Long before rovers roamed the planet and space telescopes captured high-resolution deep space images, NASA created concept art as a means to illustrate its missions. Compared to the early days, the understanding of the universe has progressed and the method of drawing has evolved, but the excitement of looking at concept art has not faded. Looking back at the history of NASA space development through concept art.
First, NASA released a cross-section of the Mercury spacecraft in April 1959, shortly following its founding. Project Mercury was conducted from 1959 to 1963 to prove that humans might live and work in space, paving the way for future manned exploration.
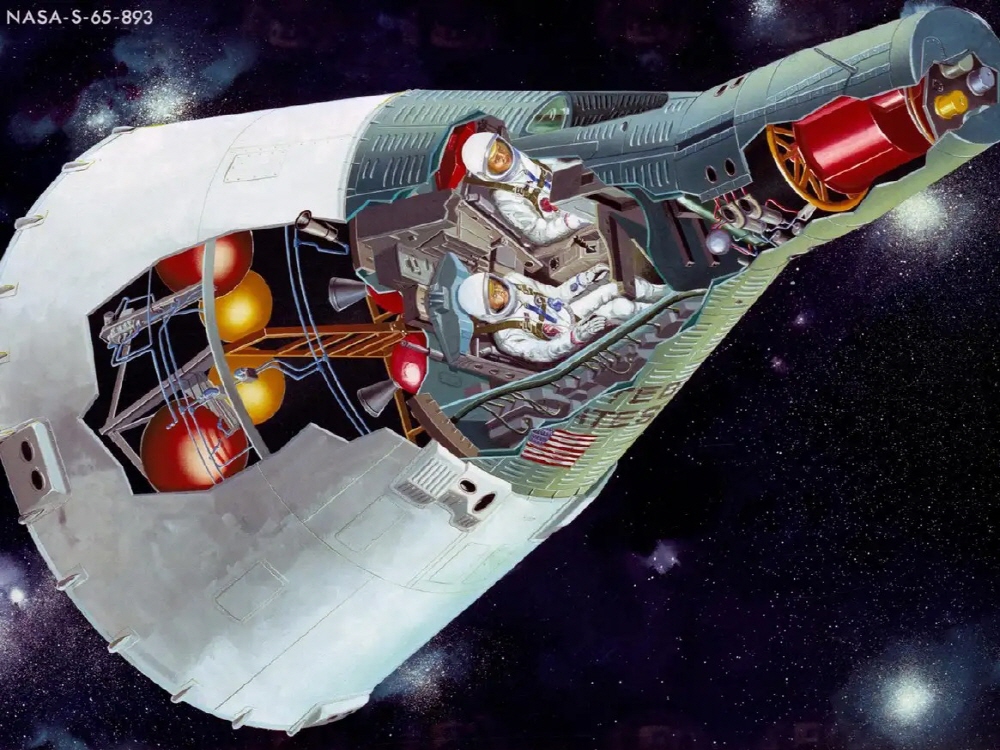
In the Gemini Project, which was carried out from 1962 to 1966 following Project Mercury, a large spacecraft was built to accommodate two astronauts. These spacecraft were used for rendezvous and docking verification among the technologies required for the Apollo program targeting the lunar surface.
