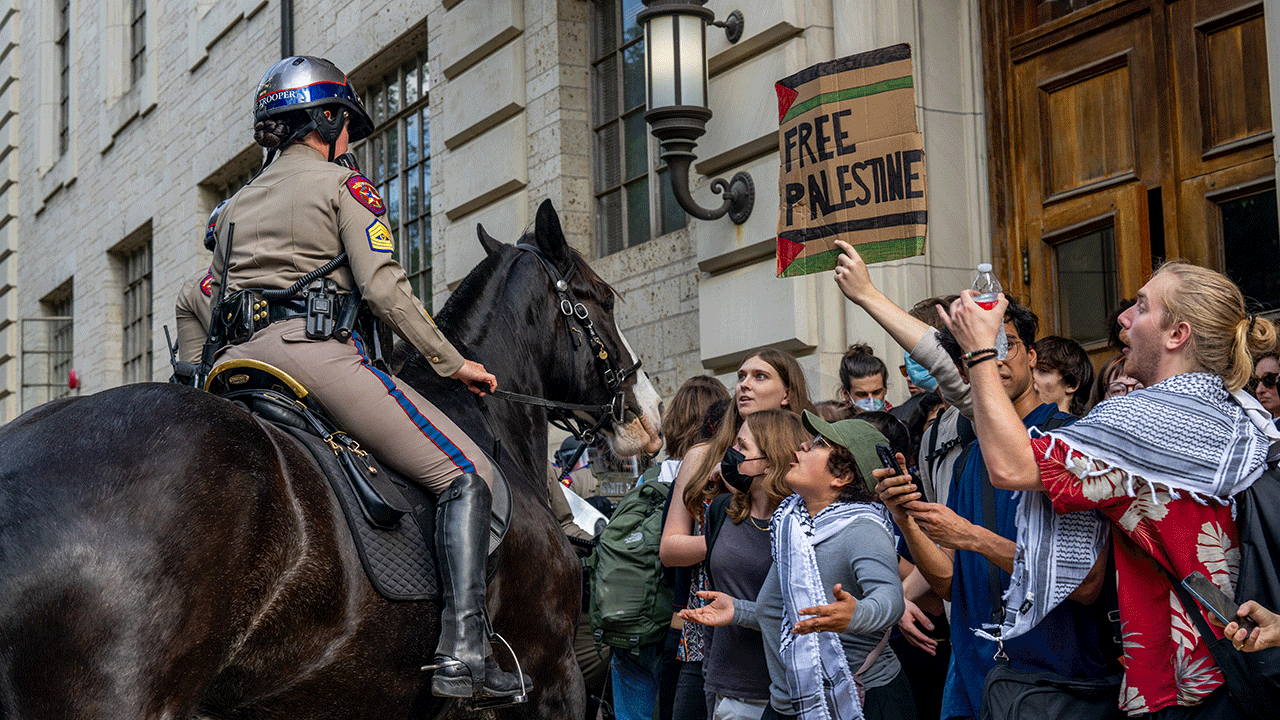A Fragile Peace: Inside the Deal to End the Gaza War
Table of Contents
- 1. A Fragile Peace: Inside the Deal to End the Gaza War
- 2. A Fragile Peace: Gaza Ceasefire Offers Glimmers of Hope Amidst Continued Tensions
- 3. what role did Qatar, the U.S.,and Egypt play in mediating the peace negotiations?
- 4. A Delicate Balance: The Road to a Fragile Ceasefire
- 5. A Delicate Path: Navigating the Middle East Peace process
- 6. How did each mediatorS unique assets contribute to their success in the recent peace negotiations between Israel and Hamas?
The air crackled with tension inside a luxurious Doha clubhouse. Months of seemingly fruitless negotiations stretched late into the night, pushing weary negotiators to their limits. On the first floor, Hamas representatives, haunted by the memory of an Israeli airstrike that tragically claimed the lives of seven family members, meticulously reviewed another proposal aimed at halting the devastating conflict. Meanwhile, on the second floor, advisors to Israel’s intelligence chief, driven by the need for justice following the October 7, 2023, attack that ignited the war, engaged in their own tense deliberations.
As mediators from Qatar, the United states, and Egypt desperately sought a resolution, a glimmer of hope emerged. could these bitter enemies, who refused to speak directly, finally reach a deal to silence the guns and bring home dozens of Israeli hostages?
