| © News1 DB |
A Korean research team discovered a protein in the body that promotes the proliferation, growth, and survival of cancer cells.
A research team led by Professor Joon-Young Seo of the School of Biomedical Sciences at Yonsei University College of Medicine announced on the 18th that they have identified the cancer metabolism control function and mechanism of action of a protein called ‘biperin’ expressed by interferon, which is known to regulate anti-cancer immunity.
Unlike normal cells, cancer cells have the characteristics of changing their metabolism so that they can proliferate, grow, metastasize, and survive even under adverse conditions such as nutrient deficiency and limited oxygen. Until now, it has been known that cancer metabolism is regulated through a biological pathway called ‘PI3K/AKT’.
Recently, the ‘JAK/STAT’ pathway, which is activated by interferon, known as a pleiotropic cytokine that causes an anti-cancer immune response, has also been found to be involved in the regulation of cancer metabolism, but a clear mechanism of action has not been identified.
Therefore, the research team analyzed the cancer metabolism control function and mechanism of action of biperin among interferon-induced proteins. As a result of analyzing cancer tissues such as stomach cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, kidney cancer, pancreatic cancer, and brain cancer, biperin expression was high, and the higher the expression level, the lower the survival rate of cancer patients.
The research team also created and analyzed a cancer cell line that regulates biperin expression. As a result, the expression of biperin was induced not only by interferon, but also by lack of oxygen and nutrients, and by promoting energy metabolism and synthesis of fatty acids in cancer cells, cancer cells were able to proliferate and survive.
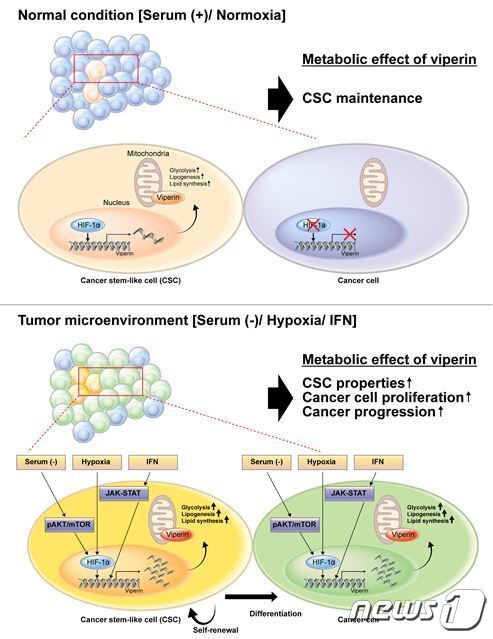 |
| Picture description) Under normal conditions where nutrients and oxygen are supplied smoothly, biperin is expressed at a low level by the HIF-1 factor of cancer stem cells, enabling cancer stem cells to maintain their characteristics and survive through metabolic regulation (above). painting) /
Under cancer microenvironmental conditions such as interferon secretion, nutrient and oxygen deprivation, biperin is expressed at high levels in cancer stem cells through various mechanisms, and by activating metabolic regulation, it exhibits characteristics such as self-renewal and differentiation of cancer stem cells into cancer cells. It promotes cancer proliferation and growth by activating metabolism by strengthening and expressing it in surrounding cancer cells (Figure below) |
The results of this study were published in the latest issue of the International Journal of Clinical Investigation (IF 19.477).