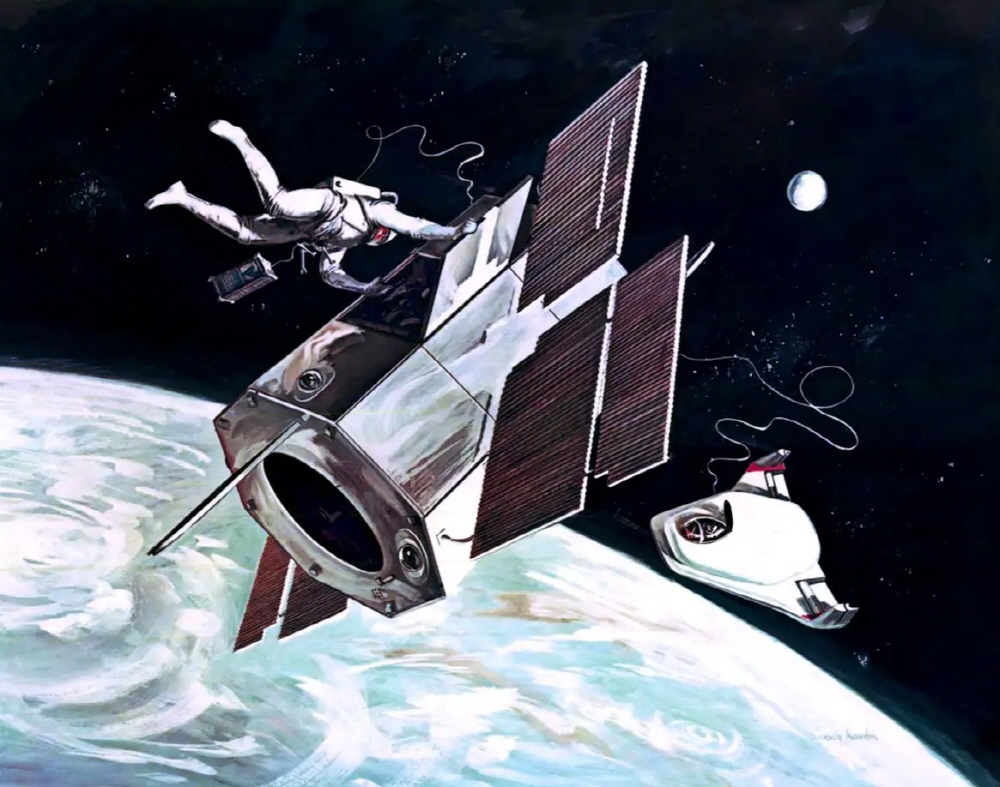

In the mid-1960s, NASA was already contemplating spacewalks to repair satellites in low Earth orbit. At the time, you can see an illustration of an astronaut repairing the Orbiting Astronomical Observatory at NASA.
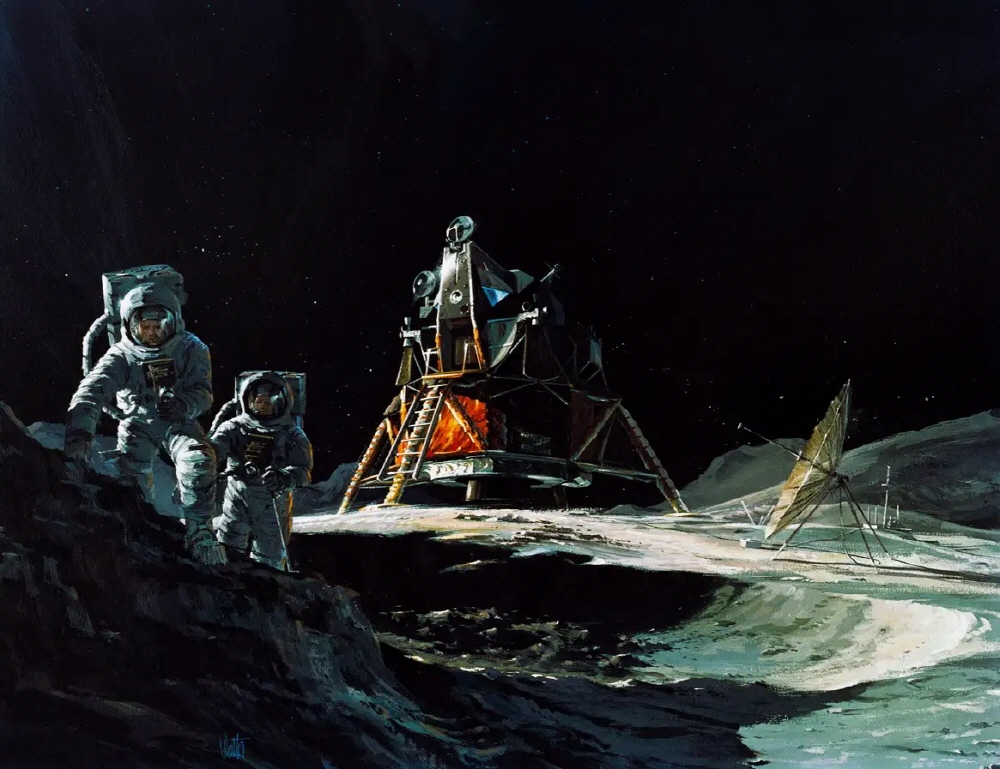

It is a concept painting depicting the famous Apollo 13 mission in 1970, when the moon landing did not take place.
