2022/07/24 10:35 Weathernews
Earthquakes on the Pacific side of the Tohoku and Kanto regions continue to stand out, with earthquakes occurring on the Noto Peninsula and inland areas of western Japan. Two earthquakes with a seismic intensity of 3 or higher occurred. (Aggregation from July 18th to 24th at 10:00)
Domestic: M5.3 in Aomori prefecture, maximum seismic intensity 4
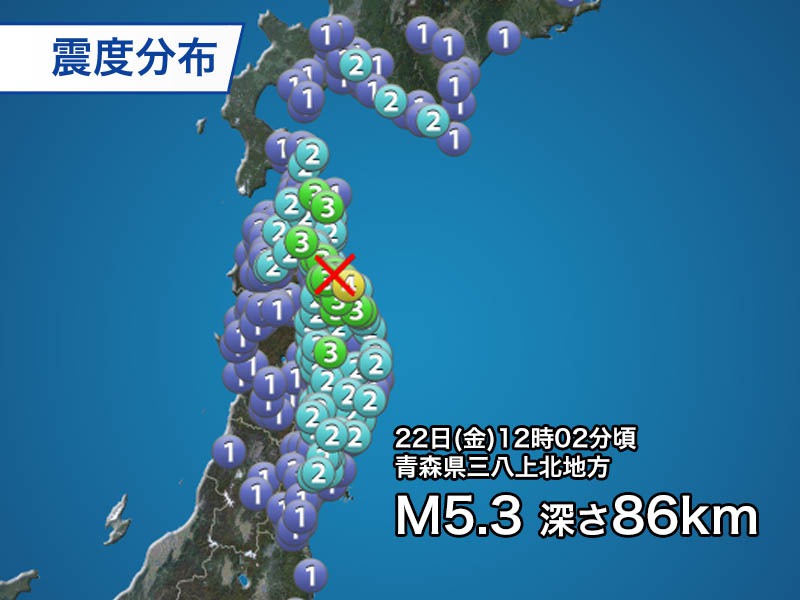
This is the first earthquake with a seismic intensity of 4 or higher originating in the Kamikita district of Aomori prefecture in regarding three years since August 2019. The mechanism of the earthquake is analyzed as a normal fault type with a tension axis in the north-south direction.
In the Sanpachi Kamikita district of Aomori prefecture, there are many earthquakes in the area of 80 to 100 km in depth and the area of regarding 30 km deeper than that due to the subduction of the plate, and this earthquake is regarding 90 km, which is the shallower one. Although the magnitude and depth of the earthquake are similar to those of the 2019 earthquake, the mechanism is different, and it seems that the force was exerted in the direction in which the plate subducted and perpendicular to it.
Domestic: Seismic intensity 3 at the epicenter in eastern Kanagawa Prefecture

The mechanism of the earthquake is analyzed as a reverse fault type with a pressure axis in the west-northwest-east-southeast direction. This is the first earthquake with a seismic intensity of 3 or higher that originated in the eastern part of Kanagawa prefecture in February this year. The February earthquake has a deep epicenter of 100 km, and if we limit it to the same shallow type of earthquake as this time, it will be the first earthquake with a magnitude of 4.6 and a depth of 26 km that occurred in February 2016.
At a depth of around 30km in the eastern part of Kanagawa Prefecture, earthquakes with a magnitude of around 5 occasionally occur. A magnitude 6.3 earthquake occurred in November 1923, which is thought to be an followingshock of the Great Kanto Earthquake or related activities.
Even in the assumption of an earthquake directly under the Tokyo metropolitan area by the Cabinet Office, earthquakes with epicenters in Kanagawa Prefecture are included, and daily countermeasures are indispensable.
Domestic: Earthquake with seismic intensity 2 in the Osaka Plain

