Thanks to spacecraft and rovers, scientists now know that the Red Planet also experiences winter, accompanied by frost (up to -123 ° C at the poles), snow and ice. But, as befits an alien winter, the Martian one has its own characteristics.
1. Two types of snow
The rarefied atmosphere of Mars is mainly composed of carbon dioxide. In the cold, it freezes, turning into the so-called dry ice, which falls to the surface in the form of snow. In spring, such snow immediately turns back into a gaseous state, bypassing the liquid one. The process is called sublimation.
Even in the Martian atmosphere there are crystals of water ice, but this type of snow evaporates, or sublimes, before it reaches the surface.
As a rule, the snow cover on Mars does not exceed a few centimeters. To ski, you would have to look for places where snow accumulates, such as a crater or a rocky slope.
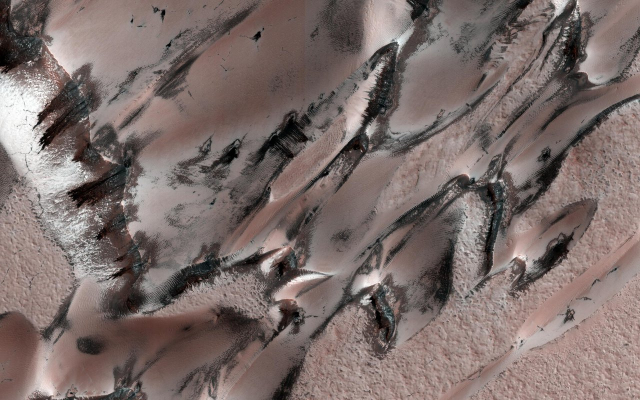

2. Cubic snowflakes
On Earth, snowflakes are made up of water molecules. (H2O), so they have a hexagonal shape. Mars has dry ice made up of carbon dioxide. (CO2), the molecules of which, when frozen, form crystals with four sides. space probe MRO showed that Martian snowflakes are smaller in diameter than the thickness of a human hair.
3. Lots of frost
On Mars, frost is much more common than snow. It can also be composed of water or carbon dioxide. Water frost was observed by the Viking spacecraft in the 1970s, and the Mars Odyssey orbiter recorded how frost forms and then sublimes in the morning sun.
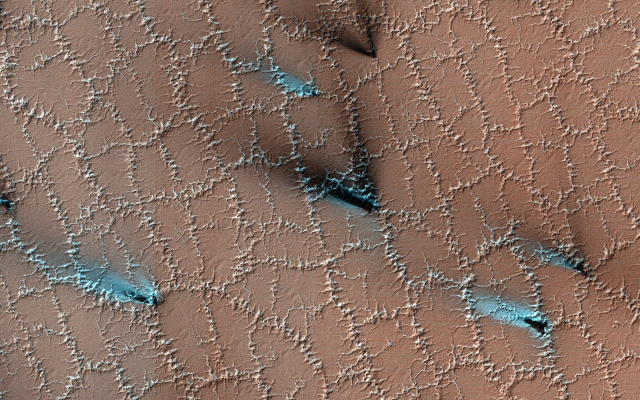

4. Miracles at the end of winter
At the end of the cold season, the ice on Mars does not melt, but sublimates into the atmosphere, acquiring bizarre shapes. In addition, the spring sun heats the gas under the layer of translucent ice, which causes it to erupt outward along with dust.