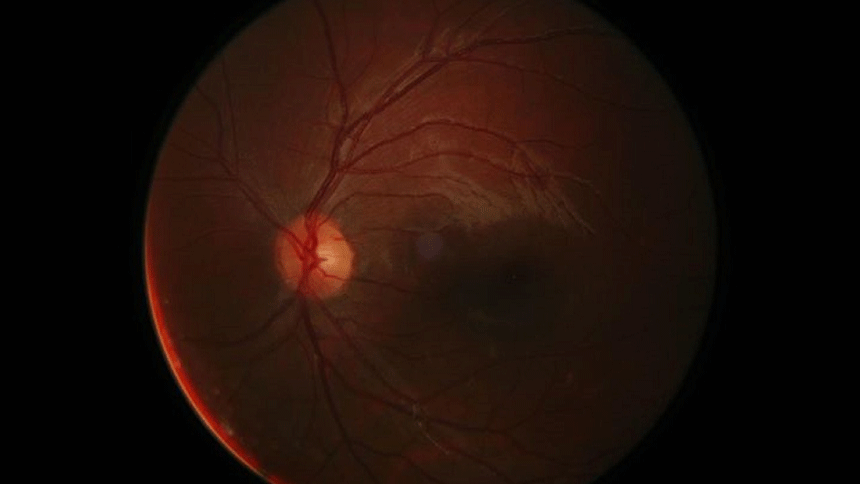
When retinal detachment occurs, the main symptoms are almost the same as those of floaters, but because it is neither painful nor itchy, and the initial vision will not be lost, patients often delay seeking medical treatment, so special attention must be paid.
Sudden floaters:In the early stage of retinal detachment, the hemorrhage and inflammatory substances caused by the retinal break are formed as dots floating in the vitreous. Patients will feel that floating black spots and clouds suddenly appear in the vision. But not all floaters cause retinal detachment, most are still caused by aging.
See the flash:The sensation of seeing a flash of light can be felt even with the eyes closed, as the retina is stimulated by pulling or a hole has formed.
Visual field defect:If part of the retina has been detached, you will see black shadows or feel that a whole black curtain covers your vision. Some people will feel that objects are distorted or there are shadows in your peripheral vision.
blurred vision:When the retinal detachment is severe, the central vision will significantly decrease, and even gradually lose vision.

Middle-aged and elderly people over 50 years old, people with myopia above 500 degrees, people who have suffered eyeball trauma, vitreous degeneration, retinitis, uveitis and other eye diseases, people who have received eye surgery, and people with a family history of retinal detachment , People who have had retinal detachment, and diabetic patients are all high-risk groups for retinal detachment. In addition, when riding a roller coaster or engaging in extreme sports, the head shakes rapidly, or the eyes turn too fast when rolling the eyes, which may stretch the retina, increasing the burden and risk.
The treatment of retinal detachment is mainly surgery, and different surgical methods are selected according to the patient’s condition and needs.
Preventive treatment before retinal tear occurs before detachment
Laser photocoagulation therapy: When a retinal tear occurs, laser light is used to burn the surrounding area, and the resulting scar allows the retina to attach to the underlying tissue. It is a preventive treatment for retinal detachment due to a tear.
Cryotherapy: Use low temperature to freeze the area around the retinal hole, causing an inflammatory reaction to cause a scar to seal the hole and fix the retina.
Gas omentopexy: This method can be used when the situation is relatively simple in the early stage of stripping. Inject a gas that can expand in the eyeball into the vitreous body of the eyeball, and use the surface tension of the gas to seal the hole, while the subretinal liquid can be absorbed by itself, and the omentum will stick back, and then use laser or freezing to fix the omentum. The success rate can reach Eighty percent.
Scleral crimping: This is the most commonly used method. The principle is to implant a piece of silicone gel on the sclera to seal the omental tear from the outside to the inside, so that the omentum can stick back. The general success rate can reach 95%.
Vitrectomy: Insert the resectator into the eyeball to remove the sick vitreous, suck out the subretinal fluid in the eye, make the retina stick back, and then seal the hole with laser light. It is a complicated operation with high risks.
Under normal circumstances, the two eyes of a person have complementary functions. When looking at the same target at the same time, the images formed by the two eyes will produce a fusion effect in the brain. The visual field defect of one eye can be filled by the visual field of the other eye, so it is difficult to detect the abnormality . If you want to detect abnormal vision early, you can usually “open one eye and close the other eye” to see if there is any difference in the visual field of the two eyes. If you find that a certain area in the visual field becomes dark or black, you should immediately seek medical advice s help.
Editor in charge: Li Zhi
This article or program is edited and produced by Voice of Hope. Please indicate Voice of Hope and include the original title and link when reprinting.



