Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha Rocket: An Analysis and Future Trends
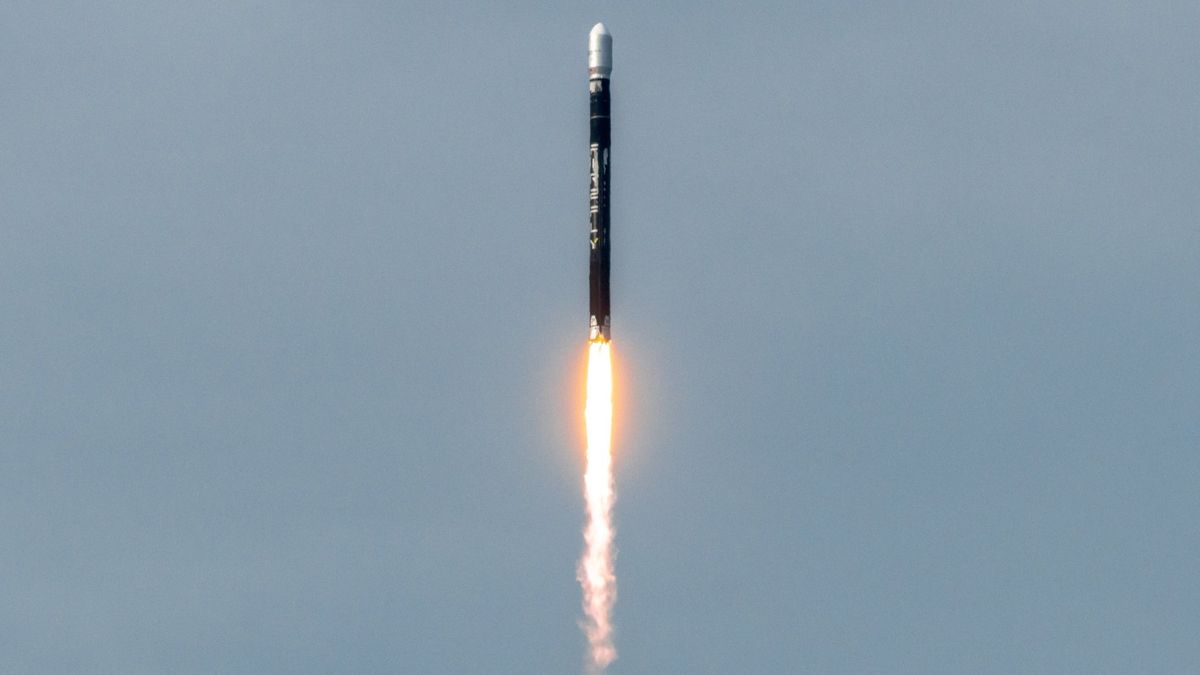
We now have a deeper understanding of the factors that led to the partial success of Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket during its Fly the Lightning mission last year. The mission, which aimed to deliver an electronically steerable antenna payload developed by Lockheed Martin to low Earth orbit (LEO), encountered a glitch in the Guidance, Navigation, and Control (GNC) software algorithm that prevented the system from sending necessary pulse commands to the Reaction Control System (RCS) thrusters before the stage two engine relight.
Firefly Aerospace recently concluded its mishap investigation and announced that corrective actions were being implemented to address the GNC software issue. The company assured that the Alpha rocket would be ready to fly once more in the coming months.
Implications and Connections to Current Events
The incident with Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket highlights the importance of robust and error-free software algorithms in space missions. As the space industry becomes increasingly reliant on advanced technology, ensuring the integrity and reliability of software systems is crucial to avoid mission failures.
This incident also draws attention to the rapid advancements in the commercial space sector. Companies like Firefly Aerospace are pushing the boundaries of innovation, aiming to offer affordable and efficient access to space. As more players enter the market, competition intensifies, spurring further innovation and driving costs down.
Furthermore, the successful deployment of the payload, despite the software glitch, demonstrates the resilience and adaptability of modern space technologies. Despite the challenges faced, Firefly Aerospace managed to accomplish the primary mission objectives, showcasing the industry’s ability to overcome obstacles and deliver results.
Potential Future Trends
Looking ahead, several trends are likely to shape the future of the space industry:
- Software Reliability: The incident with Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket underscores the need for stringent software testing and quality control processes. Companies will continue to invest in developing robust algorithms to ensure mission success.
- Increased Commercialization: The commercial space industry is expected to see continued growth and diversification. More companies will enter the market, driving competition and innovation, and expanding opportunities for space exploration and research.
- Advancements in Launch Capabilities: As rocket technologies advance, we can anticipate faster and more frequent launches. Rapid turnaround times, such as Firefly Aerospace’s record-breaking launch just 27 hours following receiving the order, will become increasingly common.
- Collaboration with Government Entities: Partnerships between private companies and government agencies, like Firefly Aerospace’s collaboration with the U.S. Space Force, will play a crucial role in advancing space exploration and national security initiatives. These alliances foster knowledge exchange and resource sharing.
Unique Predictions and Recommendations
In light of these trends and the incident with Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket, the industry should consider the following recommendations:
- Invest in Redundancy: To mitigate the impact of potential software glitches or system failures, companies should prioritize the development of redundant systems and backup mechanisms.
- Promote Collaboration: Collaboration between space companies, government agencies, and research institutions should be encouraged to foster innovation and accelerate the pace of technological advancements.
- Enhance Cybersecurity Measures: With software playing a critical role in space missions, companies must invest in robust cybersecurity measures to protect their systems from potential threats and ensure the integrity of their operations.
- Explore Emerging Technologies: Companies should actively explore emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and advanced materials, to unlock new possibilities and improve the efficiency of space technologies.
As the space industry advances, the incident with Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket serves as a reminder of the complexities and challenges associated with space exploration. Nevertheless, it also highlights the industry’s resilience and dedication to pushing boundaries. By addressing the software issue and embracing future trends, the space industry can forge ahead, unlocking new frontiers and paving the way for humanity’s continued exploration of the cosmos.