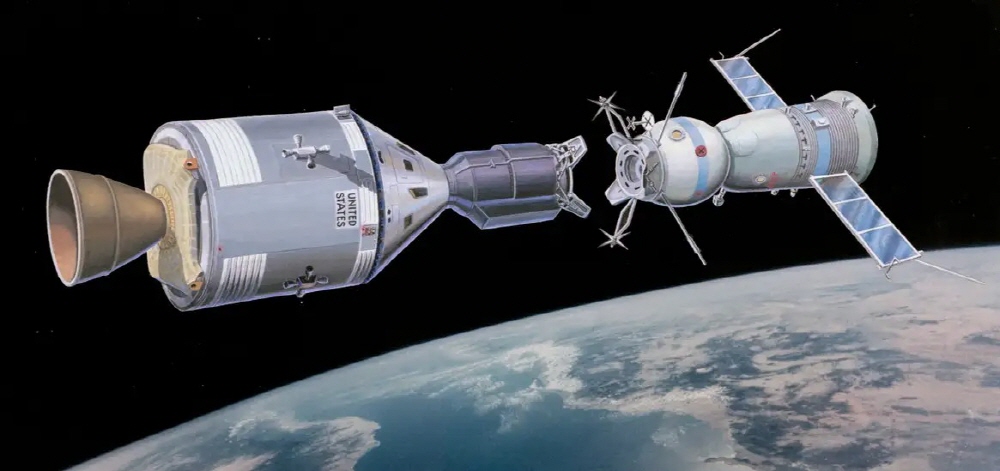
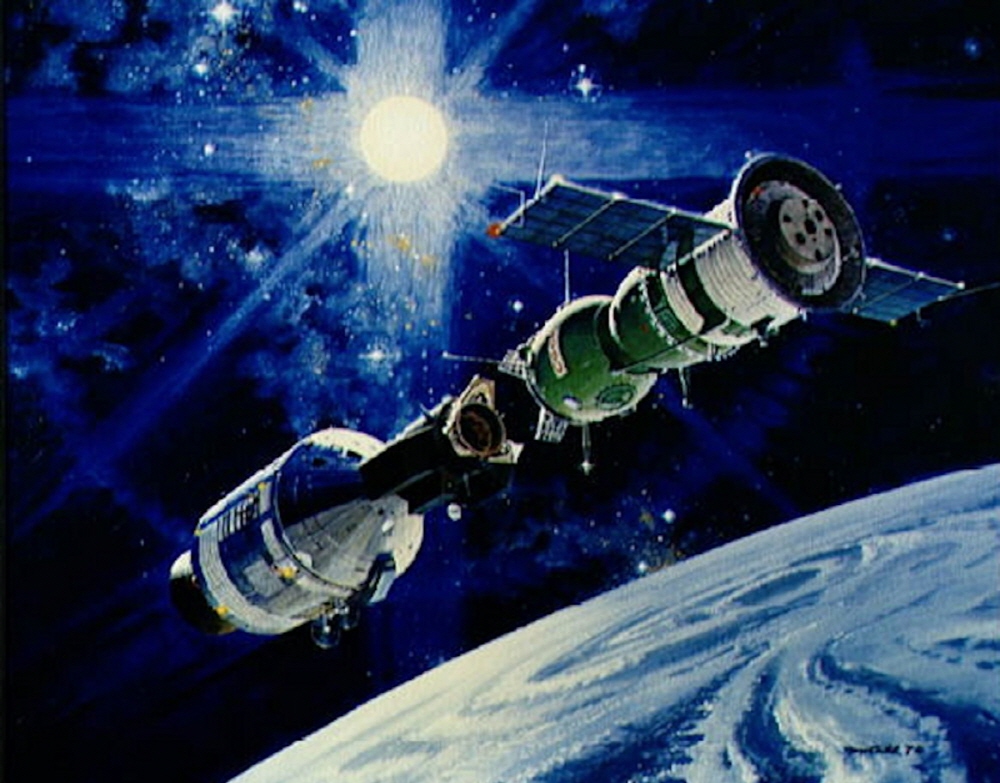
The 1975 Apollo Soyuz test project was the first joint space program between the United States and the Soviet Union. Millions of people around the world watched the docking of the two spacecraft and the smiling astronauts shook hands in low Earth orbit.

