Jupiter’s Stormy Atmosphere: A Glimpse into the Future of Planetary Exploration
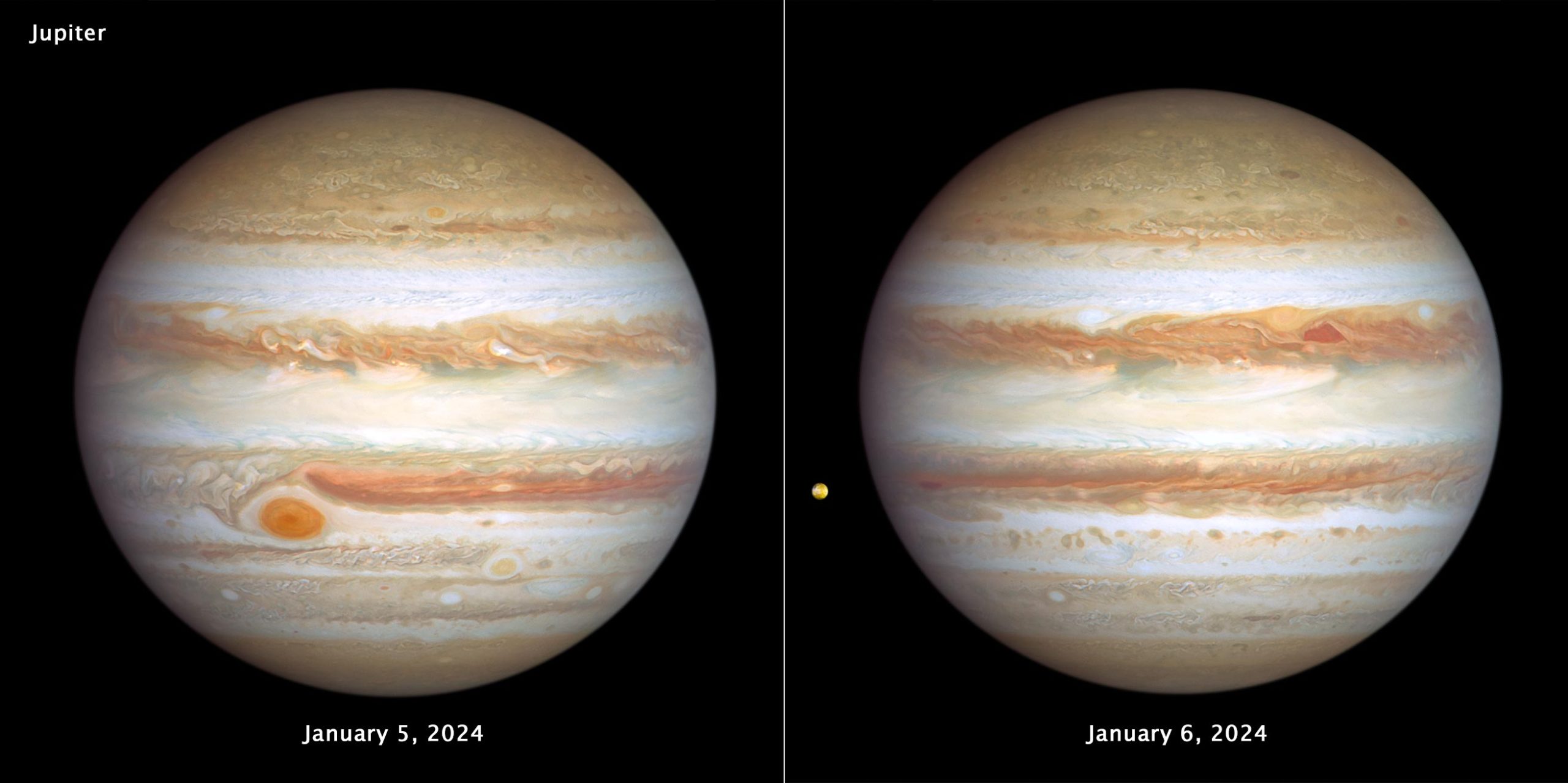
The mysterious and enchanting world of Jupiter never fails to captivate our imaginations. Its swirling clouds, intricate weather patterns, and colossal storms have been a source of fascination for scientists and astronomers for centuries. Recently, NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope delivered striking images that provide us with an unprecedented view into Jupiter’s ever-changing atmosphere.
Unveiling the Dynamic Nature of Jupiter
Jupiter’s vibrant and colorful clouds create a visually stunning spectacle. But beneath this captivating exterior lies a tumultuous world of cyclones, wind shear, and violent storms. Unlike Earth, Jupiter has no solid surface; instead, it is shrouded by ammonia ice-crystal clouds that are only 30 miles thick, covering an atmosphere that extends tens of thousands of miles deep. This unique composition gives Jupiter its banded appearance, with zones of rising air referred to as “belts,” and regions of falling air known as “belts.” The interaction of these opposing air flows gives rise to the awe-inspiring storms and turbulence that we observe on the planet’s surface.
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has been diligently monitoring Jupiter’s atmospheric dynamics, and the latest images have revealed a plethora of large storms and small white clouds, indicating a high level of activity. These visual observations, part of the annual Outer Planet Atmospheres Legacy program, provide scientists with valuable insights into the ever-changing nature of Jupiter’s atmosphere.
A Window into the Future: Implications and Trends
The fascinating images captured by Hubble not only expand our knowledge regarding Jupiter but also have profound implications for the future of planetary exploration. By closely studying the dynamic weather patterns and storms on Jupiter, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of atmospheric phenomena and better predict weather patterns on other celestial bodies. This knowledge is crucial for future missions to planets, their moons, and even exoplanets where atmospheric conditions may be similar to those of Jupiter.
Understanding the complexities of Jupiter’s stormy atmosphere can also provide valuable insights into Earth’s own weather systems. By comparing and contrasting the atmospheric behaviors of both planets, scientists can refine climate models and improve our understanding of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and cyclones, here