A year of Remarkable Discoveries: Exploring 2024’s Weirdest New Species
Table of Contents
- 1. A year of Remarkable Discoveries: Exploring 2024’s Weirdest New Species
- 2. Fishy Fungi
- 3. Three new Species of Fishy Fungi Discovered
- 4. Russula: A Diverse Genus
- 5. Newly Discovered Mushroom Species Smell Like Seafood
- 6. The Pungent World of Fungi
- 7. The Vampire Hedgehog: Unveiled from the Archives
- 8. Ghost Palms: Ethereal Beauty from the Past
- 9. Ghostly Rattan Discovered in Borneo Rainforests
- 10. Pirate Spiders Discovered on Remote Island
- 11. Kermit the Bony Salamander
- 12. Ancient ‘Kermit’ Fossil Finally Discovered, 270 Million years Later
- 13. New Species Discovered in the Peruvian Amazon
- 14. A Unique Amphibian: The “Kermit” Frog
- 15. Other Incredible Discoveries
- 16. the Biodiversity Crisis
- 17. Digital detox: Is It Really Better for Your Mental Health?
 Hylomys macarong (Credit: Alexei V Abramov)” class=”wp-image-1001″/>
Hylomys macarong (Credit: Alexei V Abramov)” class=”wp-image-1001″/>
The year 2024 has been a banner year for bizarre biological discoveries. Deep-sea expeditions have yielded a treasure trove of unusual creatures,including a new species of octopus and over 100 previously unknown marine organisms. Hidden amongst these fascinating finds are some truly remarkable examples of nature’s weird and wonderful creations.
Fishy Fungi

One such discovery is a group of fungi that bear an uncanny resemblance to fish. These unusual organisms were found in a remote corner of the ocean,adding to the growing list of bizarre and fascinating life forms that call the deep sea home.
Three new Species of Fishy Fungi Discovered
Scientists atKew Gardens have announced the discovery of three new fungi species. the intriguing species are notable for their unusual fishy aroma. These discoveries are part of a larger effort by Kew scientists and their collaborators to document and classify plant and fungal life from around the world. Over the past year alone, they have catalogued approximately 149 new plant species and 23 new fungi.
Russula: A Diverse Genus
The new fungi belong to the Russula genus, a group that encompasses roughly 800 known mushroom species. Russula mushrooms are characterized by their brittle gills and stems that resemble apple flesh.Their hyphal networks,the thread-like structures that extend through the soil,often form mutually beneficial partnerships with trees. Interestingly, some Russula species, including these newly discovered ones, produce distinct and sometimes strong odors.Newly Discovered Mushroom Species Smell Like Seafood
Scientists have identified three new mushroom species, each with a unique and surprising aroma: they smell distinctly of seafood. These fungi, all members of the Russula genus, produce trimethylamine compounds, the same chemicals responsible for the fishy odor of shrimp and other seafood.
One of the new species, Russula lapponica,was discovered in the mixed woodlands of Lapland,spanning Sweden,Norway,and Estonia.Another, Russula neopascua, makes its home among alpine willows in the high Rockies of Colorado and Montana. The third, Russula olympiana, thrives in the coniferous forests of the Pacific Northwest and British Columbia.
The Pungent World of Fungi
These new discoveries highlight the vast diversity within the fungal kingdom. While many mushrooms are known for their earthy or woodsy smells, these newfound species demonstrate the surprising range of aromas that fungi can produce. The strong fishy scent of these mushrooms is a testament to the complex chemical processes at work within these fascinating organisms.
