2023/01/01 11:16 Weather news
Earthquakes centered on land in the Kanto region and some earthquakes in the area from Kinki to Shikoku are conspicuous. There was one earthquake with a seismic intensity of 3 or higher. (Tally from December 26th to January 1st at 10:00)
Japan: Eastern Kochi Prefecture seismic intensity 3 seismic intensity 3 for the first time in 19 years
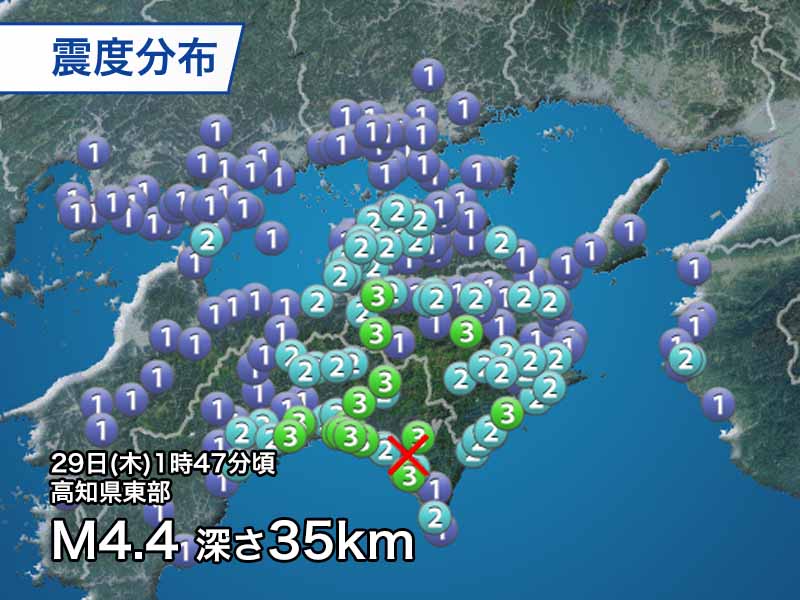
It was the first time in regarding 19 years since August 2003 that an earthquake with a seismic intensity of 3 or higher centered in eastern Kochi Prefecture. The mechanism of the earthquake is analyzed as a reverse fault type with a pressure axis in the northeast-southwest direction.
Most of the damage caused by earthquakes in Kochi Prefecture is caused by huge earthquakes along the Nankai Trough. Although it is believed that there is a fault zone extending northeastward near the epicenter of this quake, the detailed activity is unknown. There is no record of major damage caused by land earthquakes like this one in Kochi Prefecture.
Epicenters where anomalous seismic regions are likely to appear

Other than the southeastern offshore of Mie Prefecture, similar deep earthquakes often occur in the Sea of Okhotsk, the Sea of Japan, the southern offshore of Tokaido, and the sea near Torishima, and once every few years, an earthquake with a magnitude of 6 or more also occurs.
Even if the tremors were small near the epicenter, strong tremors were transmitted far away. Mie Prefecture, which is close to the epicenter, did not have any locations where felt earthquakes were observed, and the maximum seismic intensity of 4 was observed in Ibaraki and Fukushima prefectures. A large-scale earthquake may cause tremors exceeding seismic intensity 5 lower, so caution is required.
Japan: Seismic intensity 4 earthquake in northeastern Chiba Prefecture

It is the first time in two years and seven months since May 2020 that an earthquake centered in the northeastern part of Chiba Prefecture occurred. The mechanism of the earthquake is analyzed as a reverse fault type with a pressure axis in the northwest-southeast direction.
Relatively large earthquakes have occurred in the northeastern part of Chiba Prefecture, in the area close to Ibaraki Prefecture, and in the vicinity of this epicenter. In 2019, we observed a strong shaking with a maximum seismic intensity of lower 5 due to a magnitude 5.1 earthquake with an epicenter a little further inland than this time.
Japan: A strong earthquake in January this year with a seismic intensity of 4 in Hyuga Nada

This is the first earthquake with a seismic intensity of 4 or higher with its epicenter in Hyuga-nada since January 22, 2018. The mechanism of the earthquake was analyzed as a normal fault type with a tension axis in the east-west direction.
The epicenter is further south than the magnitude 6.6 earthquake that occurred in January, and the area is close to the magnitude 7.0 earthquake that occurred in 1961.
World: The world is also quiet at the end of the year, the largest earthquake is M6.0

In the early hours of Thursday, December 29 (Japan time), an earthquake estimated to have a magnitude of 6.0 and a depth of approximately 10km occurred in the South Pacific Ocean near Vanuatu. The earthquake mechanism is analyzed as strike-slip type. Since the epicenter was far from the island, there was no impact from the shaking.
Various types of earthquakes occur in the sea near Vanuatu because the boundary between the Pacific plate and the Australian plate is complicated. The epicenter of this time is a little away from the region where the earthquakes at the plate boundary are concentrated, so it seems that the earthquake is caused by the rupture inside the plate.





Reference materials, etc.
*Information on earthquake sources and seismic intensity in Japan is from the Japan Meteorological Agency unless otherwise specified. Overseas epicenter information is from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) unless otherwise specified. There may be differences in hypocenter information depending on the publishing organization.