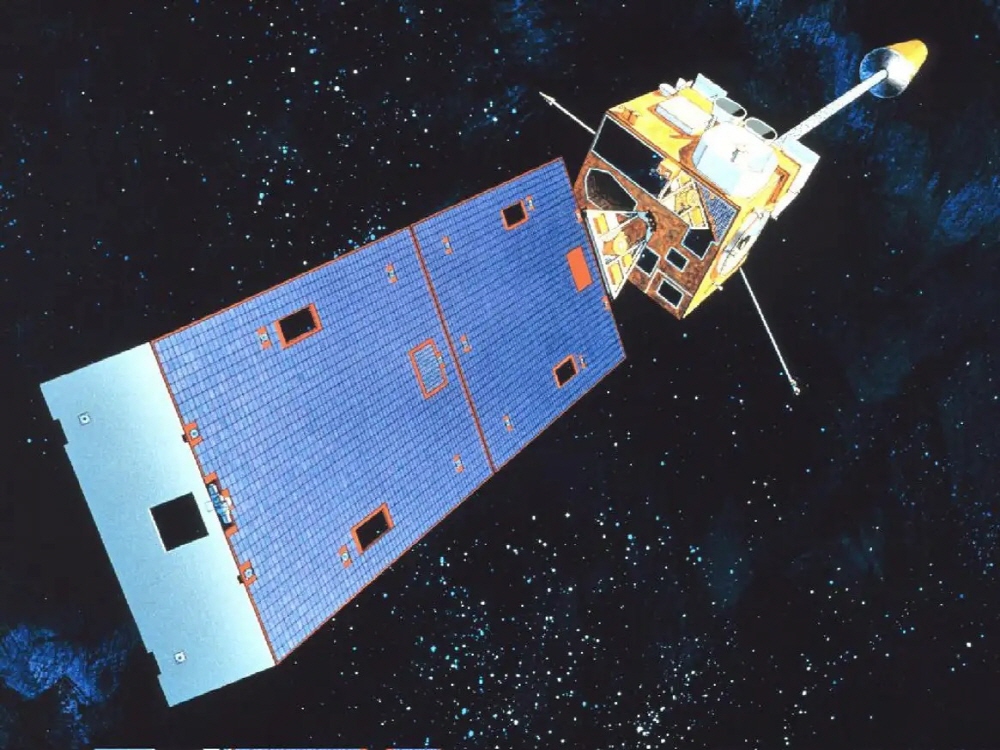
Launched on October 16, 1975, the first GOES (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites) satellites tracked surface storms from geostationary orbit and predicted global weather patterns. This program continues to this day.

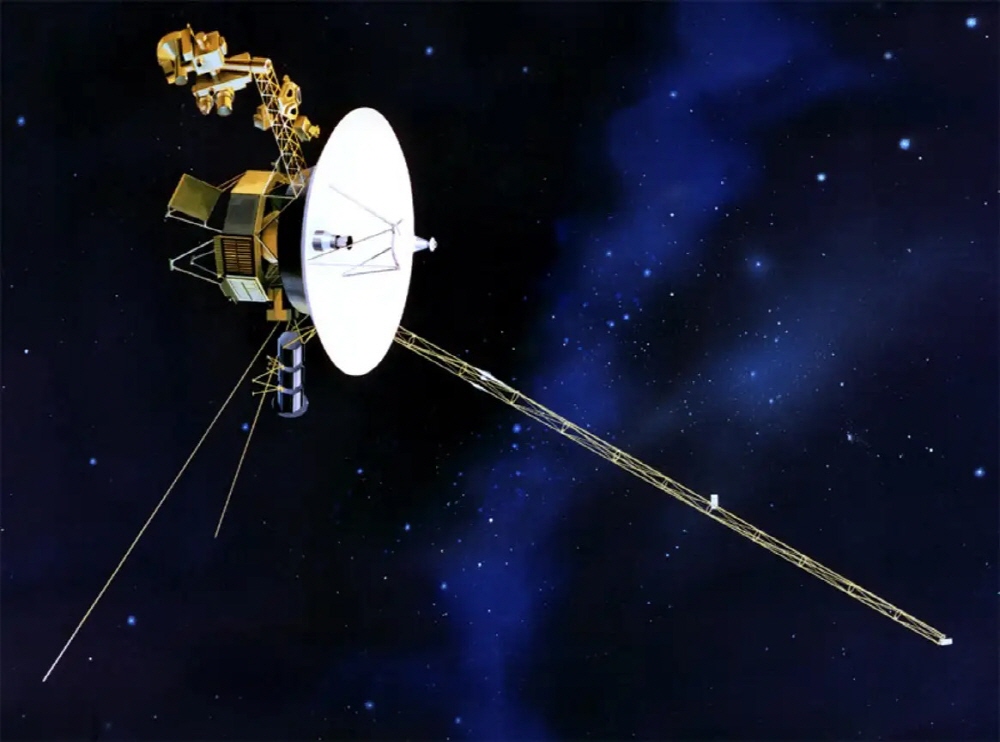
A work depicting one of the Voyager probes launched by NASA in 1977 also draws attention. Voyager 1 is currently the most distant man-made object from Earth and is expected to continue communicating until around 2025.

