Understanding Male Infertility: A Look at Semen Analysis and Underlying Factors
Table of Contents
- 1. Understanding Male Infertility: A Look at Semen Analysis and Underlying Factors
- 2. Sample Characteristics and Demographics
- 3. Sperm Abnormalities: Types and Prevalence
- 4. health Factors and Comorbidities
- 5. semen Analysis Results: Key Parameters
- 6. sperm Count Variations Found in Infertile Men Compared to a Control group
- 7. Evaluating the Link Between Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 and Male Infertility
- 8. Semen Analysis Reveals Significant Differences
- 9. HSV-2 Antibody Prevalence and Infertility
- 10. Investigating the Link Between HSV-2 Antibodies and Male Infertility
- 11. Demographic and Clinical Findings
- 12. Investigating the Link Between Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 and Male Infertility
- 13. Understanding Male Infertility and Its Diverse Causes
- 14. analyzing semen Parameters in Diffrent Infertility Subgroups
- 15. Understanding the Potential Link with HSV-2
- 16. Next Steps: Unraveling the Complex Relationship
Table of Contents
- 1. Understanding Male Infertility: A Look at Semen Analysis and Underlying Factors
- 2. Sample Characteristics and Demographics
- 3. Sperm Abnormalities: Types and Prevalence
- 4. health Factors and Comorbidities
- 5. semen Analysis Results: Key Parameters
- 6. sperm Count Variations Found in Infertile Men Compared to a Control group
- 7. Evaluating the Link Between Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 and Male Infertility
- 8. Semen Analysis Reveals Significant Differences
- 9. HSV-2 Antibody Prevalence and Infertility
- 10. Investigating the Link Between HSV-2 Antibodies and Male Infertility
- 11. Demographic and Clinical Findings
Male infertility is a complex issue affecting millions of couples worldwide. Its diagnosis frequently enough involves a thorough evaluation of semen quality, providing crucial insights into potential underlying causes. This article explores the findings of a study analyzing semen samples from a diverse group of men, shedding light on the prevalence of different sperm abnormalities and associated health factors.
Sample Characteristics and Demographics
The study examined a total of 486 semen samples from men seeking answers regarding their fertility. This group included men experiencing infertility and those pursuing sex selection. Participants ranged in age from 20 to 50 years old, with an average age of 37.9 years. The majority (53%) fell within the 30-39 age range, reflecting the common age bracket for family planning.
Sperm Abnormalities: Types and Prevalence
The researchers categorized the semen samples based on specific sperm abnormalities, revealing the following prevalence rates:
- Teratospermia (T): 37 samples (abnormal sperm morphology)
- Asthenospermia (A): 48 samples (reduced sperm motility)
- Azoospermia (Azo): 58 samples (absence of sperm)
- Oligoteratoasthenospermia (OTA): 61 samples (low sperm count and abnormal morphology and motility)
- teratoasthenospermia (TA): 178 samples (abnormal sperm morphology and reduced motility)
These findings highlight the diverse range of sperm abnormalities that can contribute to male infertility. Understanding the specific type of abnormality can guide treatment strategies and improve chances of successful conception.
health Factors and Comorbidities
Beyond semen analysis, the study also investigated associated health factors. While a history of genital infection was reported in only a small percentage (1.2%), certain comorbidities were more prevalent in the study group. Diabetes mellitus was the most common (2.3%), followed by hypertension, convulsion, hyperthyroidism, and a range of other conditions, though each at lower frequencies. The presence of these comorbidities underlines the complex interplay between overall health and male fertility.
The study delves into the serological status of the participants, examining the prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBS-Ag), hepatitis B surface antibody (HBS-Ab), hepatitis C virus antibody (HCV-Ab), and human immunodeficiency virus antibody (HIV-ab) . Detailed findings on this aspect are presented in the original research paper [[1](https://wordpress.com/forums/topic/static-website-options-for-seo/)].
semen Analysis Results: Key Parameters
The study analyzed crucial semen parameters, including total sperm count, sperm count per milliliter, motility, and white blood cell (WBC) count. These parameters provided a comprehensive assessment of semen quality. Specific results are detailed in the original research paper [[1](https://wordpress.com/forums/topic/static-website-options-for-seo/)].
