2024-10-29 17:00:00
Colon cancer is a complex disease that raises many questions, particularly about its link with heredity. Understanding how genetic factors influence the development of this disease is crucial for screening and prevention. Here we will explore the different dimensions of heredity in relation to colon cancer, addressing genetic syndromes, screening tests, and implications for families at risk.
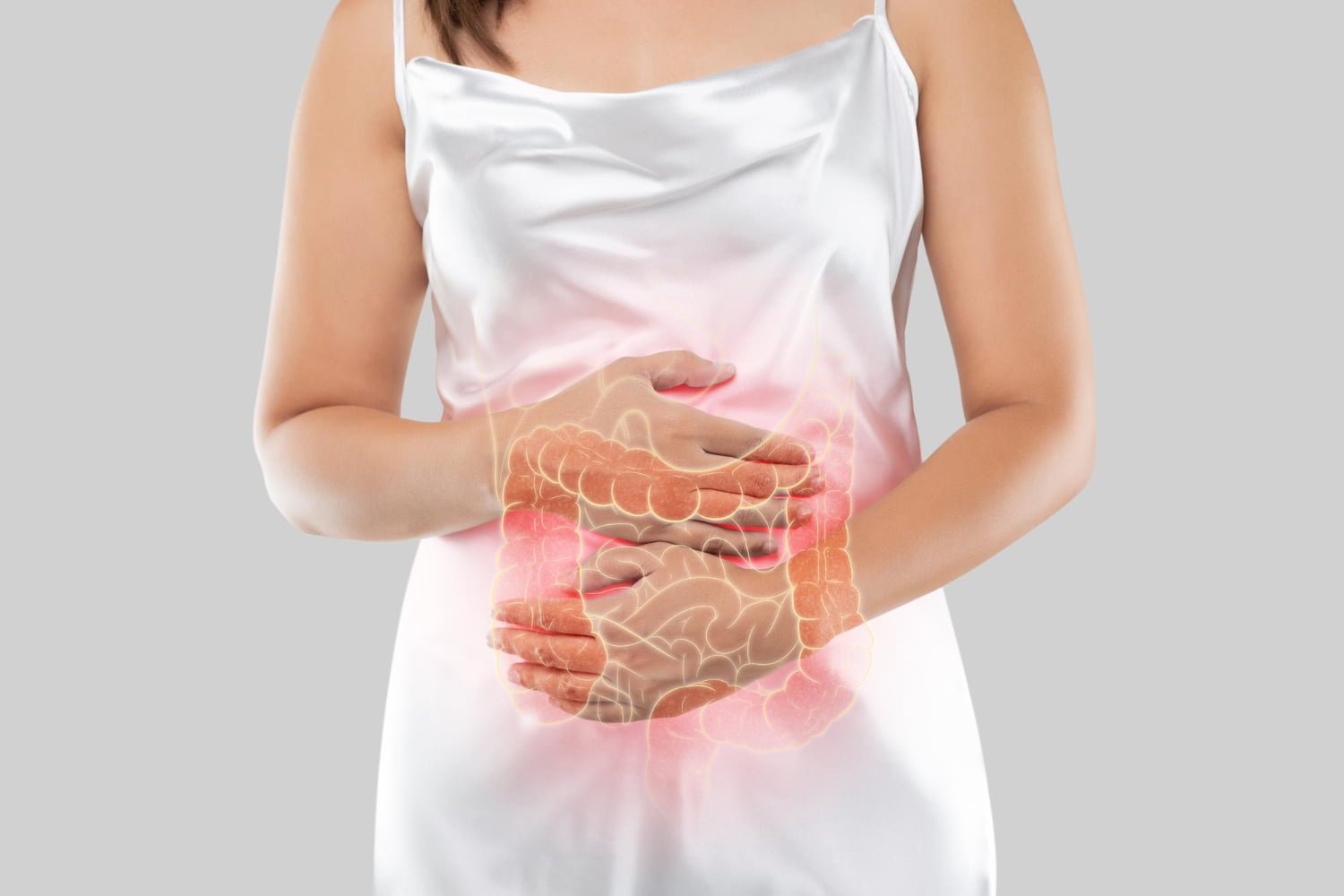
Colon cancer develops in the colon or rectum and is one of the most common cancers worldwide. It can manifest in different forms, ranging from benign polyps to malignant tumors.
Risk factors
Risk factors for colon cancer include:
Age : The risk increases with age, particularly after 50 years.
Family history : A family history of colon cancer may indicate a genetic predisposition.
Lifestyle : A diet high in fats and processed meats, as well as a lack of exercise, are aggravating factors.
Symptoms
Symptoms of colon cancer can vary, but often include:
Heredity and colon cancer
Heredity plays a significant role in the development of certain types of colon cancer. Approximately 5 to 10% of cases are attributed to hereditary syndromes.
Hereditary syndromes
There are several genetic syndromes that increase the risk of colon cancer:
Lynch syndrome : Also known as hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC), this condition increases the risk of several cancers, including colon cancer.
Familial adenomatous polyposis (PAF): This rare disease is characterized by the formation of numerous polyps in the colon, increasing the risk of cancer.
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome : This syndrome causes polyps in the digestive tract and increases the risk of various cancers.
Why consider genetic testing?
Genetic testing can help identify people at high risk of developing colon cancer. They allow:
To establish an early diagnosis: Early detection can save lives. To inform family members: If an individual carries a genetic mutation, family members can also be tested.
The genetic testing process generally includes:
Sample collection: This can be done from blood or saliva.
Analysis of results: The results are interpreted by health professionals.
It is essential that families with a history of colon cancer are aware of the risks.
Creating a family tree can help identify family members who may be at risk. This also allows hereditary links to be visualized.
Consult a specialist
If a family member is diagnosed with colon cancer, it is advisable to consult a specialist in gastroenterology. The latter can recommend appropriate screening exams for family members.
Prevention and screening
Prevention is a key strategy in the fight against colon cancer.
Screening recommendations
Recommendations for colon cancer screening vary depending on individual risks. In general :
Screening from age 45: For the general population. Earlier screening for those at risk: This may include more frequent testing or advanced screening methods, such as colonoscopy.
Lifestyle changes
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of colon cancer. Here are some tips:
Eat a balanced diet: Include fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Regular exercise: Get at least 30 minutes of physical activity per day. Avoid tobacco and alcohol: These substances increase the risk of cancer.
The challenges of genetic testing
Although genetic testing is beneficial, it can also pose challenges.
Fear of results
Fear of discovering a genetic predisposition may deter some people from getting tested. It is essential to discuss these concerns with a healthcare professional.
The psychological impact
The results of a genetic test can have a psychological impact on the individual and their family. Psychological support may be needed to manage this situation.
Treatments available
When diagnosed with colon cancer, several treatment options exist.
Treatments may include:
Surgery : To remove the tumor.
Chemotherapy : To target cancer cells.
Radiotherapy : To reduce the size of the tumor.
Regular monitoring is crucial after treatment to detect any recurrence. This may include regular consultations and screening exams.
Colon cancer is a complex disease, influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Understanding heredity and genetic testing can help better manage risk and take preventative measures. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits and remaining vigilant, it is possible to significantly reduce the risk of this disease.
5/5 – (112 votes) Did you find this article useful?
1730258509
#role #heredity #occurrence #colon #cancer