“They were extremely suspicious towards each othre. No trust at all,” confided an Egyptian official involved in the negotiations, speaking on condition of anonymity. “Both parties were looking at each word in the deal as a trap.”
Even as Qatar’s Prime Minister,Sheikh Mohammed bin Abdulrahman Al Thani,announced a ceasefire agreement last Wednesday evening,disagreements lingered.Objections arose, delays ensued, and the fragile peace hung precariously in the balance.
However, amidst this uncertainty, a breakthrough arrived. Three young Israeli women were released from captivity, and dozens of Palestinian prisoners were freed by Israel. While the agreement remained fragile, it offered a fragile hope for peace.
Mehran Kamrava, a professor of government at Georgetown University in Qatar, shed light on the unique circumstances that led to this pivotal moment. “Over the course of the last week, all the stars aligned finally in a way that, after 15 months of carnage and bloodshed, negotiations came to fruition,” he explained.
The timing was crucial. With one U.S. president preparing to hand power to another, both administrations were eager to secure a deal to free the hostages and end the conflict that had claimed the lives of approximately 1,200 Israelis and, according to Palestinian health officials, over 47,000 Palestinians in Gaza. While the health officials do not differentiate between civilians and militants, they emphasize that over half of those killed were women and children.
Stepping into the role of a neutral mediator in this volatile region, Qatar, a small but wealthy nation, provided a crucial platform for these delicate negotiations.
A Fragile Peace: Gaza Ceasefire Offers Glimmers of Hope Amidst Continued Tensions
As 2022 drew to a close, a fragile peace agreement emerged from the ashes of devastating conflict in Gaza. After weeks of intense fighting, negotiators, driven by necessity and aided by unlikely alliances, managed to broker a ceasefire between Israel and Hamas, the militant group controlling Gaza.
The path to this uneasy truce was paved with complex geopolitical maneuvering. Sheikh Mohammed bin Abdulaziz al-Thani, the Emir of Qatar, known for its diplomatic efforts in the region, played a pivotal role alongside officials representing both President Biden’s management and former president Trump. Their shared concern over escalating tensions and potential regional instability united them in this delicate endeavor.
Egypt, grappling with its own challenges stemming from Palestinian refugee influx and threats from Houthi rebels, recognized the urgency of the situation. They stepped up, actively facilitating negotiations amidst a backdrop of shattered infrastructure and mounting civilian casualties.
Though, the road to peace was fraught with obstacles. Months of negotiations stalled,hampered by disagreements surrounding the release of Israeli hostages held by Hamas,the fate of Palestinian prisoners,and the scope of an Israeli military withdrawal from Gaza. Adding fuel to the fire, the assassination of Hamas leader Ismail Haniyeh in july, widely attributed to Israel, and the discovery of six Israeli hostages’ bodies in a Gaza tunnel in August further deepened the chasm of mistrust.
“Whoever murders hostages does not want a deal,” declared Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu, highlighting the deep-seated suspicion that permeated the negotiations.
The situation spiraled further with the killing of Yahuda Sinwar, the mastermind behind the hamas attack, and a major Israeli offensive against Hezbollah, the Lebanese militia closely aligned with Hamas. Trump’s vocal demand for hostage release,coupled with a chilling threat of “hell to pay” if they remained captive,seemed to finally push both sides towards the negotiating table.
An unexpected diplomatic push emerged, spearheaded by Brett McGurk, a seasoned Middle East diplomat with experience across republican and democratic administrations, representing President Biden, and Steve Witkoff, a real estate mogul with limited diplomatic background but a close connection to then-President-elect Trump. Despite their divergent political affiliations, these unlikely partners found common ground, advocating for a resolution that defied typical partisan gridlock.
Their tireless efforts bore fruit. After weeks of intense discussions, a breakthrough emerged in early January 2023. Hamas agreed to provide a list of hostages for release in the initial phase of the agreement, a crucial step towards easing tensions.
While this fragile ceasefire offers a glimmer of hope, its future remains uncertain. Its success hinges on the unwavering commitment of both sides to uphold their promises and lay the groundwork for lasting peace. The road to lasting peace in the Middle East is undeniably long and arduous, but this tentative truce provides a fragile yet notable step forward.
-negotiated-after-tense-talks”>A Fragile Peace: Gaza ceasefire negotiated After Tense Talks
In a tense and dramatic fashion, Israel and Hamas reached a fragile ceasefire agreement following days of intense negotiations in Qatar. The deal, brokered by Qatar and mediated by Egypt, marked a pause in the devastating conflict but raised meaningful questions about its long-term viability.