There is also a concept series depicting a typical space shuttle mission sequence. The Space Shuttle operated from 1981 to 2011 and made 135 flights.

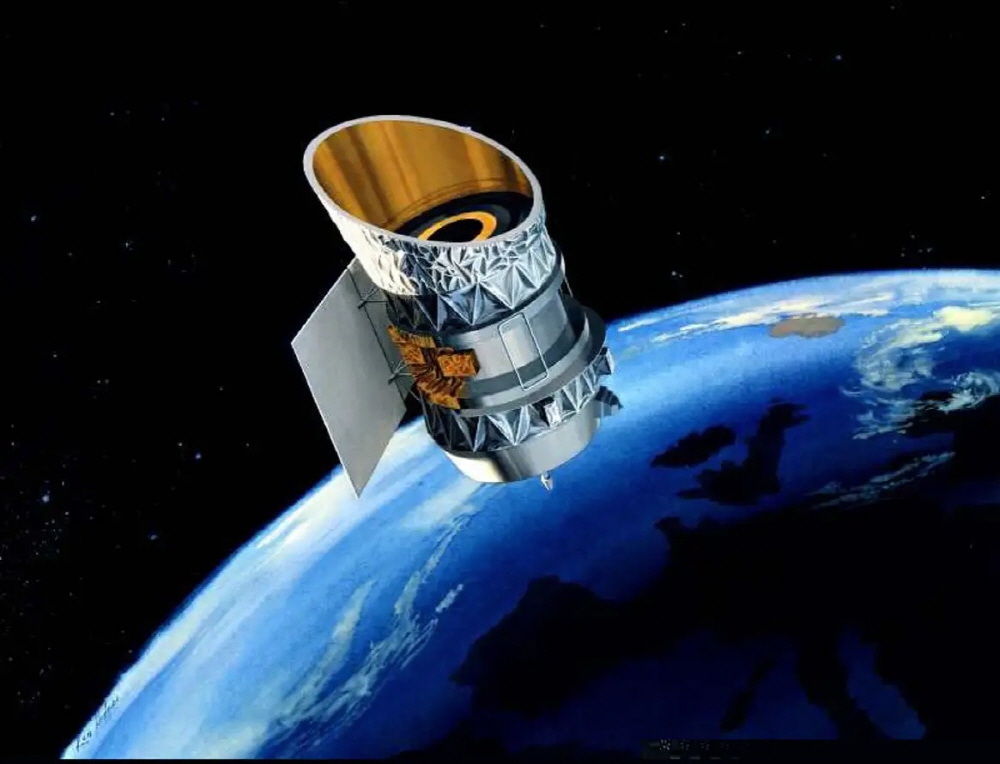
Launched in 1983, IRAS, an infrared astronomy satellite, was the first space telescope to probe in infrared wavelengths, but the mission lasted only 10 months.

