22 minutes ago
image source,SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
The WHO said it was the first time that so many cases had been reported simultaneously in widely dispersed areas.
The World Health Organization (WHO) says there have been 780 confirmed cases of monkeypox in countries where monkeypox is not normally found.
The number of confirmed cases has tripled from 257 cases regarding a week ago.
The WHO reported that the number of confirmed cases in the past three weeks may have been underestimated, and assessed the global health risk level of monkeypox as “moderate”.
The infection is usually mild, but this is the first time it has spread widely outside Central and West Africa. The WHO added that confirmed cases have been found in 27 countries that have not yet developed “endemic diseases”. This means that more cases are expected to be found in these countries.
Most of these new cases are now in North America and Europe, with small numbers in Mexico, Argentina, Morocco and the United Arab Emirates.
The UK has the most cases with 207, followed by Spain with 156 and Portugal with 138.
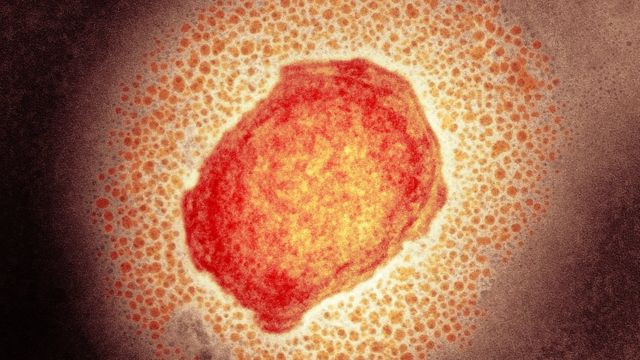
image source,Science Photo Library
monkeypox virus particle
In its latest report, the WHO said some countries had reported new cases beyond known contacts of previously confirmed cases. This suggests that some chains of virus transmission have gone undetected, the report said.
“It is highly likely that cases will be detected in other countries and the virus will spread further,” the report explained.
The report added that while the current health risk from monkeypox to the general public “remains low”, the public health risk might “become high” if the virus spreads widely in countries where it is not usually detected. There have been no reports of deaths from monkeypox.
So far, most, but not all, cases have involved men who have sex with men, the WHO said. However, there is no evidence that monkeypox is sexually transmitted, but it is spread through close contact.
The WHO added that many cases did not show typical clinical symptoms of monkeypox, and some described pustules before symptoms such as fever appeared.
Most cases of the virus clear up on their own within a few weeks. Symptoms include fever, headache, swelling, back pain, muscle aches, and a rash that goes through various stages. However, monkeypox can sometimes be more severe, and deaths from monkeypox have been reported in West Africa in the past.
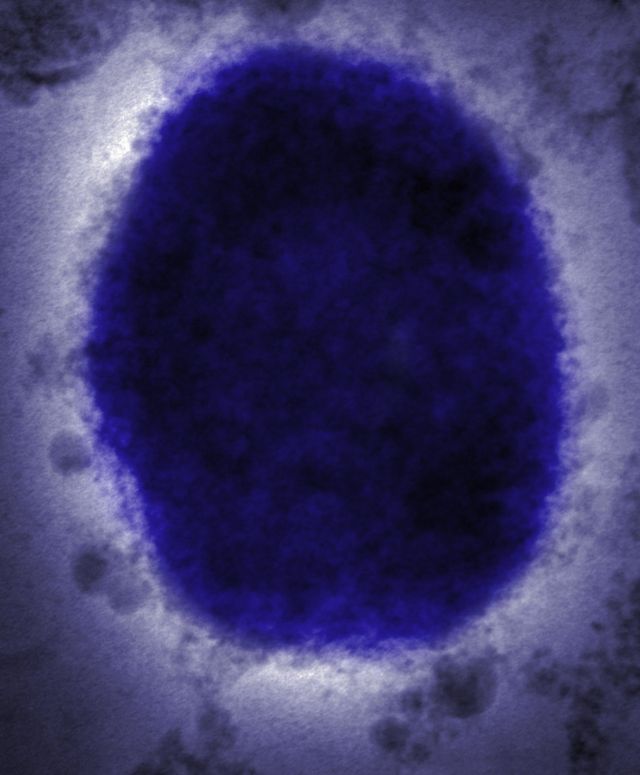
image source,Getty Images
monkeypox virus
Monkeypox is caused by the monkeypox virus, which belongs to the same family of viruses as smallpox, but is much less severe and experts say it’s very low contagious.
It occurs mainly in remote areas of Central and West African countries, close to tropical rainforest areas. It has two main strains – West and Central Africa.
Initial symptoms include fever, headache, swelling, back pain, muscle aches and general weakness. Once a fever begins, a rash develops that often starts on the face and spreads to other parts of the body, most commonly on the palms and soles of the feet.
The rash can be very itchy, going through different changes and stages before eventually the scab falls off. Broken skin may cause scarring. The infection lasts for 14 to 21 days and usually goes away on its own.
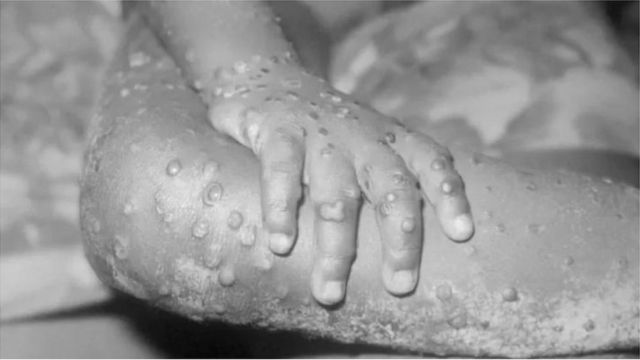
image source,Getty Images
Symptoms of monkeypox include a rash that starts on the face and spreads all over the body.



