.jpg)
In December 2024, consumer prices saw a noticeable uptick, rising by 0.2% compared to the previous month. This marked the sharpest December increase in three years,according to data from the Central Statistics Office. While the cost of goods remained stable, services experienced a 0.9% surge.The primary drivers behind these changes were higher prices for food, fuel, and services, alongside declines in costs for clothing, footwear, personal care items, and household energy resources.
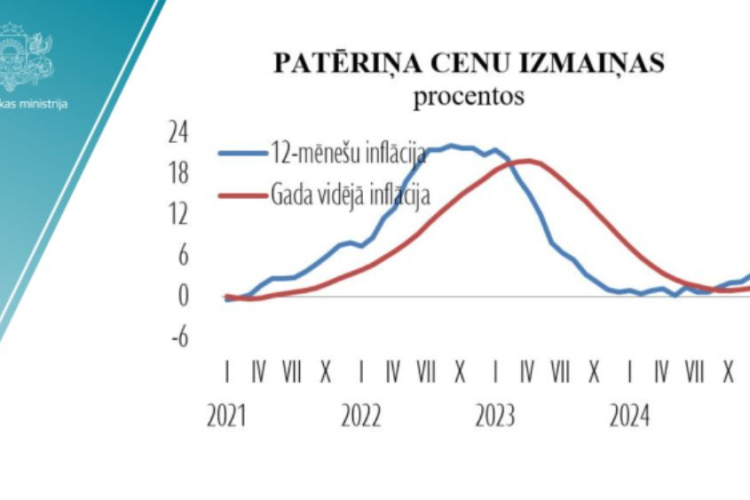
Over the course of 2024, consumer prices climbed at a faster rate than in the previous year. By December, prices had risen by 3.3% compared to the same month in 2023. This upward trend was fueled by global market fluctuations and ongoing geopolitical instability.
The rise in service costs played a pivotal role in shaping the overall price landscape. Services saw a 6.3% increase, contributing 1.6 percentage points to the total consumer price index. Key areas driving this surge included outpatient medical services, especially dental and specialist care. Additionally, recreational and cultural activities—such as TV subscriptions, sports events, museum visits, and concerts—alongside telecommunications, housing management, vehicle maintenance, waste collection, and dining out, all saw significant price hikes. In contrast, air travel costs dropped notably.
Food prices also continued their upward trajectory in 2024. The cost of groceries and non-alcoholic beverages rose steadily, adding pressure to household budgets. This trend was influenced by supply chain disruptions, higher production costs, and increased demand.While some categories, like clothing and energy, saw price reductions, the overall impact of rising food and service costs dominated the economic narrative.
As we reflect on 2024, it’s clear that the interplay of global and local factors shaped consumer spending patterns. The year underscored the importance of adaptability in navigating an ever-changing economic landscape. For businesses and consumers alike, understanding these trends is crucial for making informed decisions in the year ahead.
2024 Price Trends: Energy, Food, and fuel in Focus
In 2024, the global and local economic landscape saw significant shifts in pricing across key sectors, including energy, food, and fuel. These changes not only influenced household budgets but also reflected broader market dynamics and geopolitical developments. Let’s dive into the key trends that shaped the year.
Energy Prices: A Mixed Bag
The most notable price reduction in 2024 came from housing-related energy resources, including electricity, gas, solid fuel, and heat energy. Collectively, these reductions lowered the overall price level by 0.6 percentage points. Heat energy prices saw the most dramatic decline, dropping by 9.5% over the year. This was largely due to falling natural gas and wood chip prices, which enabled many municipalities to adjust their tariffs downward.
Electricity prices also decreased, albeit more modestly, by 3.8%. However, this decline was tempered by a January 1st increase in distribution system service tariffs, which offset some of the savings. The Baltic region’s average electricity price in the “nord Pool” system fell by 7%,driven by the growing adoption of renewable energy sources like solar,wind,and hydroelectric power,as well as a slight dip in natural gas prices across Europe.
Natural gas prices, on the other hand, saw only a marginal decrease of 0.6%. This was influenced by fluctuating tariffs and trading periods, wiht adjustments in may and November playing a significant role.
