2024-06-08 09:31:00
Six years following an enormous tidal eddy 25 kilometers in diameter was found within the Baltic Sea, specialists warn that useless zones attributable to tidal currents are nonetheless spreading in seas around the globe.
A analysis report revealed on the seventh by a global analysis crew composed of local weather, environmental and marine biologists said that between 2003 and 2020, the common measurement of world algae emergence elevated by 13%.
When algae develop in giant numbers, there can be an absence of oxygen within the water, making a useless zone the place aquatic life can not survive. Due to this, the ecosystem within the related sea areas has reached a state of collapse and requires enormous efforts to recuperate.
NASA’s Earth Observatory revealed large tidal eddies within the Gulf of Finland in 2018.
The crew started investigating the reason for the useless zone following a photograph was launched in 2018 by way of NASA’s Earth Observatory, an Earth satellite tv for pc observatory operated by the Nationwide Aeronautics and Area Administration (NASA). NASA’s Earth Observatory has launched a photograph of an enormous tidal vortex 25 kilometers in diameter protecting the Gulf of Finland within the Baltic Sea.
The investigation official defined, “This enormous whirlpool, which makes individuals really feel awe or worry of nature, seems to be like the attention of a storm.” “Stagnation is the fast and high-density look of enormous quantities of algae, dyeing the water floor inexperienced.”
“These harmful algae are increasing and showing extra steadily as a result of human actions and local weather change,” he continued, including, “In current many years, agricultural wastewater has flowed into the ocean, inflicting eutrophication, which is a significant issue in water our bodies.” The results of oversupply.
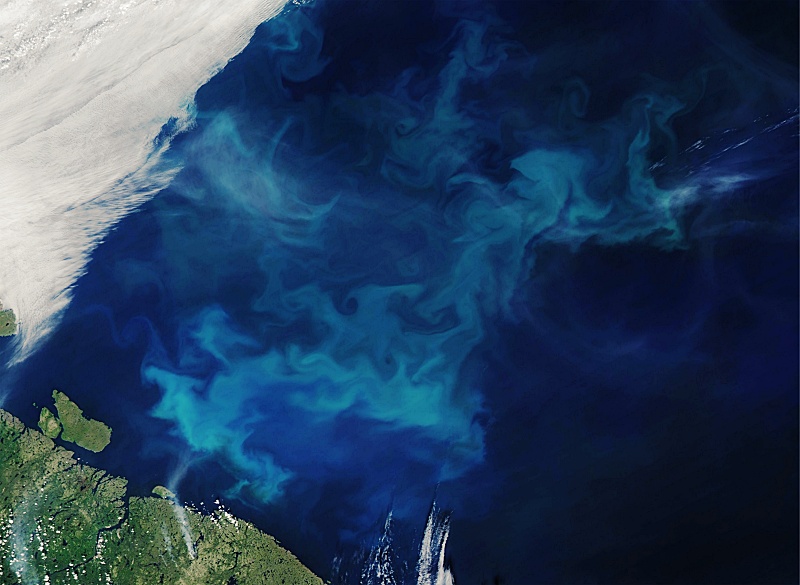

Numerous algae within the ocean produce foam on the similar time. It is known as an algae bloom.
The inexperienced vortex within the Gulf of Finland has now expanded to regarding 70,000 sq. kilometers, accounting for regarding one-third of the Korean Peninsula. The useless zone is getting greater, and as local weather change causes seawater temperatures to rise, the water can not keep its earlier oxygen ranges, so the focus of oxygen crucial for aquatic life to outlive is declining.
“Oxygen concentrations in Baltic waters are already at their lowest ranges up to now 1,500 years, in keeping with a 2018 examine. Final 12 months, the worst El Niño in historical past brought on a record-breaking rise,” mentioned a analysis official. Sea floor temperatures are rising. , so the dreaded algae might seem this summer season.
Reporter Lee Yoon-seo [email protected]
⇒Go to Sputnik Naver Put up
⇒Go to the Sputnik YouTube channel
1717882133
#Superbirds #threaten #marine #ecosystems