2024-03-10 01:12:00
2024/03/10 10:12 Weather News
The number of felt earthquakes observed in Japan in the past week has decreased compared to the previous week, returning to the same level as the week before last.
Earthquakes are noticeable on the Pacific side from western Japan to Tohoku, and there are also many earthquakes around the Noto Peninsula and Boso Peninsula. Earthquakes with a seismic intensity of 3 or higher continued to occur, with eight occurring across the country. (Tally from March 4th to March 10th at 10am)
Domestic: Earthquake of magnitude 4 off the eastern coast of Chiba Prefecture for the first time in a week
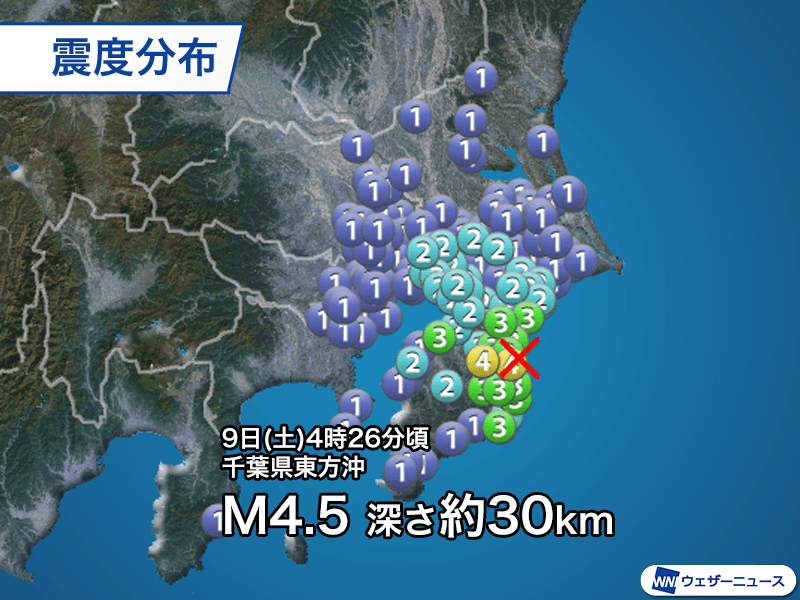
Earthquake off the eastern coast of Chiba Prefecture
This is the first time in a week that a seismic intensity of 4 was observed due to seismic activity off the eastern coast of Chiba Prefecture that has been occurring since the end of February. The mechanism of the earthquake is analyzed to be a reverse fault type with a pressure axis running north-south.
Seismic activity, thought to be caused by slow slip, continues with repeated rises and falls, with two felt earthquakes occurring on the 8th (Friday) and 9th (Saturday). There have been cases of similar activity in the past that continued for several months, so we need to be careful regarding strong shaking for a while.
Domestic: Intensity 3 earthquake twice a day in northern Miyazaki Prefecture
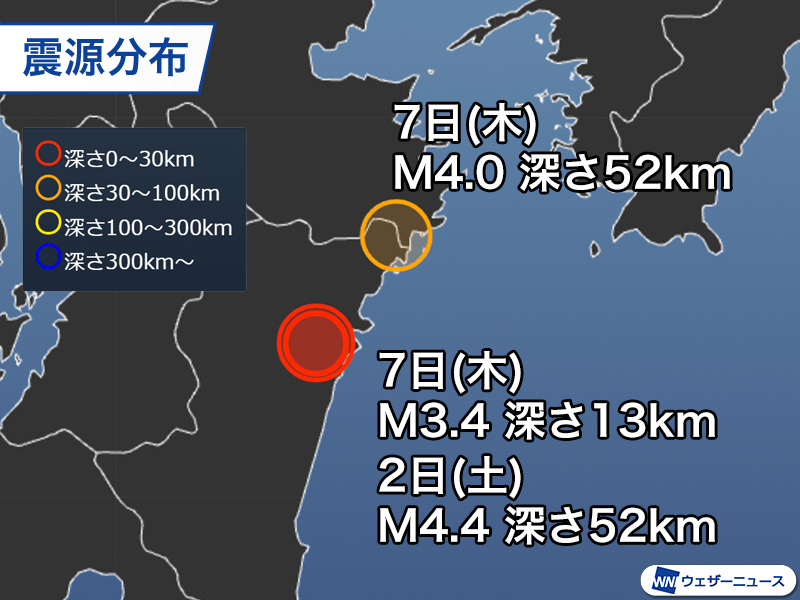
Earthquake in the northern plains of Miyazaki Prefecture
The epicenter and mechanism are almost the same as the magnitude 4.3, maximum seismic intensity 4 earthquake that occurred on the 2nd (Saturday).