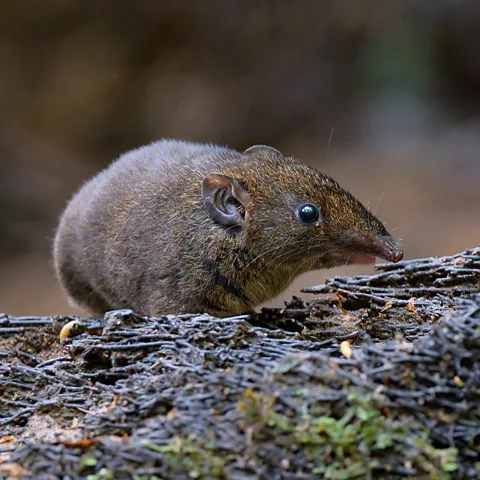

The world of zoology is constantly evolving, with new species being discovered even in this age of scientific advancement. Recently, a unique little creature has emerged from the shadows of a museum archive, a discovery that highlights the fascinating biodiversity hidden right beneath our noses.
The Vampire Hedgehog: Unveiled from the Archives
Meet the Hylomys macarong , a soft-furred hedgehog with a surprising twist: long, fang-like teeth earned it the moniker “vampire hedgehog” due to the Vietnamese word “Ma cà rồng” meaning “vampire”. This diminutive mammal, measuring just 14cm long, resembles a cross between a mouse and a shrew. Its discovery in Vietnam is not entirely new; the species was first captured in 2009 by the Russian Vietnamese Research Centre,but the specimen remained unidentified,tucked away in the archives of the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural history in Washington DC since 1961.

The rediscovery of the vampire hedgehog, along with four other new species of soft-furred hedgehogs, sheds light on the incredible biodiversity within Southeast Asia. it also serves as a reminder that even in well-studied areas, hidden wonders await discovery.
Ghost Palms: Ethereal Beauty from the Past
Moving from the forests of Southeast Asia to the ancient landscapes of South America, we encounter another fascinating rediscovery: the “Ghost Palms”. These ancient palm trees, once thoght to be extinct, have reappeared after decades of being lost to science.
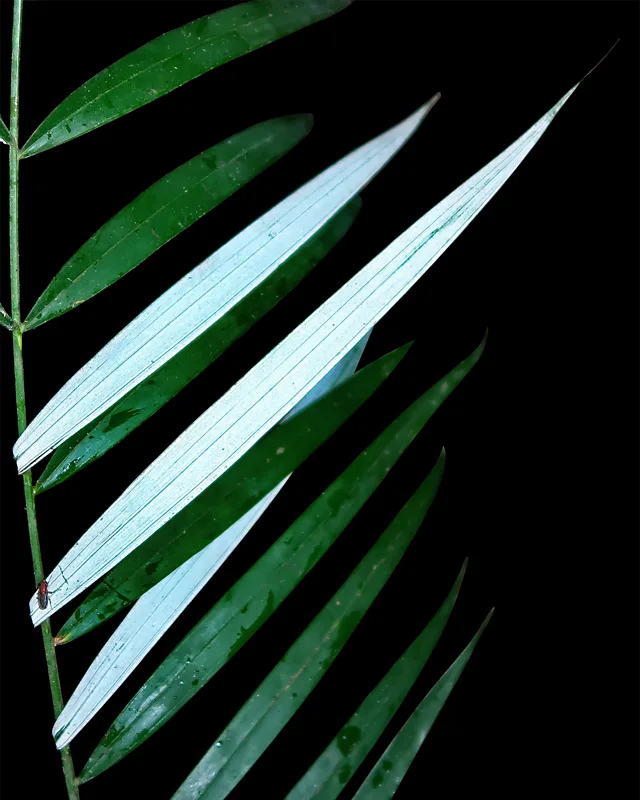

Why the evocative “Ghost Palm” moniker? These remarkable trees are truly remnants of a bygone era,their fossilized remains offering a glimpse into prehistoric ecosystems. Their rediscovery offers a unique prospect to study evolutionary patterns and understand the changing landscapes of our planet.