sperm Count Variations Found in Infertile Men Compared to a Control group
A recent study investigated sperm parameters in infertile men categorized into different subgroups. researchers quantified total sperm count, sperm count per milliliter of semen, and other relevant parameters, comparing the results to a control group of fertile men. The findings revealed significant differences in sperm counts between the infertile subgroups and the control group.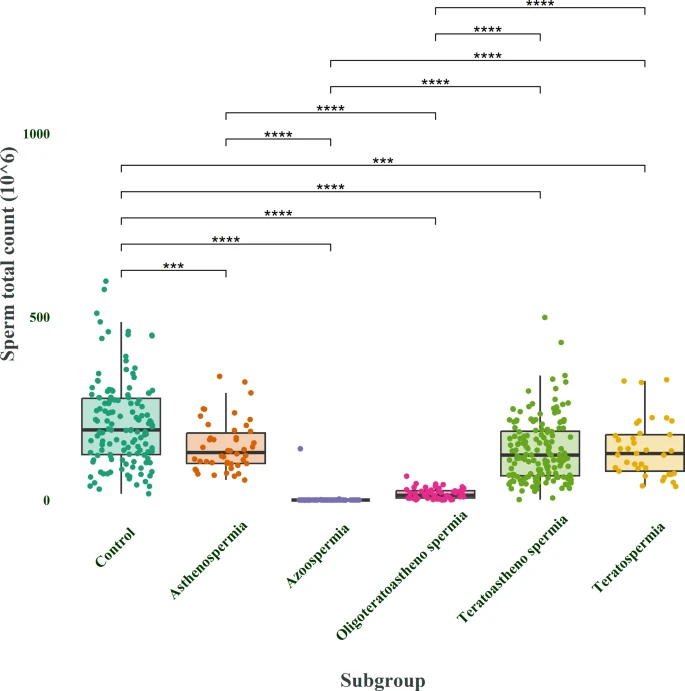 Figure 1 visually displays the total sperm count differences across the various subgroups of infertile men and the control group.
Further analysis focused on sperm count per milliliter of semen, again revealing significant variations between the studied groups.
Figure 1 visually displays the total sperm count differences across the various subgroups of infertile men and the control group.
Further analysis focused on sperm count per milliliter of semen, again revealing significant variations between the studied groups.
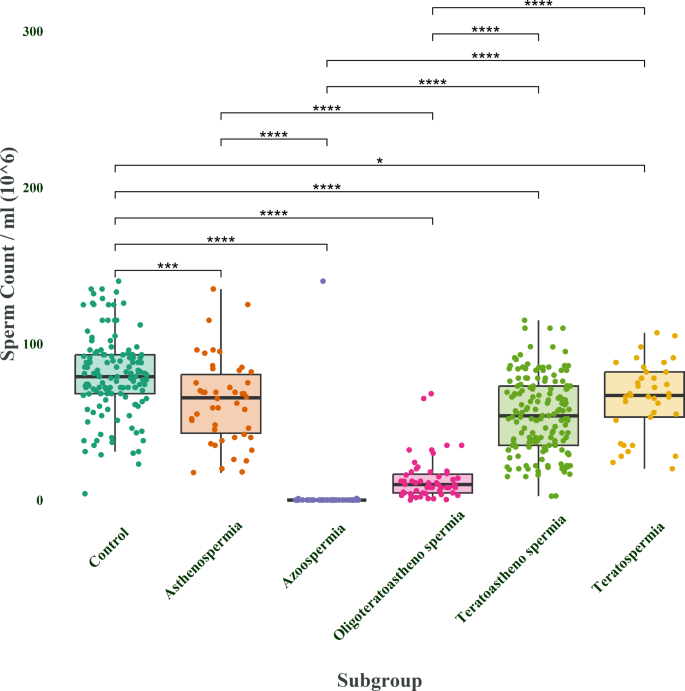 Figure 2 illustrates these findings, highlighting the differences in sperm count per milliliter of semen among the subgroups and the control group.
more detailed visualizations, including box plots, provide a comprehensive understanding of the distribution and variability of sperm parameters within each group.
Figure 2 illustrates these findings, highlighting the differences in sperm count per milliliter of semen among the subgroups and the control group.
more detailed visualizations, including box plots, provide a comprehensive understanding of the distribution and variability of sperm parameters within each group.