Driven by the urgency of the situation, the negotiations began during the Jewish Sabbath. The breakthrough came when Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu agreed to send senior intelligence and security officials back to Doha, were Qatari prime Minister sheikh Mohammed bin Abdulrahman Al Thani played a pivotal role. Secret talks, shrouded in secrecy, unfolded within the confines of the Qatari Prime Minister’s private office, lasting well into the night.
“But the Hamas and israeli delegations never crossed paths,” revealed an official privy to the negotiations, underlining the delicate nature of the talks.
The intricate details of the ceasefire agreement were meticulously hammered out by teams of experts, working separately on different floors over many hours. ”Until late the first hours of Wednesday we were working tirelessly to resolve last-minute disputes,” admitted an Egyptian official involved in the process, highlighting the grueling effort required to reach a consensus.
Despite coming close to a resolution, the agreement hit a snag in the final hours. A “last-minute hiccup, last-minute requests from both sides,” according to a source, forced a delay that left the world on tenterhooks. Israel claimed Hamas attempted to alter pre-agreed arrangements along the Gaza border with egypt,a charge vehemently denied by Hamas as “nonsense.”
A senior U.S. official, closely involved in the negotiations, revealed that Hamas negotiators made several last-minute demands, but added, “We held vrey firm.” This determination undoubtedly played a role in securing the eventual agreement.
The dramatic culmination of the talks occurred when the Qatari prime Minister, after separate meetings with the Israeli and U.S.envoys, announced the parties had reached a fragile peace deal. Though, even after this declaration, negotiations continued the next day, delving into the intricacies of the agreement’s implementation and the mechanisms for its enforcement. These discussions concluded at 4 a.m., showcasing the immense commitment required to secure lasting peace.
Israeli President Isaac Herzog expressed optimism that the agreement woudl usher in a period of national goodwill, healing, and rebuilding. Yet,the ultimate success of the ceasefire remains uncertain.
The next stage of dialogue is set to commence in just over a week.The goal is to address the release of all remaining hostages, living and dead, and to establish a permanent ceasefire. Though, observers acknowledge that achieving these objectives will be formidable. “Getting there,” predicts one expert,”will likely be even tougher.”
what role did Qatar, the U.S.,and Egypt play in mediating the peace negotiations?
archyde News: An Interview with Dr. Leila Al-Sayyid, Middle East Peace Negotiations Expert
Archyde: Welcome, Dr.al-Sayyid. Your insights on the recent Middle East peace negotiations have been invaluable. Can
A Delicate Balance: The Road to a Fragile Ceasefire
The path to peace in the Middle East is often paved with tension and uncertainty. A recent ceasefire, born from arduous negotiations, offered a glimmer of hope but also highlighted the fragility of the situation. Dr. Leila Al-Sayyid, a leading expert on Middle Eastern conflict resolution, sheds light on the final stages of this critical period.
“The final stages of these negotiations were indeed tense and delicate,” Dr.Al-Sayyid recounts. “Both sides had reached a point of exhaustion, but the prospect of ending the conflict and saving lives pushed them to keep going.”
at the heart of the negotiations were key issues – the release of Israeli hostages held by Hamas, the fate of Palestinian prisoners in Israeli custody, the scope of Israel’s military withdrawal from Gaza, and long-term security arrangements. These points of contention fueled the anxieties and mistrust that have long characterized the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
The role of mediators, including Qatar, the United States, and Egypt, proved crucial. Qatar, with its neutral stance and diplomatic experience, provided a vital platform for talks. The United States, under both President Biden and former President Trump, exerted pressure and offered incentives to push both sides toward a deal. Egypt, facing its own internal challenges, played a critical role in facilitating the discussions and ensuring regional stability.
Though, the path to peace was fraught with setbacks. The assassination of Hamas leader Ismail Haniyeh and the revelation of Israeli hostages’ bodies in Gaza tunnels seemed to further strain relations. “Those events indeed added complexity to an already delicate situation,” Dr. Al-Sayyid notes, “They highlighted the deep distrust between the two sides and made it harder for them to find common ground. However, they also underscored the urgency of reaching a deal to prevent further escalation and loss of lives.”
Fortunately, a breakthrough emerged in early January 2023.Several factors converged: the international community’s pressure on both sides,the mounting human cost of the conflict – over 1,200 Israelis and tens of thousands of Palestinians,mostly civilians,had been killed – and the desire of both administrations to secure a deal before the U.S. presidential transition.