In addition, at around 17:14 on the 7th (Thursday), an earthquake estimated to have a magnitude of 4.0 and a depth of 52 km occurred in the northern plains of Miyazaki Prefecture, with a maximum seismic intensity of 3 in Saeki City, Oita Prefecture, and Nobeoka, Miyazaki Prefecture. Tremors with a seismic intensity of 2 were observed in the city and Ubuyama Village, Kumamoto Prefecture.
Although the earthquake had its epicenter in the northern plains of Miyazaki Prefecture, it was of a different type because it was north of the epicenter at 2:00 pm and at a different depth. It appears to have occurred near the boundary between the subducting Philippine Sea plate and land plate.
Be careful of shaking with a seismic intensity of less than 5
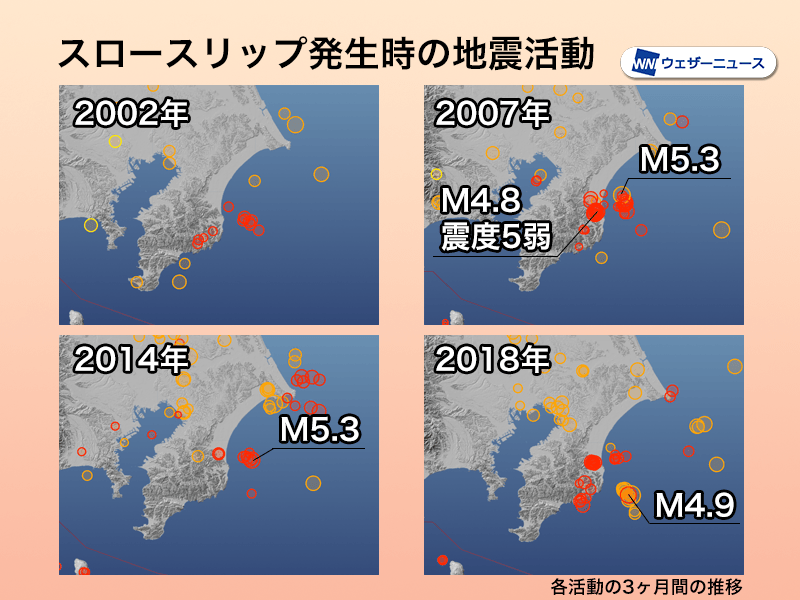
When slow slips occurred in the past, seismic activity increased, although there were slight differences from year to year. In 2007 and 2018, the number of earthquakes was particularly high, and land-based earthquakes were also noticeable. Strong shaking with a maximum seismic intensity of just under 5 was observed during the magnitude 4.8 earthquake on August 18, 2007.
The government’s Headquarters for Earthquake Research Promotion conducted an evaluation of a series of seismic activities and concluded that the earthquake was caused by slow slip off the coast of the Boso Peninsula.
As in the past, the activity is expected to continue for a week to several months, and depending on the scale of the earthquake and the location of the epicenter, it is thought that it may be accompanied by shaking with a seismic intensity of regarding 5 lower. Caution should be taken once morest strong shaking in areas close to the activity area.
The southern Kanto region, including the Boso Peninsula, experiences many magnitude 7 class earthquakes due to plate subduction. Even if there is no major earthquake during this activity, the area is at high risk, so it would be a good idea to double check to see if earthquake countermeasures are in place.
Domestic: M4.5 seismic intensity 3 observed off the coast of Urakawa
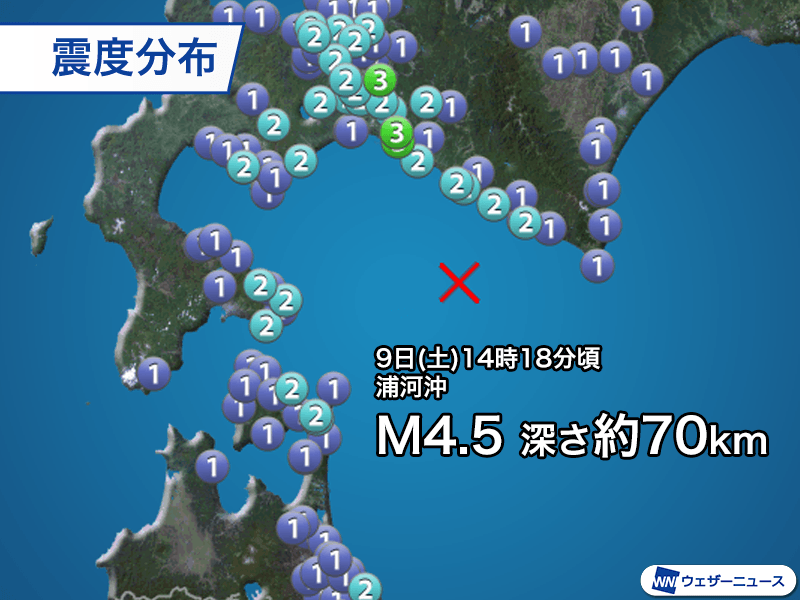
Earthquake off the coast of Urakawa
This is the second earthquake this year with a seismic intensity of 3 or higher that occurred off the coast of Urakawa on the 28th of last month. The mechanism of the earthquake is analyzed to be a reverse fault type with a pressure axis running northwest-southeast.