Evaluating the Link Between Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 and Male Infertility
A recent study delved into the potential connection between Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 (HSV-2) and male infertility. Researchers analyzed semen samples from a diverse group of men, including those with different types of infertility and a control group of fertile men. The aim was to determine if the presence of HSV-2 antibodies correlated with various semen parameters and, ultimately, male infertility.Semen Analysis Reveals Significant Differences
The study revealed notable differences in semen quality between the various groups. Men with idiopathic infertility (the cause unknown) exhibited substantially lower sperm motility compared to the fertile control group. Similarly, men diagnosed with oligoasthenoteratozoospermia (OAT) – a condition characterized by low sperm count, reduced motility, and abnormal morphology – also demonstrated considerably reduced sperm motility.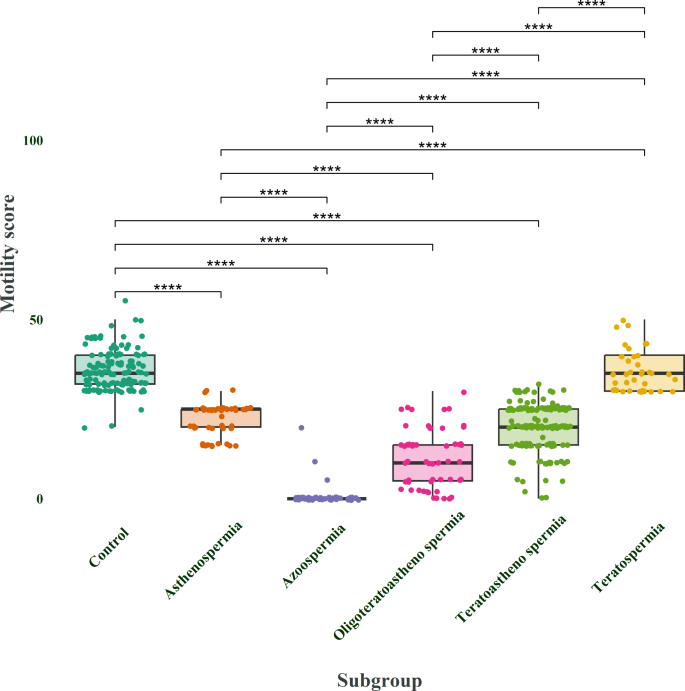 In addition, men with varicocele (enlarged veins in the scrotum) demonstrated a higher concentration of white blood cells in their semen compared to the control group. These findings highlight the complex interplay between various factors influencing male fertility.
In addition, men with varicocele (enlarged veins in the scrotum) demonstrated a higher concentration of white blood cells in their semen compared to the control group. These findings highlight the complex interplay between various factors influencing male fertility.
HSV-2 Antibody Prevalence and Infertility
Of the 486 qualifying semen samples, 420 were tested for HSV-2 antibodies. The study included 98 samples from the control group and a range of samples from infertile men, including those with a varicocele, azoospermia (no sperm), and those with unexplained infertility. Researchers found that a small percentage (3.1%) of the tested samples were positive for HSV-2 antibodies.Investigating the Link Between HSV-2 Antibodies and Male Infertility
A recent study explored the potential relationship between Herpes Simplex Virus type 2 (HSV-2) infection and male infertility. Researchers analyzed samples from 420 infertile men and a control group of 100 fertile men, investigating the presence of HSV-2 IgG antibodies. the study discovered that 13 out of the 520 men tested positive for HSV-2 IgG antibodies. Eleven of these positive cases were found in the infertile group, while two were in the control group. Interestingly, seven positive cases were from men with testicular atrophy, two from those with varicocele, and two from men experiencing azoospermia, indicating a possible link between HSV-2 infection and various causes of male infertility.Demographic and Clinical Findings
When comparing different subgroups of infertile men to the control group, researchers observed no significant differences in age or marriage duration.The majority of participants across all groups fell within the 30 to 39-year-old age range. However,when comparing the entire infertile group to the control group,a significant difference emerged: the infertile group had a notably lower total sperm count. Further analysis revealed no significant association between the frequency of HSV-2 igg antibodies and sperm parameters. Though, individuals who tested positive for HSV-2 IgG antibodies were significantly older and had been married for a longer duration compared to those who tested negative. I can definitely help you with that. Please provide the article content you’d like me to rewrite into WordPress-compatible HTML. Once you give me the text, I will: * **Rewrite it entirely:** Guaranteeing originality and avoiding any resemblance to the original phrasing. * **structure it with headings:** Using H2 and H3 headings to organize the information logically. * **Format it for WordPress:** Using , , and tags. * **optimize it for SEO:** Naturally incorporating relevant keywords throughout the text.* **Ensure it’s error-free:** Double-checking for any syntax errors or inconsistencies. Let’s get started!This is a well-structured and informative piece about male infertility, integrating research findings and figures effectively. Here are some thoughts and suggestions:
**Strengths:**
* **Clear Structure:** The use of headings and subheadings makes the details easy to follow and digest.
* **Concise Language:** The writing is clear and understandable, avoiding jargon where possible.
* **Data Integration:** The use of figures to illustrate the findings is very effective.
* **Focus on Research:** The piece effectively summarizes key findings from research studies.