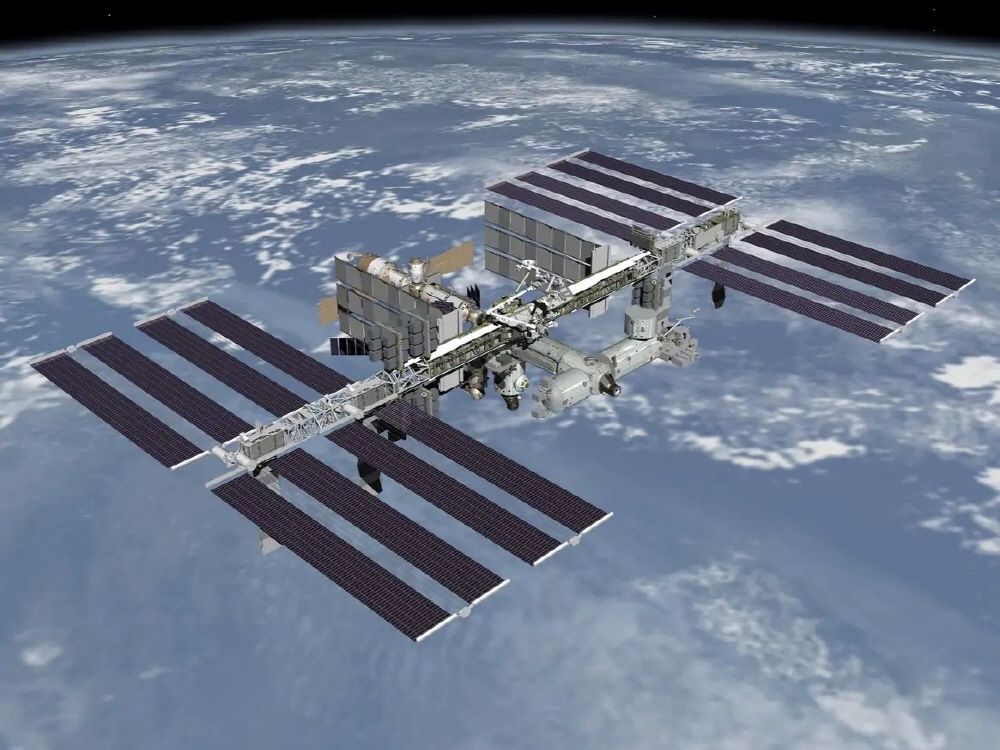
There is also a CG image depicting the International Space Station (ISS). Launched in 1998, the ISS is scheduled to operate until 2030.

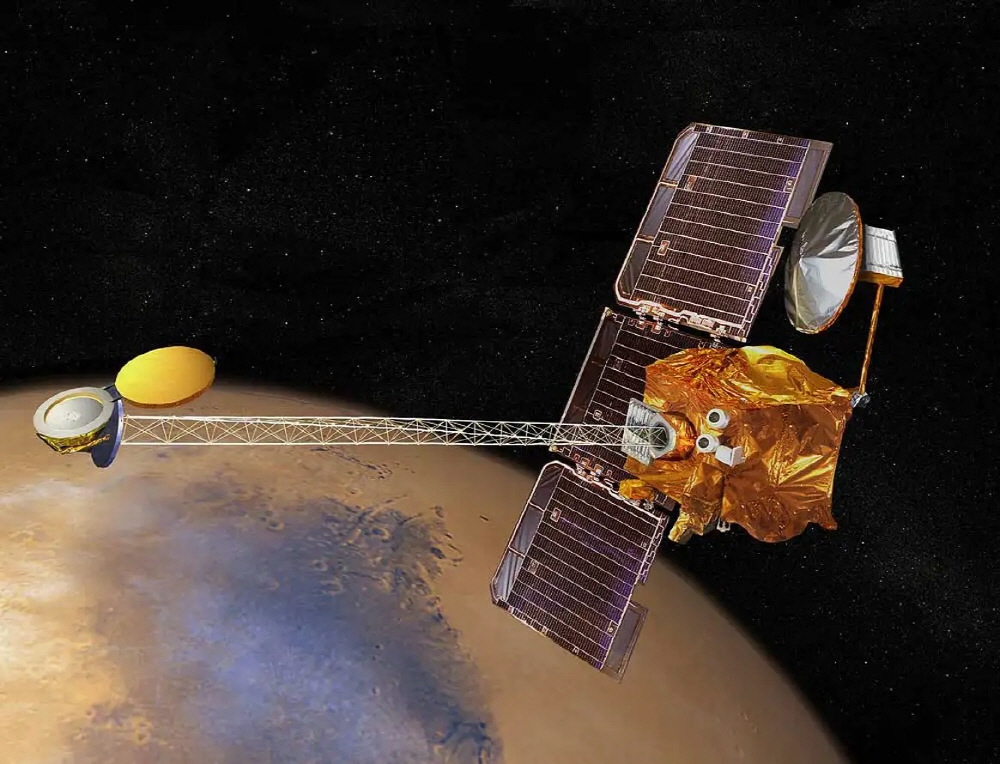
NASA’s Mars Odessey was launched in 2001 and has been scanning Mars’ surface composition. The probe data suggested that there is a lot of icy water in the polar regions of Mars.

