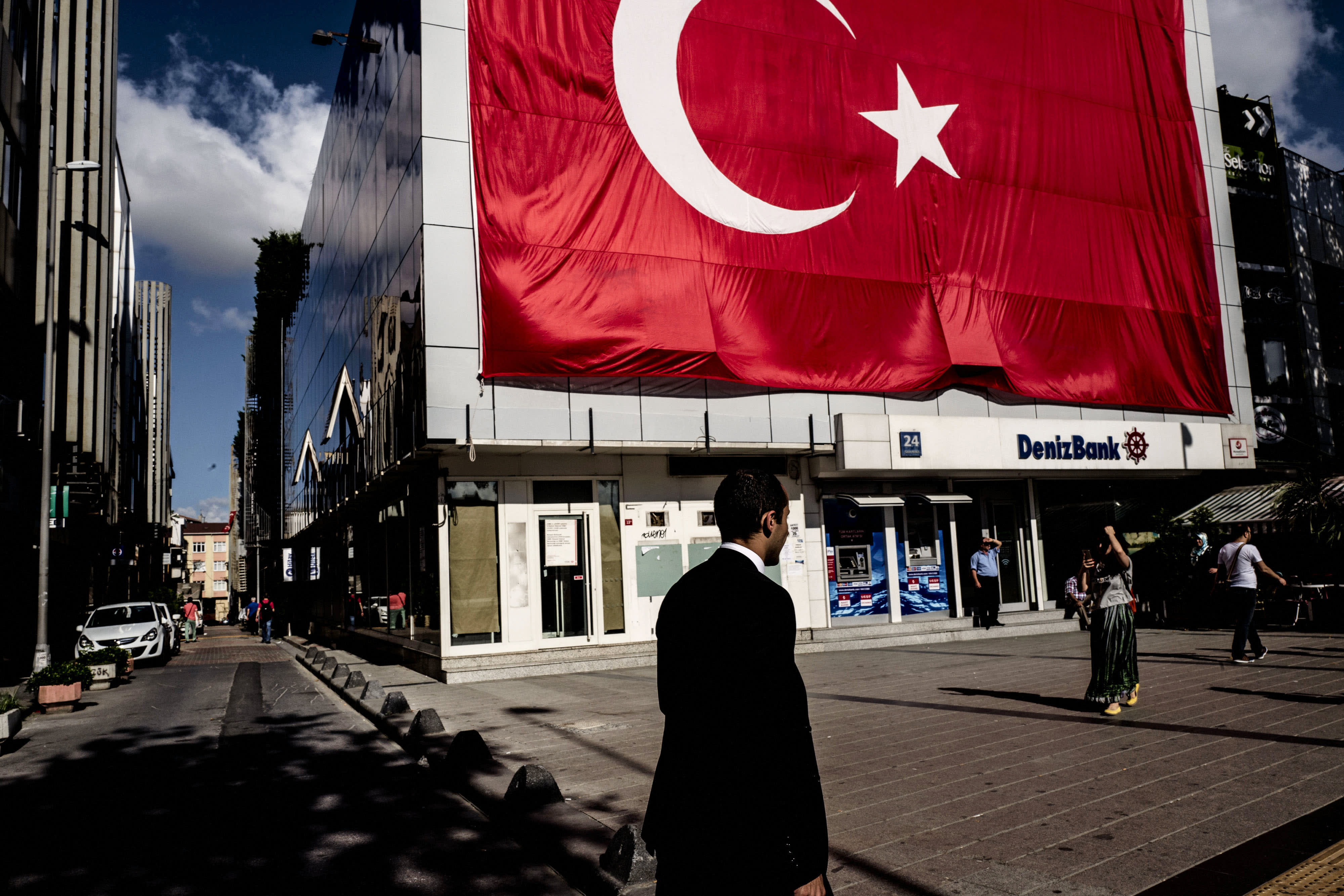
Turkey’s central bank decided to keep its key interest rate at 45%, despite soaring inflation. This move was expected as the bank had indicated that the previous interest rate hikes would be its last for the year, despite inflation reaching approximately 65%. This decision by the central bank indicates consistency with the strategy of its newly appointed governor, Fatih Karahan, who took office in early February. Analysts view the accompanying press statement from the central bank as hawkish, indicating that there will be no easing of rates in the near future.
The country’s consumer prices rose 6.7% from December, marking its biggest monthly jump since August. Year-on-year, prices increased by 64.8% in January. Despite the high inflation, economists expect the current interest rate to be maintained for much of 2024. They also anticipate inflation to roughly halve by the year’s end, which might potentially lead to monetary easing in the future.
An extended interest rate pause is likely in the coming months, according to Liam Peach, a senior emerging markets economist at Capital Economics. He predicts that interest rates will remain on hold throughout this year and rate cuts will only occur in early next year. However, with the possibility of inflation ending the year at 30-35%, there is still a chance that the central bank may initiate an easing cycle before the end of 2024.
Analyzing the Implications
The decision of Turkey’s central bank to maintain the interest rate at 45% might have significant implications for the country’s economy. With inflation at such high levels, there is a risk of eroding purchasing power and increasing costs for consumers. This can lead to a slowdown in economic growth and put pressure on businesses, particularly those reliant on consumer spending.
However, the central bank’s commitment to holding rates suggests a cautious approach to managing inflation. By keeping rates high, the bank aims to stabilize prices and prevent further inflationary pressures. This strategy signals the bank’s determination to combat inflation and maintain the stability of the Turkish economy.
Looking at current events and emerging trends, it is evident that many countries are grappling with the challenge of managing inflation while sustaining economic growth. Turkey’s experience provides valuable insights into the trade-offs and policy decisions necessary to address this issue.
Predictions and Recommendations
Based on the current scenario and the potential future trends, it is crucial for Turkey’s central bank to closely monitor inflation and adjust its policies accordingly. If inflation continues to rise, the bank may need to consider further interest rate hikes to put a brake on price increases and restore stability. On the other hand, if inflation begins to ease and economic growth shows signs of weakness, the bank should be prepared to implement monetary easing measures to stimulate the economy.
Additionally, the Turkish government should focus on structural reforms that promote price stability and improve the country’s economic competitiveness. This might involve measures such as fiscal discipline, enhancing productivity, and attracting foreign investment. By addressing these underlying factors, Turkey can build a strong foundation for sustainable economic growth and mitigate the risks associated with inflation.
Overall, Turkey’s central bank’s decision to hold the interest rate steady reflects its commitment to combating inflation and maintaining stability. The implications of this decision are significant for the country’s economy, and careful monitoring of inflation and policy adjustments will be necessary going forward. By implementing appropriate measures and reforms, Turkey can navigate the challenges posed by inflation and position itself for long-term economic prosperity.