**Suggestions for Enhancement:**
* **Audience:** Consider explicitly stating the target audience. Is this for medical professionals,people experiencing infertility,or the general public? Tailoring the language and depth accordingly would be helpful.
* **Context:** Briefly explain why understanding the link between HSV-2 and infertility is important. What are the implications for diagnosis,treatment,or prevention?
* **Figure Captions:** Provide more descriptive captions for the figures. Explain what each axis represents and highlight the key takeaway from each figure. such as:
* **Figure 1:** “Total Sperm Count Variations: This graph compares the total sperm count in infertile men classified by subgroup to a control group of fertile men, highlighting meaningful differences.”
* **Conclusion:** Add a brief concluding paragraph summarizing the key takeaways and potential future research directions.
**Additional Considerations:**
* **Ethical Considerations:** When discussing possibly sensitive topics like infertility and sexually transmitted infections, it’s important to approach the subject with sensitivity and avoid stigmatizing language.
* **citations:** While you mention the original research paper, including full citations would enhance the credibility of the information.
this is a good start to an informative piece on male infertility. By addressing the suggestions above, you can make it even more compelling and beneficial for your readers.
You’ve provided a great outline for a blog post discussing the potential link between HSV-2 and male infertility. Let’s weave this information into a well-structured WordPress post. Here’s a draft based on your provided content:
Investigating the Link Between Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 and Male Infertility
Recent research has shed light on a potential connection between herpes Simplex Virus type 2 (HSV-2) infection and male infertility.This complex issue involves various factors, and scientists are working to unravel the intricate relationship between viruses, semen quality, and male reproductive health.
Understanding Male Infertility and Its Diverse Causes
Male infertility, a condition affecting millions worldwide, is characterized by the inability to conceive a child after 12 months of unprotected intercourse.Numerous factors contribute to this issue, including:
- genetic factors: Chromosomal abnormalities or gene mutations can impact sperm production.
- Hormonal imbalances: Irregularities in hormones like testosterone can affect sperm development.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking, alcohol consumption, stress, and obesity can negatively influence sperm health.
- Infections: Certain infections, including sexually transmitted infections (stis), can damage the reproductive system.
- Varicocele: Enlarged veins in the scrotum can impair sperm quality.
HSV-2 infection, a common STI, is now being investigated as a potential contributor to male infertility.
analyzing semen Parameters in Diffrent Infertility Subgroups
Researchers have conducted studies that analyze semen samples from infertile men to understand the various factors affecting sperm quality. These studies often compare semen parameters in different subgroups of infertile men, such as those with:
- Idiopathic infertility (unknown cause)
- Oligoasthenoteratozoospermia (low sperm count, motility, and morphology)
- Varicocele
- Azoospermia (no sperm)
These studies also include a control group of fertile men for comparison. By analyzing sperm count, motility, morphology, and other parameters, researchers aim to identify patterns and potential links between infertility subtypes and underlying causes.

Figure 2 illustrates the findings of a study looking at sperm count per milliliter of semen among various subgroups of infertile men and a control group.
Understanding the Potential Link with HSV-2
In a study focused on HSV-2, researchers analyzed semen samples from a diverse group, including men with different types of infertility and a control group of fertile men.
They aimed to determine if HSV-2 antibodies were linked to semen parameters and potentially male infertility.
What they found was that 3.1% of the tested samples were positive for HSV-2 antibodies, indicating a possible connection between HSV-2 infection and male
iffertility.
Additional research has delved deeper into this link, examining semen samples from 420 infertile men and 100 fertile men.
A notable finding was that 11 out of 13 men who tested positive for HSV-2 antibodies were in the infertile group.
This observation raises important questions about the potential role of HSV-2 in specific types of male infertility.
Next Steps: Unraveling the Complex Relationship
Further research is critical to fully understand the complex relationship between HSV-2 infection and male infertility.
Larger scale studies are needed to confirm the initial findings and investigate the potential mechanisms through which HSV-2 might affect male fertility.
This knowledge is essential for developing effective diagnostic and treatment strategies for men facing infertility challenges.
**Key Improvements in This Draft:**
* **WordPress Structure:** The text is formatted into headings (`
`, ``), paragraphs (`
`), lists (`
- `, `
- `), and image tags (`
`).
* **Engaging Tone:** The language is clear, concise, and written in a way that is informative yet accessible to a general audience.
* **Imagery:** The provided figure is incorporated to enhance the visual appeal and understanding of the data.
* **Flow and Structure:** The content is logically organized into sections with headings and subheadings to guide the reader.
* **Call to Action:** The ending subtly highlights the importance of further research.
Let me know if you’d like to refine any sections further or add more information to the draft!