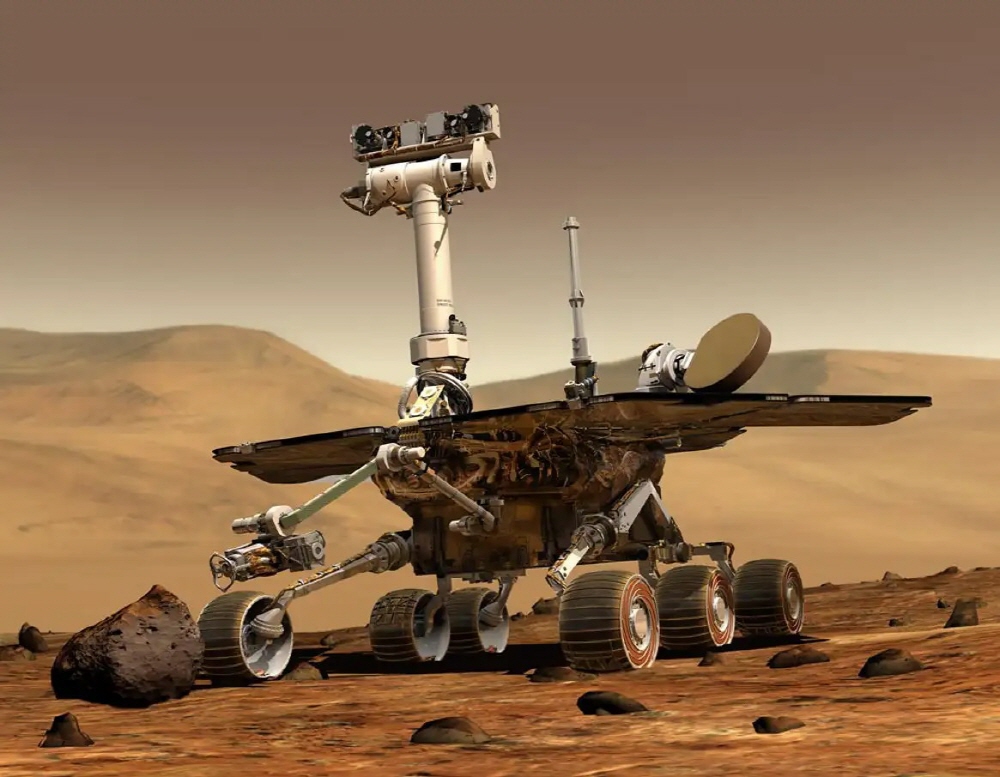
Two Spirit and Opportunity rovers landed on Mars in 2004. The purpose of the mission is to find evidence of the presence of water in Martian rocks and soil, and NASA is ready for the rovers Curiosity and Perseverance.

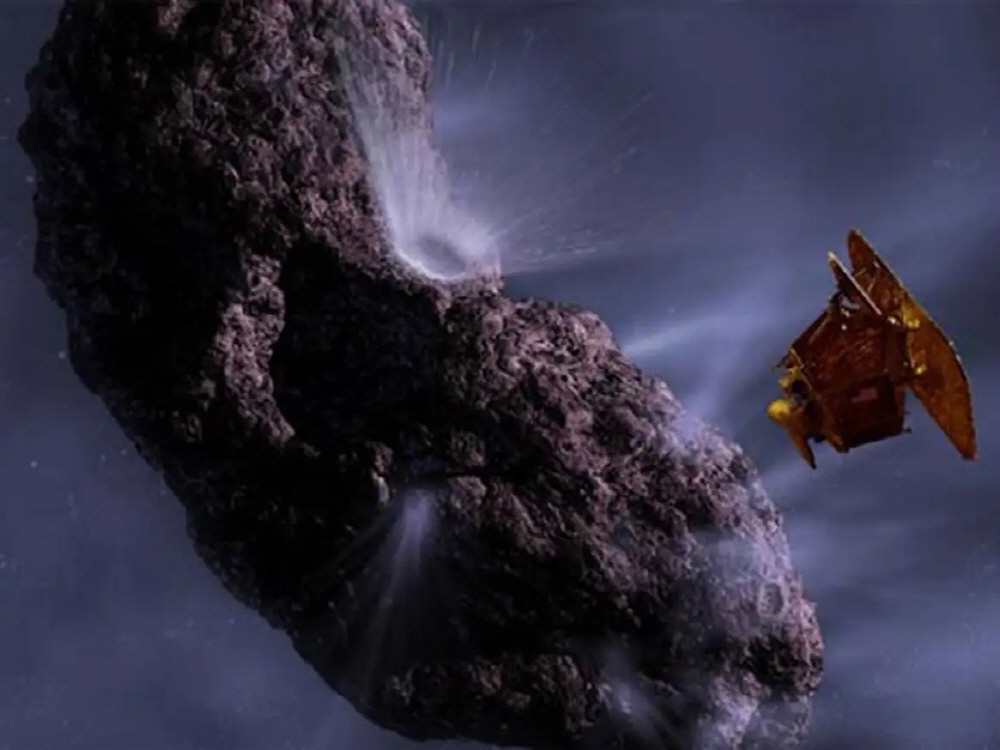
In July 2005, NASA’s Deep Impact spacecraft launched a 360kg impactor at Comet Tempel 1 and hit it. The impact formed a crater and produced a huge amount of debris. In this experiment, Comet Tempel 1 appeared to be more dusty and less icy than expected.

