In the last century, the average world of life expectancy has been prolonged, which is due in large part to advances in science and medicine, thanks to the development of vaccines, preventive medical care and sanitation systems.
According to the last study of the commission Economic for Latin America and the Caribbean (Cepal), life expectancy increased by close to 30% in the last 70 years throughout the world. However, although the life span of people has increased, there is a gap between some countries that have a higher life expectancy compared to others. But, what is the difference in years due to?
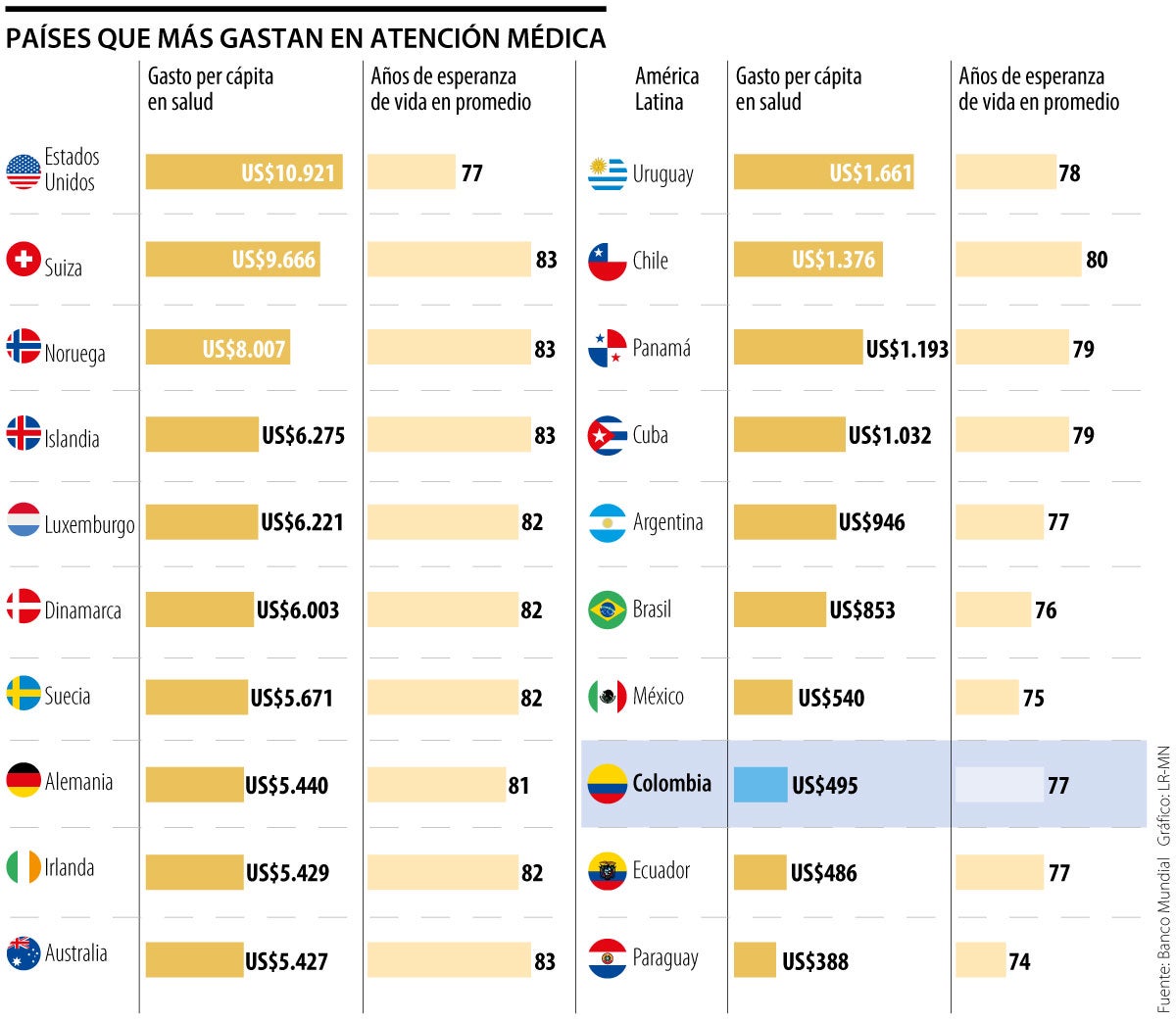
According to World Bank data, compiled by Truman Du and Visual Capitalist, the explanation may be related to the amount of money countries invest in health care services.
The United States is the country that invests the most in medical services, with a per capita expenditure of US$10,921 and an average life expectancy of 77 years; the second is Switzerland, with US$9,666 and an approximate life of 83 years; Norway, $8,007 (age 83); Iceland, $6,275 (age 83); and Luxembourg, US$6,221 (82 years).
Japan, for its part, is the country with the longest average life expectancy, with 85 years and a per capita investment in medical care of US$4,360; followed by Singapore, with 84 years and an expense in these services of US$2,633.
Regarding the countries that invest the least in health care, Madagascar was found to lead with a per capita expenditure of US$20 and only 67 years of life expectancy; followed by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, with US$21 and 61 years; Burundi, with US$21 and 62 years; South Sudan, US$23 and 58 years old; and Eritrea, US$25 and 67 years of life.
When analyzing the figures, it became clear that countries that have higher per capita spending on medical care tend to have more years of life expectancy on average.
However, there are some exceptions, for example, there is the case of the United States. Although this country has the highest per capita spending on health care, its average life expectancy is lower than that of other countries that spend less money on such services. This can happen due to other factors such as the US being the nation with the highest rate of obesity in the world and registering high rates of violence among young adults.
At the same time, other countries such as Japan, Singapore and South Korea have a long life expectancy despite the fact that their per capita spending on medical services is relatively low.
How is Latin America? Colombia is the eighth country in the region that spends the most on health care, with a per capita investment of US$495 and an average life expectancy of 77 years. The first is Uruguay, with US$1,661 and 78 years of life; followed by Chile, with US$1,376 and 80 years; then there is Panama, with US$1,193 and 79 years; continues Cuba, with US$1,032 and 79 years; Argentina, with US$946 and 77 years; Brazil, US$853 and 76 years old; and Mexico, US$540 and 75 years.
Regarding the countries that spend the least on medical services, Bolivia leads with a per capita investment of US$246 and a life expectancy of 72 years; followed by El Salvador, with US$300 and an average life of 74 years; then there is Guyana, with US$326 and 70 years; Venezuela, with US$339 and 72 years; Peru, with US$370 and 77 years; Paraguay, with US$388 and 74 years; and Ecuador ends, with US$486 and 77 years.
The report highlights that, despite the lengthening of human life spans in the last 70 years, the pandemic affected population growth in Latin America and the Caribbean, since according to the ECLAC study, the region lost 2.9 years of life expectancy between 2019 and 2021.
“The loss of years of life in 2020 and 2021 is greater than in any other period in the recent history of the region. The projections foresee a recovery in 2022, which will have different rhythms in the countries due to the differences in the vaccination process and the measures taken to combat the pandemic. However, life expectancy at birth will not return to pre-pandemic levels until 2025,” the report says.
How long can life expectancy be extended in the coming years?
According to the latest research published in the scientific journal Nature Communications, if people’s quality of life continues to increase and advances in medicine, human beings might live up to 150 years. In addition, according to projections of the United Nations Organization (UN), life growth will be divided according to the conditions of each country, that is, the most advanced nations will have more years of life compared to developing countries. .



