- Jonathan Amos
- BBC science correspondent
39 minutes ago
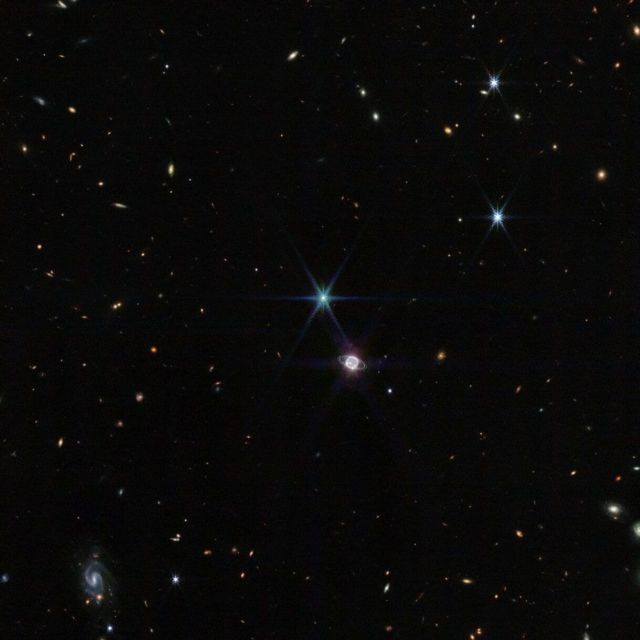
Details unseen in more than three decades are evident in the images of the James Webb Telescope
The recently launched James Webb Super Space Telescope has captured stunning new images of Neptune.
The astronomical observatory’s infrared instruments have highlighted features not seen with such clarity in detail since the Voyager 2 probe flew past the planet in 1989.
These features include the rings and dust circles that surround the frozen giant planet.
Scientists are also fascinated by the different compositions of clouds, which should tell them something new regarding how Neptune’s atmosphere works.
Beyond the planet itself are seven of the giant planet’s 14 moons, the most important of which is Triton.
This moon appears as a star in the images taken by the telescope.
This is due to the fact that Neptune appears dark in telescope images due to its absorption of methane gas at infrared wavelengths. On the other hand, Triton reflects an average of 70 percent of the sun’s rays that fall on its ice-covered surface. It looks very bright.
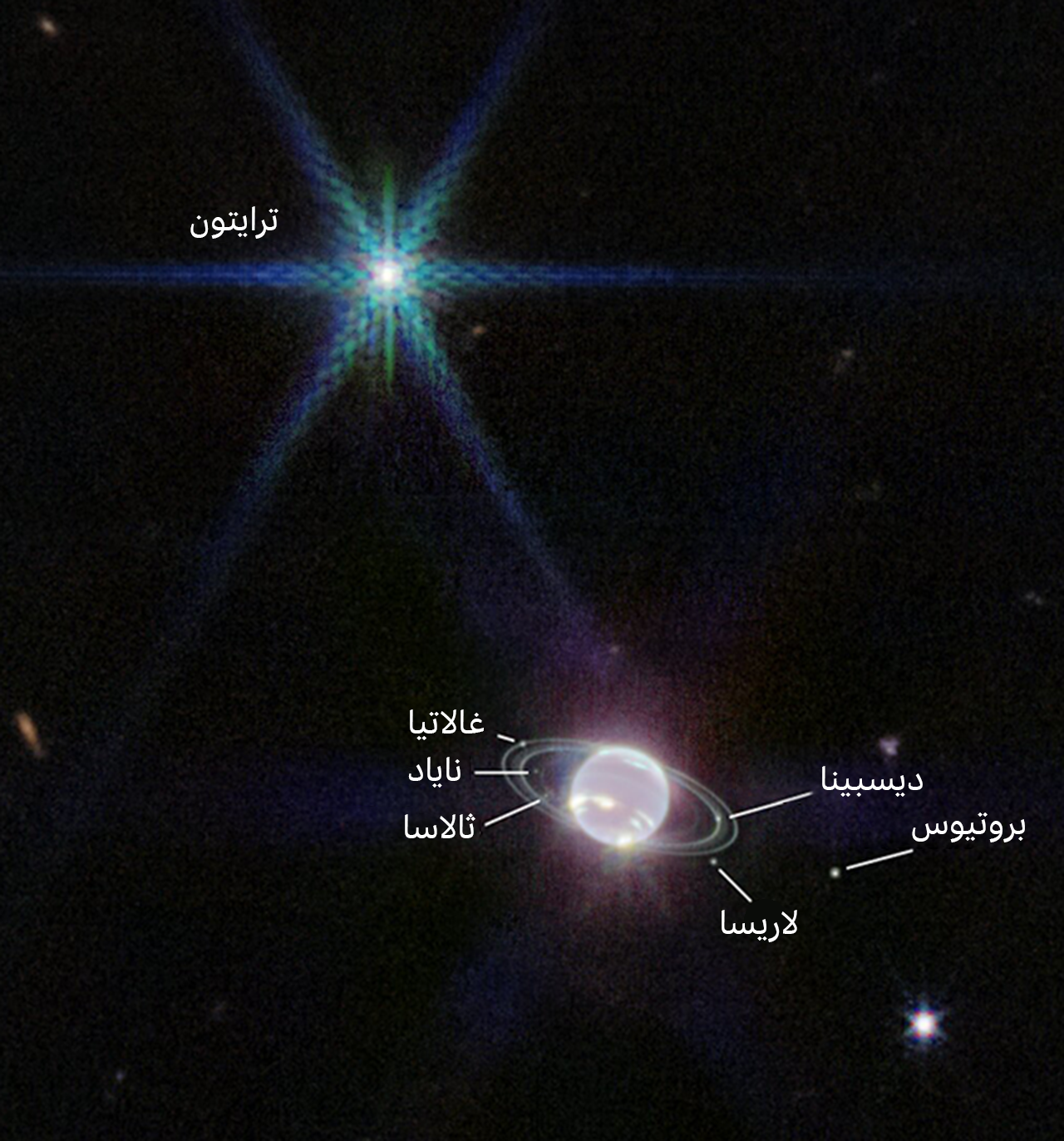
photo released, NASA/ESA/CSA/STSCI
The giant planet Neptune has 14 moons, the largest of which is the geologically active Triton
“It’s good to see how excited everyone is,” Professor Lee Fletcher, from the University of Leicester, who is at the Europlanet science conference in Granada, Spain, told BBC News.
“Long wavelengths are something new that can open a window for us into deep distribution patterns, with a bright equatorial circle that looks a bit like the bright rings around Jupiter and Saturn,” Fletcher said.
“Powerful Neptune storms are as active as ever, and the entire Neptune family is represented here, with these ringed moons and Triton,” he added.
Neptune is the farthest planet in our solar system, beyond Uranus and Saturn, but lies within the orbit of the dwarf planet Pluto.
It orbits the Sun from a distance of approximately 4.5 billion km, and takes 164.8 years to complete its rotation.
In this wide view, one can see the ovals and spirals of galaxies far from our Milky Way.
Like the other distant giant planets in the solar system, its atmosphere contains a lot of hydrogen and helium. But there is a very strong presence of ice, water, ammonia and methane.
Neptune is regarding 50,000 kilometers in diameter, or nearly four times the diameter of Earth.