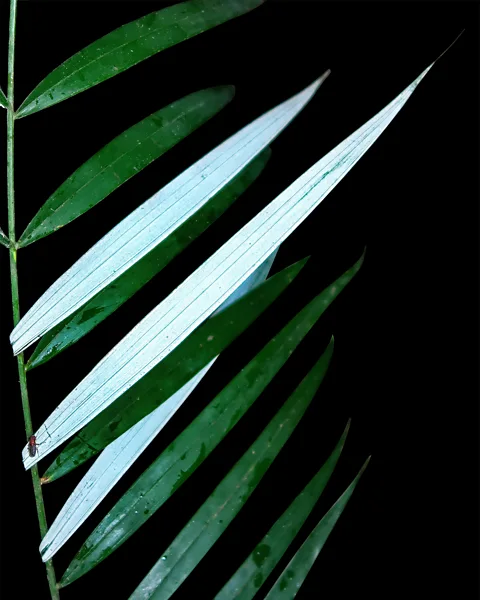

Ghostly Rattan Discovered in Borneo Rainforests
Deep within the protected rainforests of Malaysia and Indonesia, a new species of rattan palm has been unveiled, adding to the biodiversity of this fascinating region. Locally known as “wi mukoup” or “wee mukup,” the plant’s ghostly appearance has earned it the official scientific name *Plectocomiopsis hantu* – “hantu” being the Malay and Indonesian word for ghost. Until recently, this rattan, characterized by its eerie white-underside leaves and gray stems, lacked a formal scientific description. The discovery, made by researchers at the Royal Botanic Gardens, kew, highlights the incredible diversity still waiting to be uncovered in the world’s rainforests. Traditionally used by local communities for basket weaving, the “ghost rattan” now has a place in the scientific record. This formal identification is crucial for future conservation efforts aimed at protecting this unique and vulnerable species. Deep in the Pacific Ocean, off the coast of New Zealand’s South Island, lies a remarkable expanse called the Bounty Trough. This 800km-long underwater canyon has recently become a goldmine for marine biologists, yielding the discovery of over 100 new species. During a three-week expedition as part of the Ocean census project, researchers plunged to depths of 4,800 meters. their efforts resulted in a stunning collection of previously unknown marine life. Among their findings were dozens of molluscs, three unique fish species, a new shrimp, a cephalopod, and a new genus of coral. One notably intriguing discovery baffled scientists. Initially mistaken for a sea star or sea anemone, this organism is now believed to be a new species of octocoral. Cao Bang Crocodile Newt In Vietnam, another exciting discovery has taken place.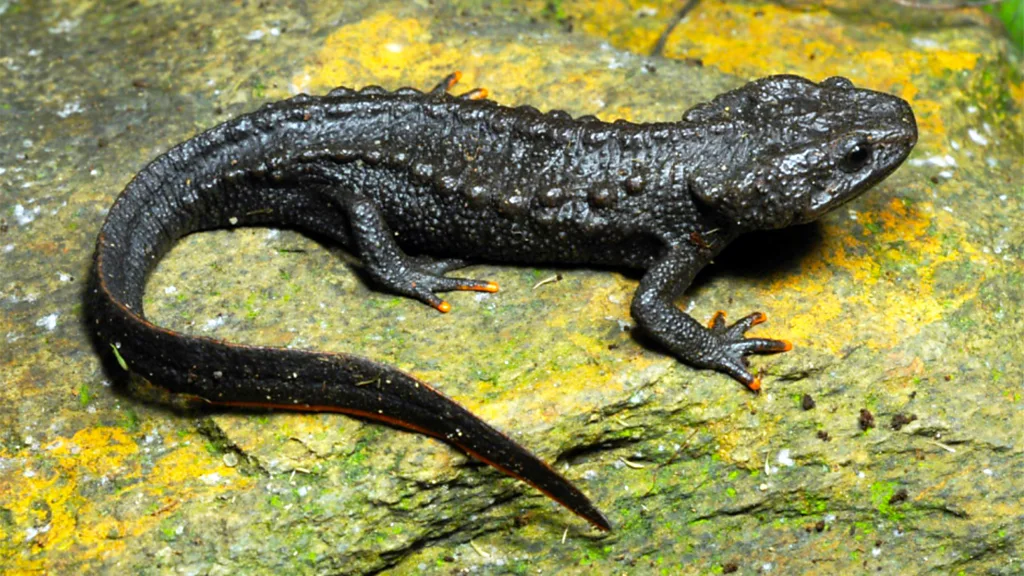 
The Cao Bang crocodile newt, discovered in a subterranean cave in Vietnam, is a creature that seems worthy of its name. With its textured, crocodile-like skin and glistening black eyes, this amphibian is a testament to the hidden wonders still waiting to be unearthed in the world’s diverse ecosystems.