A significant step forward was Hamas’s agreement to provide a list of hostages to be released in an initial phase. “This is a crucial step towards easing tensions,” Dr. Al-Sayyid emphasizes. “It shows Hamas’s commitment to the deal and signals a willingness to engage in further negotiations. However, the success of this fragile agreement depends on both sides honoring their commitments and building upon this foundation.”
Dr. Al-Sayyid concludes, “The path to lasting peace in the Middle East is long and arduous. It requires sustained effort, trust-building measures, and a genuine commitment to addressing the underlying issues that fuel the conflict.” The recent ceasefire offers a chance for progress,but the future remains uncertain as both sides navigate the delicate balancing act between security and peace.
A Delicate Path: Navigating the Middle East Peace process
Achieving lasting peace in the Middle East is an intricate and multifaceted challenge,requiring nuanced diplomacy and unwavering commitment from all stakeholders. Dr. Leila Al-Sayyid, a leading expert on the region, recently shed light on the complexities of this delicate process, emphasizing the need for sustained effort and goodwill.
“The next steps involve implementing the agreed-upon measures, such as the release of prisoners and the lifting of certain restrictions on Gaza,” Dr. Al-Sayyid explained. “both sides must also address the underlying issues, including the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and the right to self-determination.”
She underscored that this is a long-term endeavor, requiring “continued diplomatic efforts and goodwill from all parties involved.” Dr.Al-Sayyid believes that while the road to peace is arduous, the recent ceasefire holds promise.
“The road to peace is long, but I hope this ceasefire marks a step in the right direction,” she shared.
How did each mediatorS unique assets contribute to their success in the recent peace negotiations between Israel and Hamas?
Dr. Al-Sayyid, could you walk us through the roles played by Qatar, the United States, and Egypt in the recent peace negotiations between Israel and Hamas?
Dr. Leila Al-Sayyid: certainly. The mediation efforts in this case were multilateral and complex, with each mediator bringing unique assets to the table.
- Qatar: Qatar played a pivotal role as a neutral host and a trusted interlocutor for both Israel and Hamas. Throughout the negotiations, Qatar’s emir, Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani, and his Prime Minister, Sheikh Mohammed bin Abdulrahman Al Thani, worked tirelessly to build trust and facilitate dialogues.
– Safe Haven: Qatar provided a safe haven for Hamas officials and a platform for negotiations, given the restrictions on direct talks with Israel.
– Financial Support: Qatar also provided significant financial support to Hamas-controlled Gaza, easing the humanitarian situation and buying goodwill.
– Diplomatic ties: Qatar’s diplomatic ties with both Israel and various Palestinian factions, including Hamas, enabled it to act as a credible middleman.
- The United States: The U.S. maintained a robust diplomatic presence, leveraging its influence and resources to encourage a peaceful resolution.
– Bilateral Pressure: Both the Biden and Trump administrations exerted pressure on Israel and hamas, warning of potential consequences if the conflict escalated further.
– Incentives: The U.S. offered incentives, such as economic aid, to encourage compromise. For example, President Biden’s governance was reportedly discussing a plan to provide $150 million in humanitarian aid to Gaza as part of the ceasefire deal.
– Regional Coordination: The U.S. worked closely with regional allies, including Egypt and Qatar, to synchronize their diplomatic efforts.
- Egypt: Egypt’s role was crucial in facilitating negotiations and ensuring regional stability, despite its own internal challenges.
– Direct Talks: Egypt hosted direct talks between Israeli and Palestinian representatives, and also indirect talks through Egyptian mediators.
– Ceasefire Management: Egypt has long played a role in managing ceasefires between Israel and Palestinian factions in Gaza. they maintained their border with Gaza open for humanitarian aid and mediated the movement of people and goods.
– Security Concerns: Egypt, concerned about the impact of the conflict on its own stability, pushed for a deal that would address Israel’s security concerns while also improving conditions for Palestinians in Gaza.
Each of these actors played a distinct but complementary role in the negotiation process. Their collective efforts were essential in brokering the fragile ceasefire, but sustaining and building on this progress will require continued diplomatic engagement and a commitment to addressing the root causes of the conflict.


:strip_icc():format(jpeg)/kly-media-production/medias/4293087/original/032057900_1673917421-088723300_1662604716-iPhone_14_Pro.jpg)