2023-04-20 03:00:00
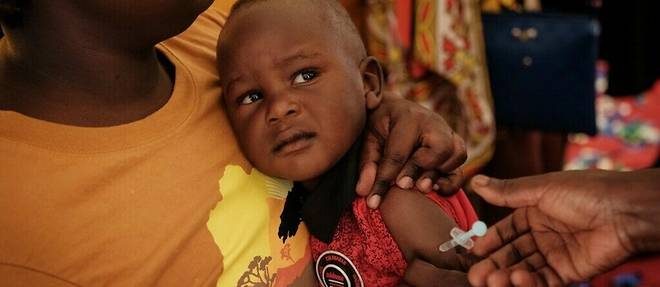
According to a UNICEF report, 67 million children were at least partially deprived of vaccines between 2019 and 2021, due to the health crisis.
By QM with AFP
© YASUYOSHI CHIBA / AFP
Published on
Subscriber-only audio playback
Un alarming global health finding. Between 2019 and 2021, 67 million children were totally or partially deprived of life-saving vaccines due to the disruptions linked to the Covid-19 epidemic. A figure that brings the world back more than ten years in terms of childhood vaccination, alarms the UN.
In three years, due to constraints on health systems or pandemic-related lockdowns, “more than a decade of progress in routine childhood immunizations has been undermined”, and “recovering the right path will be a challenge, ”underlines the UNICEF report published on Wednesday April 19, which is concerned regarding the risk of epidemics of measles or polio.
According to the UN agency, this vaccination coverage is down in 112 countries. And between 2019 and 2021, the global childhood immunization rate fell by 5 percentage points, to 81%, a level not seen since 2008: 67 million children missed out on vaccines, particularly in Africa and South Asia, and 48 million of them received no dose of any kind.
READ ALSOThe French and the vaccine: I love you, me neither
Over 4 million lives saved each year
A situation all the more worrying as this decline occurred at the end of a decade when “the growth of childhood vaccination was stagnating”, following the massive increase in the 1980s, underlines the UN agency. “Vaccines have played a really important role in enabling children to live long, healthy lives”, so “any decline in vaccination rates is worrying”, Brian Keeley, editor in chief, told Agence France-Presse. report leader.
READ ALSO#TouchePasAMesEnfants: when Twitter ignites on childhood vaccination
Childhood immunization saves 4.4 million lives each year, says UNICEF, a number that might rise to 5.8 million if the world managed to halve the number of deprived children by 2030. of essential vaccines and to achieve 90% coverage for key life-saving vaccines.
Before the introduction of the vaccine in 1963, measles killed some 2.6 million people a year, mostly children. A figure dropped to 128,000 in 2021 for this disease which today is of particular concern to the UN. In three years, the vaccination rate once morest measles – so contagious that it requires 95% vaccinations in a community to achieve herd immunity – has dropped from 86% to 81%, according to the report. And the number of measles cases doubled in 2022 compared to 2021.
READ ALSOSébastien Le Fol – Measles: quickly, a vaccine once morest stupidity!
A decline in confidence in vaccination in many countries
The fall in the vaccination rate, similar for polio, diphtheria or whooping cough, is also occurring in a broader context of the “survival crisis” of children, notes UNICEF, highlighting an overlapping of crises (malnutrition, impacts climate change, poverty, etc.). “It is increasingly difficult for health systems and governments to meet the need for vaccinations,” said Brian Keeley.
READ ALSOCovid-19 vaccine: where is Africa really?
To improve vaccination coverage, however, it is necessary to “strengthen primary health care and provide front-line staff, mostly women, with the resources and support they need”, insists UNICEF. Not to mention the 67 million children deprived of vaccines during the Covid who will come out of the age group targeted by vaccinations, argues Brian Keeley, calling for them for a “determined catch-up program”.
READ ALSOCovid-19: “Vaccine mistrust resurfaces”
At the same time, while the debates around Covid have put antivaccines back in the spotlight, the report is concerned regarding a drop in confidence in vaccination in 52 out of 55 countries studied. “These data are a worrying warning signal,” warned UNICEF boss Catherine Russell in a statement.
“Encouraging” data for 2022
“Trust in routine immunization must not be a casualty of the pandemic as well, or large numbers of children will soon die of measles, diphtheria or other diseases. avoidable”. In half of these 55 countries, “notoriously changing” vaccine confidence remains above 80%, however, tempers UNICEF.
READ ALSOThe Congo facing Covid-19: the reasons for mistrust
And despite this mistrust, “there is reason to be optimistic that services are resuming in a number of countries,” said Brian Keeley, referring to “encouraging” preliminary data for vaccinations in 2022.
But “even if we manage to get back to where we were before the pandemic, hopefully in a few years”, progress will still have to be made to vaccinate those who were deprived of their injections already before the Covid, insists. -he.
1682022288
#alarming #effects #Covid19 #epidemic #lifesaving #vaccines