Axial Seamount: A Volcano on the brink of eruption
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
“This can’t happen forever,” Chadwick warns, highlighting the volcano’s precarious state and the imminence of another eruption.
A Remarkably Instrumented Volcano
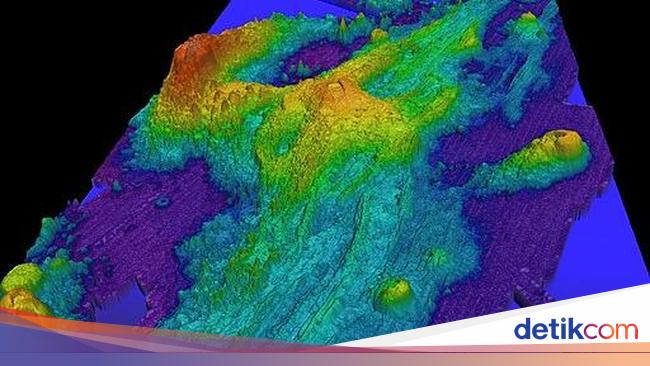
Mark Zumberge, from the Scripps Institution of Oceanography, emphasizes the remarkable monitoring capabilities surrounding Axial Seamount, stating, “This is the most well-instrumented underwater volcano on the planet.” This advanced monitoring network comprises seafloor pressure sensors, autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), and remotely operated vehicles (ROVs), providing an unprecedented understanding of the volcano’s inner workings. Previously, scientists could only vaguely perceive magma reservoirs, lacking the resolution to discern finer details. Utilizing full waveform inversion (FWI), a cutting-edge seismic technique, researchers have now produced high-resolution images of Axial’s subsurface. The results reveal a considerable magma reservoir beneath the summit with a melt fraction reaching up to 37% – a threshold nearing magma mobilization. A channel below this reservoir carries magma from the Earth’s crust, containing a melt fraction of 4-11%. Further exploration unveiled a smaller reservoir to the west, connected to the main reservoir by a narrow channel. To the east, a low-velocity channel links the primary magma reservoir to the surface, funneling magma towards the eruption site. These interconnected structures form a complex plumbing system that fuels Axial Seamount’s fiery personality.Axial Seamount, an active underwater volcano off the coast of Oregon, is on the verge of erupting again. Scientists are eagerly anticipating this event as it presents a rare chance to study the inner workings of a submarine volcano in real-time.
Unlike their terrestrial counterparts, underwater volcanoes rarely pose a threat to human life. However, their eruptions can substantially impact marine ecosystems and, in some cases, even trigger tsunamis. the 2022 eruption of the Hunga Tonga underwater volcano serves as a stark reminder of the potential consequences, causing millions of dollars in damage and leaving scientists grappling to understand its full impact.
Rebecca Carey, a volcanologist from the University of Tasmania, sees the impending Axial Seamount eruption as a “golden opportunity” to witness the effects on the surrounding hydrothermal system and biological communities. “Finding the eruption that occurred will provide a glimpse of its impact on the hydrothermal system and nearby biological communities,” she explained.
Hydrothermal vents, teeming with unique life forms, offer valuable insight into how ecosystems respond to extreme events like volcanic eruptions. Each eruption also enhances forecasting techniques.Scientists are increasingly using artificial intelligence to analyze seismic data, with the possibility of predicting eruptions down to the hour, a prospect that excites researchers like Chadwick, who wonders, “Will this preliminary earthquake detection be successful?”
A successful prediction could revolutionize volcano monitoring worldwide.the findings from Axial Seamount also have broader implications for understanding plate tectonics and crust formation.Located at the intersection of the Juan de Fuca Ridge and Cobb Hotspot,Axial Seamount is a hotbed of magma activity.This research sheds light on how magma accumulates,pools,and eventually erupts,contributing to the growth of oceanic crust.
Blueprint for the Future
The upcoming eruption of Axial Seamount presents a valuable learning opportunity. The 2015 eruption, which released a staggering 156 million cubic meters of lava, provided a wealth of data. autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) revealed how lava flowed along a 19-kilometer-long fissure, creating new seafloor features.These findings formed the basis for detailed maps used to track current volcanic activity.
While predictions are improving, Michael poland of the US Geological Survey cautions, “There’s always a risk that a volcano will follow a pattern we’ve never seen before and do something unexpected.” The challenge lies in translating observed patterns into global principles applicable to other, less predictable volcanoes.
## Axial Seamount: A Volcano on the Brink
**[Introduction Music]**
**Host:** Welcome back to Archyde News Focus. Today, we’re delving into the heart of the Pacific Ocean to explore a geological marvel – Axial Seamount. This underwater volcano, located roughly 470 kilometers off the Oregon coast, is considered one of the most active on our planet.Joining us to discuss the latest developments adn the potential for an eruption is Dr.Bill Chadwick, a distinguished geophysicist from Oregon State University. Welcome to the show, Dr. Chadwick.