## A New Crocodile Newt Discovered in Vietnam
A petite, knobbly amphibian, recently discovered in the mountains of northeastern Vietnam, has been given the moniker Cao Bang Crocodile newt. This shy creature, scientifically named _Tylototriton koliaensis_, was found nestled beneath rocks in a slow-moving stream on a farm. Its namesake, the Kolia Organic farm, is located in the Kolia Mountain Pass within Cao Bang province, near the Chinese border.

Pirate Spiders Discovered on Remote Island
Two new species of spider with a penchant for pirating have been discovered on a remote island in the Atlantic Ocean. Researchers stumbled upon these arachnids while studying the threatened cloud forest ecosystem of St. Helena, a British Overseas territory.These spiders are known for their aggressive behavior, violently taking over the webs of other spiders and eliminating the original inhabitants.
Kermit the Bony Salamander
Ancient ‘Kermit’ Fossil Finally Discovered, 270 Million years Later
A fossilized skull, hidden away for decades in the Smithsonian national Museum of Natural History, has finally been identified and given a fitting name: *Kermitops gratus*. This extinct creature, a type of bony salamander, lived approximately 270 million years ago and owes its moniker to its striking resemblance to a certain beloved amphibian.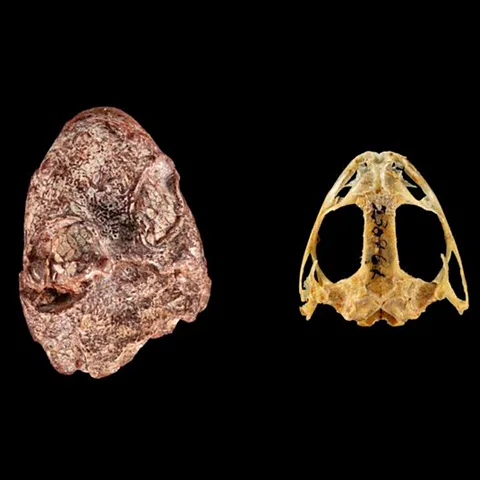
Kermitops gratus is an extinct bony salamander that lived 270 million years ago. The fossilized skull is shown next to a modern frog skull (Credit: Brittany M Hance/ Smithsonian)
The fossil’s bug-eyed appearance and slightly crooked smile, a result of being crushed during fossilization, proved too charming for researchers to resist naming it after the famous Muppet frog. “The bug-eyed appearance, along with the slightly crooked smile that the fossil has from being crushed as it fossilized, inspired researchers to name it after the famous puppet frog,” reads a statement about the discovery.New Species Discovered in the Peruvian Amazon
Scientists have discovered 27 new species in a recent expedition to the Peruvian Amazon. Among these remarkable findings are a bizarre “blob-headed” fish, a semi-aquatic mouse, and a frog-like amphibian named after a beloved television character.
A Unique Amphibian: The “Kermit” Frog
While named after the iconic Muppet, the new amphibian species, christened ‘Kermit,’ bears a closer resemblance to a stout, bony salamander than a frog. This prehistoric creature lived approximately 270 million years ago in what is now Texas. Its diet likely consisted of grub-like insects.