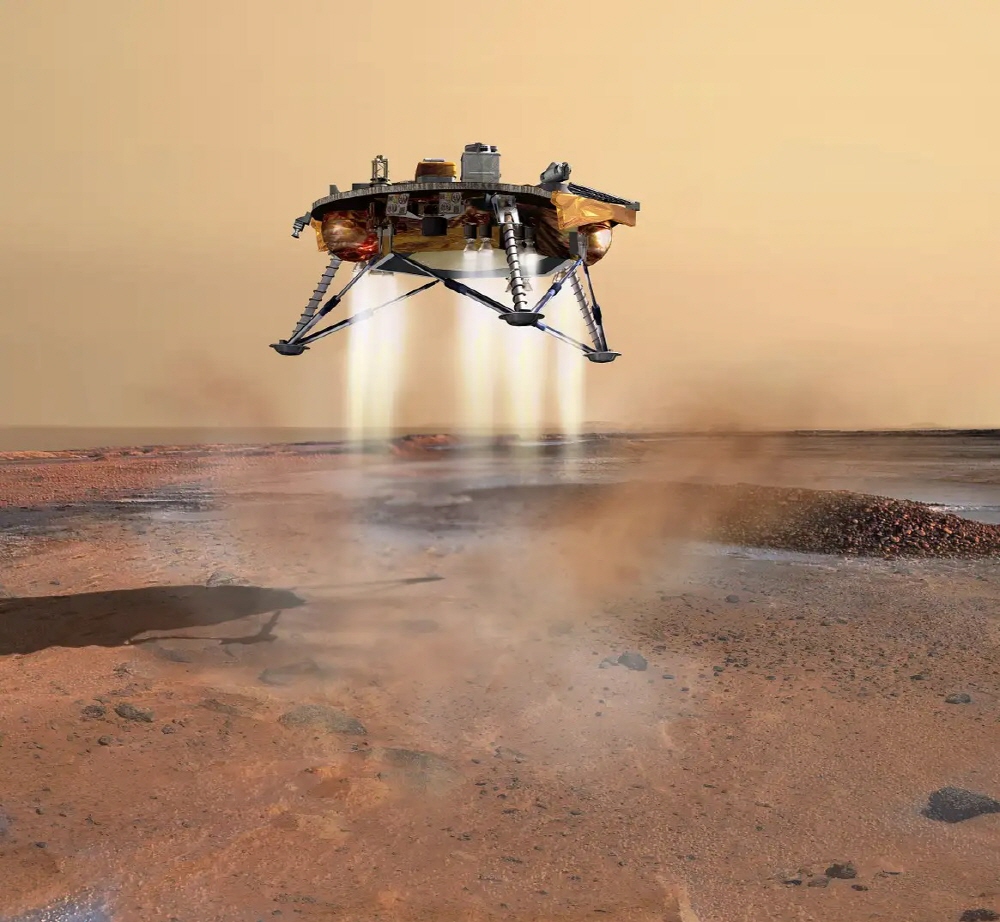
NASA’s Phoenix probe was the first probe to land on the Martian poles in 2008. It was designed to excavate below the surface in anticipation of water and ice detection, but it was short-lived. Related information this placecan be found in

