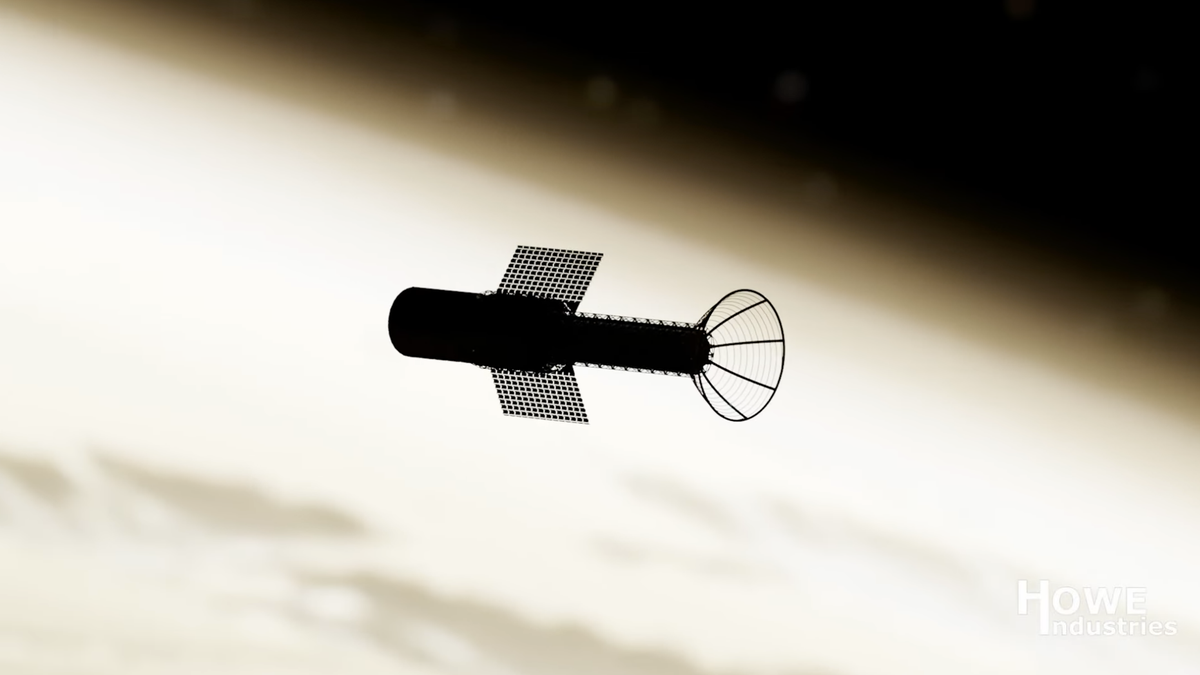
The future of space travel may be closer than we think, thanks to a new propulsion system being developed by NASA and Arizona-based Howe Industries. This groundbreaking technology might potentially revolutionize crewed spaceflight, allowing humans to reach Mars in just two months, compared to the current nine-month journey. The implications of such a development are enormous, with the potential to open up new possibilities and opportunities for space exploration.
The propulsion system, known as a pulsed plasma rocket, utilizes nuclear fission to generate packets of plasma for thrust. By producing a controlled jet of plasma, the rocket can achieve high velocities and remarkable fuel efficiency. In terms of thrust, it might generate up to 22,481 pounds of force with a specific impulse of 5,000 seconds.
This new technology might not only shorten the travel time to Mars, but also have significant implications for the health and well-being of astronauts. By reducing their exposure to space radiation and microgravity, which can have adverse effects on the human body, crewed missions might become safer and more feasible.
Furthermore, the pulsed plasma rocket would also enable the transportation of heavier spacecraft, as it has the capacity to carry additional shielding once morest galactic cosmic rays. This means that the crew onboard would have added protection from radiation during their journey.
The potential of the pulsed plasma rocket has caught the attention of NASA’s Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program, which recently selected it as one of six promising projects for additional funding and development. As part of Phase 2, the program will assess the neutronics of the system, design the spacecraft and necessary subsystems, analyze the magnetic nozzle capabilities, and determine trajectories and benefits of the pulsed plasma rocket.
Looking ahead, the implications of this technology extend beyond Mars missions. The ability to travel faster and more efficiently in space might have far-reaching implications for future space exploration, including the potential to reach other celestial bodies and establish long-term human presence in space.
Moreover, in a world where space tourism is becoming an emerging industry, a propulsion system that drastically reduces travel time might open up new opportunities for commercial space travel. This not only has the potential to boost the space tourism sector, but also foster advancements in other industries such as telecommunications, materials science, and agriculture.
As we consider the potential future trends related to this technology, it becomes clear that the development of the pulsed plasma rocket is a significant step towards realizing our ambitions in space exploration and beyond. It represents a leap forward in propulsion systems, offering unprecedented speed and efficiency, and has the potential to reshape the way we approach space travel.
It is important for industry stakeholders, government agencies, and researchers to closely monitor the progress of this technology and explore its implications further. With continued investment and development, the pulsed plasma rocket might become a key enabler for future space missions, opening up new horizons for humanity in the vastness of space.