In this region, the Pacific plate is subducting under the land plate, and large earthquakes often occur. Recently, in 2016, an earthquake with a magnitude of 6.7 and a maximum seismic intensity of just under 5 occurred, and in 1982, an earthquake with a magnitude of 7.1 and a maximum seismic intensity of 6 (class at the time) occurred.
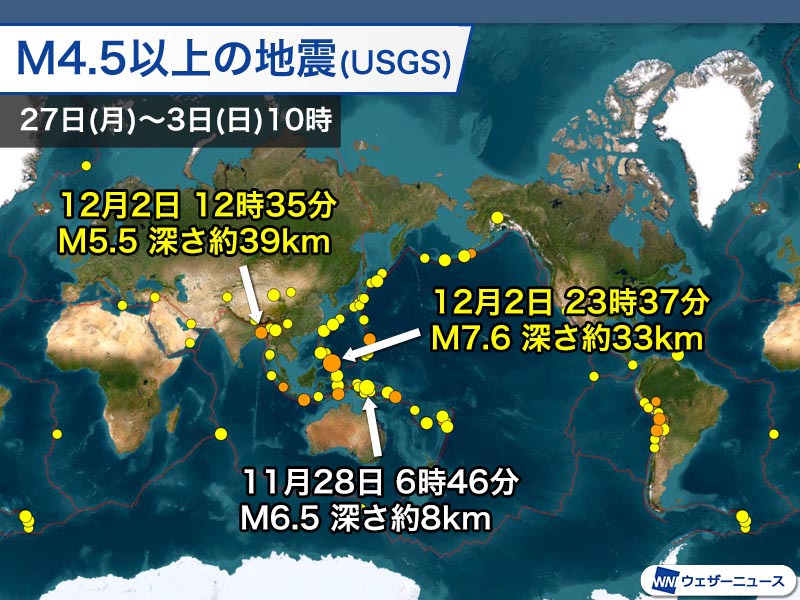
World: M6.7 earthquake near Antarctica
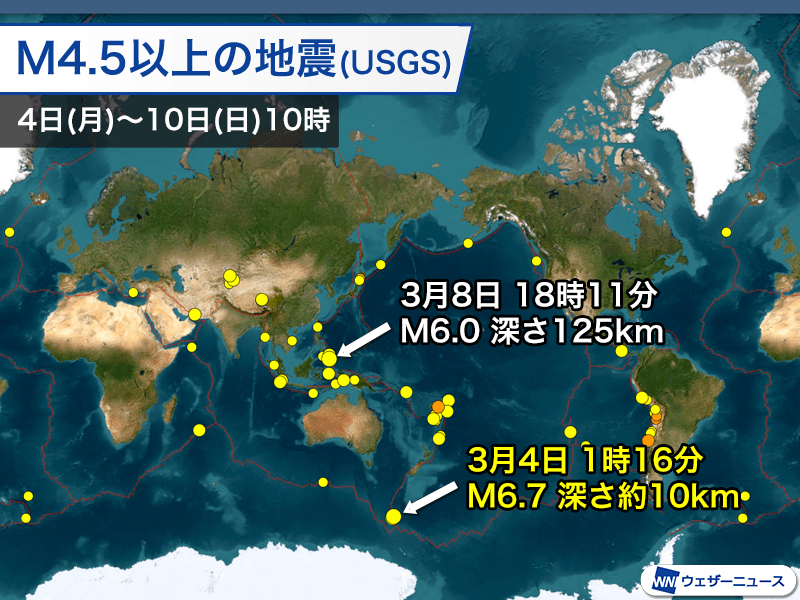
Earthquakes of M4.5 or higher around the world (USGS homepage quote/Weather News processing)
In the early hours of the 4th (Monday) Japan time, an earthquake estimated to have a magnitude of 6.7 and a depth of approximately 10km occurred in the waters south of Macquarie Island. The mechanism of the earthquake is analyzed to be strike-slip type.
