IBS “Cognitive function is restored by inhibiting the enzyme Maobi, a star cell in the brain”
The research team led by Chang-Jun Lee, Director of the Center for Cognitive and Sociality Research at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and Professor Sang-Yun Jeong of Bundang CHA Hospital, announced on the 26th that they had found a clue to improve cognitive disorders such as forgetfulness and memory loss in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
The research team conducted an animal experiment with interleukin-1beta (IL-1β), an inflammatory substance found throughout the body, that affects astrocytes in the hippocampus in the brain. It was confirmed that it activates ‘GABA’, which inhibits neurotransmission.
As a result of analyzing ‘synovial cells’ isolated from joint tissues of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, it was also revealed that Maobi, which is known to be mainly expressed in astrocytes, is also present in synovial cells in the joints and is expressed in proportion to the degree of inflammation.
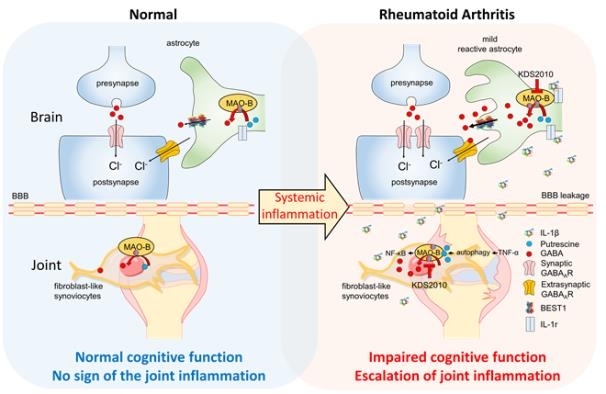
Then, when the Maobi inhibitor ‘KDS2010’, which is currently in phase 1 clinical trial, was administered to an animal model of rheumatoid arthritis, joint inflammation was reduced and cognitive function was restored.
The research team explained that this proves that Maobi in the brain stellate cells and joint synovial cells is an effective therapeutic target that can alleviate joint inflammation while improving cognitive impairment.
Director Chang-Jun Lee said, “This is the first study that suggested that cognitive impairment in rheumatoid arthritis patients is caused by reactive astrocytes caused by chronic inflammation. said.
/yunhap news



/s3/static.nrc.nl/images/gn4/stripped/data126476494-b5e95c.jpg)