The US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) announced the successful completion of the third of seven phases of alignment of the 6-meter mirror of the James Webb Space Telescope. This means that the device has become even closer to turning into a full-fledged space observatory and starting scientific research.
Image Source: Northrop Grumman
It is expected that the process of setting up and commissioning the James Webb telescope will take several more months. Scientists from NASA go to the goal in accordance with the plan. One of the latest achievements of the JWST team was the elimination of large deviations in the positioning of the 18 elements of the telescope’s main mirror relative to each other.
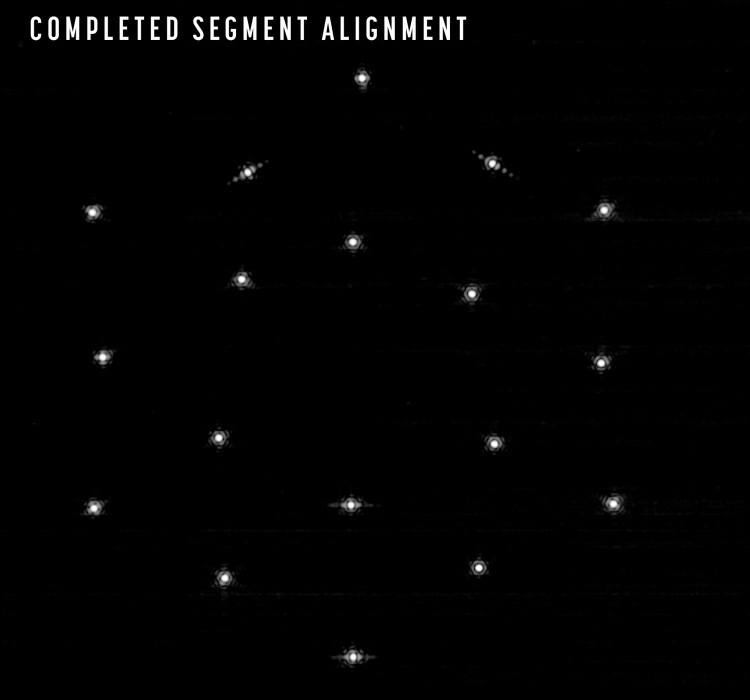
Image Source: NASA
First, the telescope formed 18 out-of-focus images of the same star using separate mirror segments. After that, the primary and secondary mirrors were aligned in such a way that a symmetrical picture was obtained (photo above). Then the segments changed positions so that the reflected photons hit the infrared sensor of the NIRCam instrument. Ultimately, it was possible to ensure that the focused shots from each of the segments were superimposed on each other, giving a single image of the star, as in the photo below.
“We still have work to do, but we are increasingly satisfied with the results achieved. Years of planning and testing are paying off and the team is looking forward to the next weeks and months.”says Lee Feinberg, JWST optics specialist.

Image Source: NASA
Although scientists have been able to piece together individual images of the star, the segments of the mirror continue to operate like 18 small telescopes. In order for them to function as a whole, scientists will have to fine-tune the position of all elements of the mirror. Now begins the fourth stage of mirror alignment, during which scientists must determine and eliminate vertical offsets between the mirror segments, as well as small differences in their height relative to each other. Due to this, “James Webb” will be able to get even better focused and sharper images, which will bring it even closer to the start of scientific observations.
If you notice an error, select it with the mouse and press CTRL + ENTER.