Although the frequency of earthquakes is not so high in southern Osaka, there are occasional earthquakes with a magnitude of around 3 and a depth of around 10 km. In August 2000, a rather large earthquake with a magnitude of 4.1 occurred, resulting in a maximum seismic intensity of 4.
The Uemachi fault zone, which is distributed from north to south, is known in the Osaka Plain. Although there has been no noticeable activity in recent years, the government’s Headquarters for Earthquake Research Promotion has set a 2-3% probability of an earthquake with a magnitude of 7.5 within the next 30 years. If a direct earthquake occurs due to the Uemachi fault zone, there is a concern that the city of Osaka will be seriously damaged, so be careful.
In the past there was a M6.0 earthquake

Most of the earthquakes are concentrated in the depth of regarding 10km even in the depth of the east-west cross section. There are few occurrences deeper than 20km, but slightly more deeper than 100km. Earthquakes that occur near the boundary between the Pacific and Eurasian plates and inside the Pacific plate.
Most deep-focus earthquakes have a magnitude of around 4, but in May 2014, a large-scale earthquake with a magnitude of 6.0 occurred. In this earthquake, a maximum seismic intensity of 5 lower was observed in Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo, and a seismic intensity of 3 to 4 was observed in a wide area of the Kanto region, causing damage such as injuries.
World: M5.9 earthquake in Myanmar
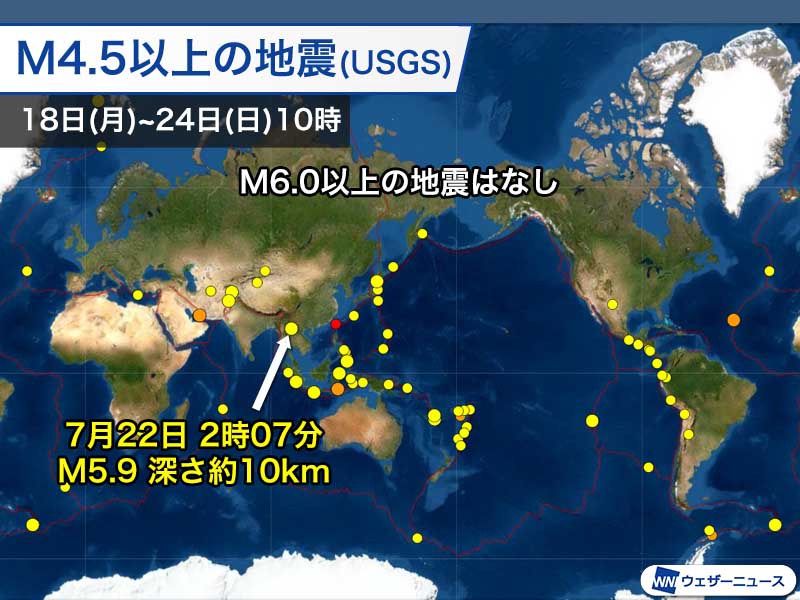
An earthquake with a magnitude of 5.9 and a depth of regarding 10 km occurred in the eastern part of Myanmar before dawn on the 22nd (Friday) of Japan time. Since the epicenter was in the mountains, it seems that there was no damage due to the shaking. The mechanism of the earthquake is analyzed as a strike-slip type.
Myanmar is located on the border between the Eurasian plate and the Indian plate and is an earthquake-prone area. A magnitude 6.9 earthquake struck near the epicenter in 2011, causing many human casualties. In addition, large earthquakes in the latter half of magnitude 7 often occur throughout Myanmar, and the 1988 magnitude 7.7 earthquake killed more than 700 people.
M5.5 near the Strait of Gibraltar

The Strait of Gibraltar is the strait that separates Europe and Africa, and is also the boundary between the Eurasian plate and the African plate. Since it is not a subduction zone, there are many strike-slip earthquakes, and the magnitude 6.3 and 2004 magnitude 6.4 earthquakes that occurred in 2016 have the same mechanism.
Since there are many shallow earthquakes, if it occurs near the land or in the land area, it will cause strong shaking near the epicenter.




Reference materials, etc.
* Information on the epicenter and seismic intensity in Japan is from the Japan Meteorological Agency unless otherwise stated. Information on overseas epicenters is from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) unless otherwise stated. The epicenter information may differ depending on the issuing organization.