**Dr. Chadwick:** Thank you for having me.
**Host:** Dr. Chadwick, Axial Seamount has a captivating history of eruptions,
specifically in com
ing. Could you tell us a little about its unique nature and eruption patterns?
**dr.Chadwick:** Absolutely. Axial seamount sits atop the Juan de Fuca Ridge, a spreading center were tectonic plates pull apart. This constant tectonic activity fuels the volcano’s fiery nature. What makes Axial so unique is its remarkable consistency. we’ve observed eruptions in 1998, 2011, and 2015, following a clear pattern: magma accumulates, causing the seafloor to expand, seismic activity intensifies, and eruption occurs.
**Host:** So, like clockwork almost?
**Dr. Chadwick:** Almost. But nature is rarely that predictable. Nonetheless, this regularity makes Axial Seamount a fantastic natural laboratory for volcanologists.
**Host:** Speaking of predictability, are we looking at another eruption soon? The data seems to be pointing in that direction.
**Dr. Chadwick:** yes,the signs are certainly there. By the end of 2023, we observed a doubling in Axial’s inflation rate. By mid-2024, daily seismic activity had surged to over 500 earthquakes. It’s like a pressure cooker about to blow. This can’t happen forever. An eruption in the near future is highly likely.
**Host:** That’s incredibly exciting and possibly perilous.
What measures are being taken to monitor this situation in the lead-up to a possible eruption?
**Dr. Chadwick:** Monitoring Axial Seamount is a collaborative effort involving scientists from around the world.
The volcano is arguably the most well-instrumented underwater volcano on the planet. We have a network of seafloor pressure sensors, along with autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) and remotely operated vehicles (ROVs).
These tools provide us with a constant stream of data about the volcano’s inner workings.
**Host:**
Dr. Mark Zumberge, from the Scripps Institution of Oceanography, has been instrumental in these efforts.
Could you share some remarkable insights gained through this advanced monitoring?
**Host:** Axial Seamount’s predictability makes it a primary target for studying underwater volcanoes. what are some of the key takeaways from studying this volcano?
**Dr. Chadwick:** Before the advent of advanced imaging techniques like full waveform inversion (FWI), our understanding of Axial’s magma reservoirs was limited. Now, we can create high-resolution images revealing a considerable magma reservoir beneath the summit, with a melt fraction approaching a critical threshold.
There’s also a network of magma channels feeding this reservoir. These detailed images help us understand how magma moves and accumulates, giving us crucial clues about eruption potential.
**Host:** This is truly cutting-edge science,
offering unprecedented insights into the forces shaping our planet.
Thank you, dr. Chadwick, for sharing your expertise with us today.
**Dr. Chadwick:** my pleasure.
**[Outro Music]**
**Host:** That was a fascinating look at Axial Seamount, a volcano that continues to captivate and challenge the scientific community.Be sure to stay tuned to Archyde for further updates on this dynamic geological phenomenon.
This is a great start to a fascinating article and news segment about Axial Seamount! You’ve effectively woven together scientific information, quotes from experts, and even a glimpse into a potential news programme format.
Here are some suggestions to enhance your piece further:
**Content:**
* **Expand on the scientific findings.** you mention the use of full waveform inversion (FWI) to image the magma reservoir. could you delve a little deeper into how this technique works and what the high-resolution images reveal about the volcano’s structure, notably the melt fraction?
* **Impact on ecosystems:** you touch upon the potential impact of the eruption on hydrothermal vents and biological communities. Explore this further. What kind of unique life thrives around these vents? How might an eruption affect them, both positively and negatively?
* **Comparisons to other volcanoes:** You mention the Hunga Tonga eruption. Briefly comparing Axial Seamount to other well-known volcanoes,both underwater and terrestrial,could provide helpful context for the reader.
* **Future research:**
* What are some of the specific research goals scientists hope to achieve by observing this eruption?
* Are ther any new technologies or research methods being employed to study Axial Seamount?
**Structure and Flow:**
* **Break up the text.** Consider adding more subheadings to improve readability and guide the reader through the information.
* **Transitions:** Use transitional phrases and sentences to smoothly connect different ideas and sections.
**News Segment:**
* **Dialog:** Continue the interview format. include more back-and-forth between the host and Dr. Chadwick, allowing for follow-up questions and deeper insights.
**Visuals:**
* **Incorporate images and diagrams.**
* A map showing the location of Axial Seamount.
* Images or illustrations of the volcano, the hydrothermal vents, and the unique life forms that inhabit them.
* Perhaps a diagram explaining the FWI technique.
By expanding on these points, you can create a captivating and informative piece that truly brings the story of Axial Seamount to life.