Although the earthquake was somewhat large, it was a strike-slip earthquake, so no tsunami was generated.
This area is the boundary between the Pacific and Australian plates. The boundary between these two plates has a complex structure with different movements depending on the area. . In addition to strike-slip earthquakes similar to this one, reverse-fault earthquakes can also occur near the epicenter of this earthquake, such as the magnitude 7.1 earthquake in 2008.
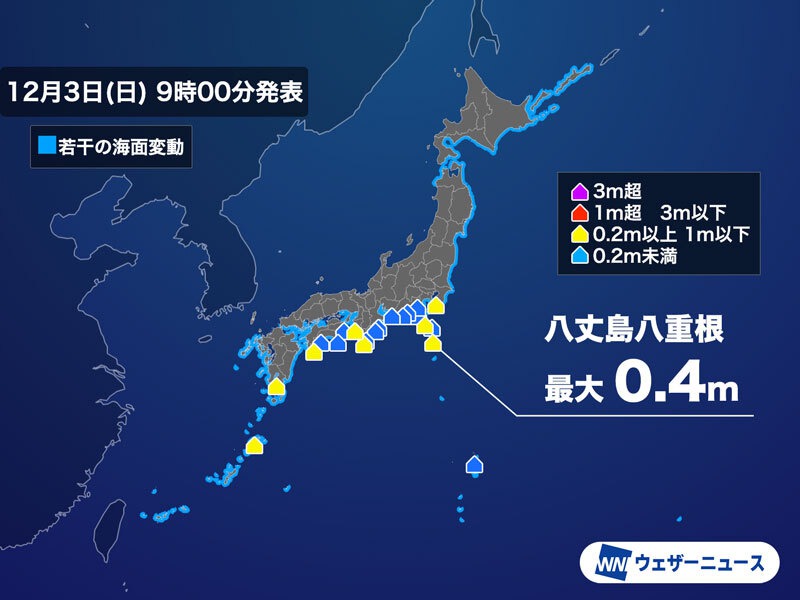
World: Tsunami of up to 40cm in Izu Islands and Hachijojima
The earthquake was large and the epicenter was relatively shallow, causing a tsunami. In the Philippines, a tidal level change of 8cm was observed in Davao, Mindanao. Because Davao is located deep in a narrow bay, it is possible that a larger tsunami might have reached coastal areas closer to the epicenter.
The tsunami reached Japan in the early hours of the 3rd (Sunday), with a maximum height of 40 cm on the Izu Islands and Hachijo Island, and 10 to 20 cm on the Pacific coast from Kanto to Kyushu and Amami. The Japan Meteorological Agency issued a tsunami advisory shortly following the earthquake occurred, and all advisories were lifted at 9:00 a.m. on the 3rd (Sunday).
Large earthquakes frequently occur around the Philippines due to the subduction of the Philippine Sea plate into the Eurasian plate. On the 17th of last month, there was a magnitude 6.7 earthquake in the south of Mindanao. Even if we restrict ourselves to areas near the epicenter of this earthquake, there were earthquakes of magnitude 7.0 in 1991 and magnitude 7.6 in 1989.
M5.5 earthquake in Bangladesh
In addition, around noon on the 2nd (Saturday) Japan time, an earthquake estimated to have a magnitude of 5.5 and a depth of approximately 39 km occurred with its epicenter in the southern part of Bangladesh. The mechanism of the earthquake is analyzed to be strike-slip type.
Because the epicenter was on land, the shaking was somewhat strong near the epicenter, and the shaking was equivalent to V on the revised Mercalli seismic intensity scale, or 4 on Japan’s seismic intensity scale, although a strict comparison is not possible. Although the epicenter was not far from the capital Dhaka, the area affected by the strong shaking was small and no major damage was reported.
Bangladesh is located near the boundary between the Indian plate and the Eurasian plate. Earthquakes with a magnitude of 6 or more occur from time to time, and the most recent one was a magnitude 6.0 earthquake in 1997. There is a very old record of a magnitude 7.1 event occurring in 1918.
Source/Reference
*Information on the epicenter and intensity in Japan is from the Japan Meteorological Agency unless otherwise specified. Information on overseas epicenters is from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) unless otherwise noted. There may be differences in the epicenter information depending on the publishing organization.
Reference materials etc.
1710047838
#Weekly #Earthquake #Information #2024.3.10 #Seismic #intensity #occurs #eastern #coast #Chiba #Prefecture #time #week #Earthquakes #occur #repeatedly #Miyazaki #Prefecture #Weather #News