 Robinson Olivera/ conservation International
Robinson Olivera/ conservation InternationalOther Incredible Discoveries
The expedition also unveiled a semi-aquatic mouse, showcasing the incredible biodiversity of the Amazon rainforest. Further studies of these newly discovered species will continue to deepen our understanding of this vital ecosystem.
During a month-long expedition to the remote Alto Mayo region of Peru, a team of researchers unearthed an astonishing 27 new species. Among the remarkable discoveries were a rare amphibious mouse and an unusually-shaped fish. Unexpected Discoveries in Peru’s Alto Mayo The expedition, which took place over 38 days, focused on the biodiversity of this often-overlooked region in northwestern Peru. The team, led by Conservation International, made groundbreaking finds in the area’s diverse ecosystems, including cloud forests, mountain streams, and swampy lowlands. A “Shocking Discovery”: The Blob-Headed Fish One of the most surprising finds was a bizarre fish with an exceptionally bulbous head. described by the scientists as a “shocking discovery,” the creature belongs to a group known as bistlemouth armored catfish. While it was already familiar to the local Indigenous Awajun people, this marked its first identification by the scientific community. The fish was found in the rocky mountain streams of Alto Mayo.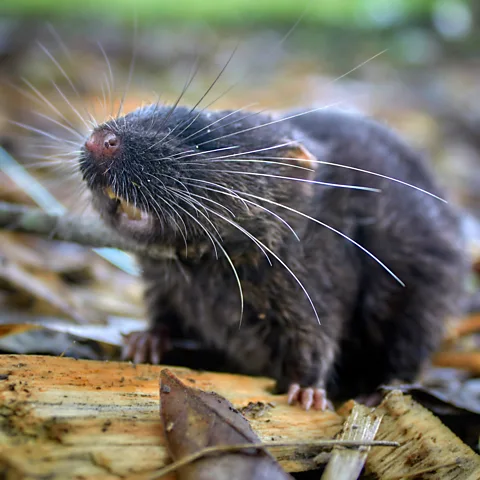 The Semi-Aquatic Mouse: A Threatened Home
another highlight of the expedition was the discovery of a unique semi-aquatic mouse. this newly identified species of _Daptomys_ has webbed toes, perfectly adapted to its life in the swampy forests it calls home.However, the researchers emphasized that this delicate ecosystem is already under threat from encroaching agriculture.
The Semi-Aquatic Mouse: A Threatened Home
another highlight of the expedition was the discovery of a unique semi-aquatic mouse. this newly identified species of _Daptomys_ has webbed toes, perfectly adapted to its life in the swampy forests it calls home.However, the researchers emphasized that this delicate ecosystem is already under threat from encroaching agriculture.
Experts in the field of biodiversity were thrilled by the discovery of new and exciting species of plants, animals, and fungi in 2024. These discoveries, however, serve as a stark reminder of the pressing threat posed by human activity to the planet’s biodiversity.
the Biodiversity Crisis
Martin cheek, a senior research leader at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, emphasizes the concerning trend of finding new species on the verge of extinction. “We increasingly see that new species are being found on the edge of extinction, or even become extinct as we find them, and it’s the destruction of their habitat by humans that is most frequently enough to blame,” he explains.
As we move into 2025, the scientific community anticipates the unveiling of even more novel species, underscoring the critical need to prioritize conservation efforts.
“Ultimately, the biodiversity crisis affects us all and it has never been more important that we take an interest in and more consciously support global conservation efforts before we wake up one morning and realize that it’s too late to do anything,” Cheek adds.
* This article has been updated on 30 December 2024 to clarify that not all Russula fungi produce a fishy odour and that the genus includes species that produce other odours.
technology,-environment-and-health-stories-from-the-bbc,-follow-us-on">For more science, technology, environment and health stories from the BBC, follow us on Facebook.
Digital detox: Is It Really Better for Your Mental Health?
In today’s technologically-driven world, we’re constantly bombarded with notifications, updates, and details. This constant connectivity can leave many feeling overwhelmed and burnt out, leading to a rise in interest in “digital detoxes” – taking a break from digital devices.