Food Prices: A Global Ripple Effect
Food prices experienced a 5.5% increase in 2024, contributing to a 1.4 percentage point rise in overall consumer prices. Dairy products and non-alcoholic beverages were the primary drivers of this uptick. globally, food prices rose by 6.7% in December 2024 compared to the previous year, with vegetable oils and dairy products leading the charge.
vegetable oil prices surged due to lower-than-expected production and concerns about output declines in major producing countries. Dairy prices were pushed higher by strong demand and limited stocks, particularly in Western Europe. Meanwhile,cereal and sugar prices bucked the trend,with cereals benefiting from increased exports from the Black Sea region and Russia,and sugar prices dropping due to higher production in India,Thailand,and Brazil.
Over the past five years, global food prices have risen by 26%, while in Latvia, the increase was a staggering 51.4%.
Alcoholic Beverages and Tobacco: Steady Increases
The average price level for alcoholic beverages and tobacco products rose by 6.6% in 2024, adding 0.5 percentage points to the overall price level. Alcoholic beverages saw a 3.2% increase, while tobacco products jumped by an average of 13%. The most significant impact came from the rising cost of cigarettes.
fuel Prices: A Year of Volatility
fuel prices in Latvia decreased by 0.8% over the year, reducing the overall price level by 0.1 percentage points. Diesel prices fell, while gasoline prices remained relatively stable. The year was marked by volatility,with price spikes at the beginning and end of the year offset by sharper declines in May-June and august-September.
Globally, oil prices in December 2024 were down 5.4% compared to December 2023. The year began with rising prices due to OPEC+ production cuts, geopolitical tensions, and attacks on Russian refineries by Ukraine. However, prices plummeted in August-September, reaching a low of $69 per barrel in early September—the lowest since December 2021. This drop was driven by increased oil supply expectations, particularly from Saudi Arabia and Libya, as well as concerns about slowing demand from China.
By October, oil prices rebounded to $81 per barrel due to escalating Middle East tensions, only to fall again to $73 by month’s end.
Key Takeaways
2024 was a year of contrasts, with significant price reductions in energy resources offset by rising costs in food, beverages, and tobacco. fuel prices remained volatile, reflecting the ongoing influence of global geopolitical and economic factors. As we move into 2025, these trends highlight the interconnectedness of local and global markets, underscoring the importance of staying informed about broader economic shifts.
Economic Outlook for 2025: Stability, Inflation, and Global Influences
As we step into 2025, the global economic landscape continues to evolve, shaped by a mix of regional developments, policy changes, and geopolitical dynamics. In Latvia, the economic forecast remains cautiously optimistic, with inflation and purchasing power taking center stage in the national conversation.
Latvia’s Inflation Trends: A Closer Look
in 2024, Latvia recorded an average annual inflation rate of 1.3%, a figure that reflects relative stability in the country’s price levels. Looking ahead, experts predict that inflation will rise slightly to around 2% in 2025. This uptick is attributed to several factors, including new tax reforms and increased purchasing power among the population.
Tax changes are expected to play a dual role in shaping the economy.On the supply side, higher taxes and tariffs may influence production costs, while on the demand side, post-tax salary increases are likely to boost consumer spending. As the Ministry of Economy notes, “The main impact will be the new tax changes, both from the supply side in connection with the increase in taxes and tariffs, and from the demand side, with the increase in the salary after paying taxes, which will increase the purchasing power of the population.”
Global Influences on Latvia’s Economy
While domestic policies are crucial, Latvia’s economic trajectory is also deeply intertwined with global developments. Geopolitical tensions, fluctuations in global markets, and shifts in international trade policies all have the potential to impact local price levels and economic stability.
As an example, the oil market remains a significant wildcard. Despite a modest economic recovery in China during December 2024, driven by government stimulus, the oil sector faces considerable uncertainty. Factors such as the risk of a supply glut,ongoing geopolitical conflicts,and potential changes in U.S. oil policy under a new administration could all influence global energy prices and, by extension, Latvia’s economy.
Regional Stability and Economic Confidence
In recent months, regional conflicts have shown signs of de-escalation, particularly in the Middle East. Israel’s measured response to tensions has been more restrained than anticipated, easing market fears and fostering hopes for further stability. This cautious optimism has contributed to a more favorable economic outlook in the region, which could have ripple effects on global markets.
What Lies Ahead?
As we navigate 2025, Latvia’s economic stability will depend on a delicate balance between domestic reforms and external influences. While inflation is expected to rise slightly, the overall price level is projected to remain stable, supported by increased purchasing power and strategic policy adjustments.
However, the global landscape remains unpredictable. Geopolitical developments, oil market dynamics, and international trade policies will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping Latvia’s economic future. Staying informed and adaptable will be key to navigating these uncertainties.
Ministry of Economy