But is disconnecting from the digital world truly beneficial for our mental well-being? Experts say the answer isn’t so simple.
Some studies suggest that taking breaks from screens can reduce stress and anxiety, improve sleep quality, and even boost productivity.
“there’s definitely a link between excessive screen time and increased mental health issues,” says Dr. Sarah jones, a clinical psychologist specializing in technology addiction.
“Constantly checking social media and comparing ourselves to others can lead to feelings of inadequacy and loneliness. Taking a break can help us reconnect with ourselves and the world around us.”
However, others argue that completely disconnecting isn’t always feasible or necessary. They emphasize the importance of finding a healthy balance and using technology mindfully.
“Technology plays a vital role in our lives, allowing us to connect with loved ones, access information, and pursue various interests,” notes Dr. Mark Wilson,a digital sociologist. “It’s about finding a enduring and healthy relationship with technology,rather than trying to eliminate it altogether.”
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to embark on a digital detox is a personal one. It’s essential to evaluate your own relationship with technology and determine what feels right for you. If you find that your digital habits are negatively impacting your mental health, taking a conscious break could be beneficial. However, if you can establish healthy boundaries and use technology in a mindful way, you may be able to reap its benefits without sacrificing your well-being.
Want to take a break from social media but not sure where to start? 📵
— BBC Future (@BBC_Future) May 15, 2023
Here are some tips for a healthy digital detox: ➡️ Set realistic goals.
➡️ Identify your triggers.
➡️ Find alternative activities.
➡️ Tell your friends and family.
➡️ Don’t be afraid to unplug! https://t.co/U8zJq3LxlT #digitalwellbeing #mentalhealth #socialmediadetox
For more information and tips on managing your digital wellbeing, you can visit the following resources:
This is a interesting article, combining different stories too highlight both the wonder of biodiversity and the urgent need for conservation. here’s a breakdown of its strengths and areas for betterment:
**Strengths:**
* **Engaging Introduction:** Starting with the Kermit frog immediately captures attention with its unusual name and unique characteristics.
* **Storytelling Approach:** Weaving together the frog discovery with the broader expedition and other findings creates a compelling narrative.
* **Visual Appeal:** The inclusion of images helps readers visualize the fascinating creatures and their habitats.
* **Highlighting the Importance of Biodiversity:** The article effectively emphasizes the importance of studying and protecting biodiversity, reminding us of the interconnectedness of all life on Earth.
* **Addressing the Biodiversity Crisis:** The article skillfully transitions from the excitement of discovery to the sobering reality of threats to biodiversity.
* Quotes from experts add authority and urgency to the message.
**Areas for Improvement:**
* **structural Coherence:** While the narrative is engaging, the connection between the different stories could be stronger. Consider using smoother transitions or organizing them thematically.
* **Scientific Accuracy:** Be cautious about statements that could be misinterpreted. Such as, specifying whether the “fishy” odour of some Russula fungi is universally present or limited to specific species would enhance accuracy.
* **Concluding thought:** The abrupt shift to a digital detox topic at the end feels disconnected and lacks context.
Consider these suggestions:
1.**Strengthen Transitions:** Use phrases like “And while these discoveries inspire wonder…” or “However, this joyful exploration also reveals a stark reality…” to bridge different sections more smoothly.
2. **Develop a Stronger Conclusion:** Tie the themes of biodiversity and human impact together in a concluding paragraph,perhaps emphasizing the importance of our individual and collective actions.
3. **Expand on Digital Detox:** If you choose to keep the digital detox topic, integrate it more organically. Perhaps explore how digital overload can disconnect us from nature and the importance of balance.
4. **Fact-Checking:** Double-check all factual details and provide sources for your information.
**Overall:**
This article is a promising piece with the potential to engage and inform readers about both the wonders of biodiversity and the urgent need for its protection. With a few refinements, it might very well be even more impactful.


