[생활의 발견]deals with subjects closely related to our lives. It includes everything you eat, wear, and live in. We are always by our side, but we are going to tell the behind stories regarding the facts that we did not know well in an easy and fun way. [생활의 발견]If you read the various stories contained in the book, you will become an insider before you know it. Please have fun. [편집자]
As interest in health increases due to Corona, the number of people eating nutritional supplements is also increasing. According to the Health Functional Food Association, the domestic health functional food (dry food) market exceeded 6 trillion won last year. The domestic dry food market has grown by 25% in 4 years from 4.8 trillion won in 2019. That means more and more people are looking for nutritional supplements.
Nutrients help health in various parts by type, but if you eat a lot, you can return to harm. Today, we will learn regarding the daily appropriate (recommended) intake for each type of supplement and the possible side effects of overdosing.
Vitamin A, which is abundant in liver and egg yolks, has effects such as eye health, bone maintenance, immune function improvement, and antioxidants. It is known that the recommended daily intake is 600 to 700 mcg (micrograms). In case of overdose, symptoms such as hair loss and headache may occur, so caution is required.
*Nutritional unit: 1000mcg(ug)=1mg, 1000mg=1g.
There are so many types of B vitamins, and the difference between proper intake and optimal intake is huge, so it’s easy to get confused. The common feature is that since it is a water-soluble vitamin, it is not stored in the body but excreted, so most side effects do not appear, so I don’t think you need to worry too much.
Vitamin B1, also called thiamine, helps to generate energy and help recover from fatigue. The recommended daily intake is 1 to 1.2 mg, but the optimal intake is 50 to 100 mg, which varies greatly. Although this is unlikely, headaches and anxiety may occur if you take a dose that is hundreds or thousands of times the recommended intake.
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) also helps produce energy and plays a role in making nails, hair, and skin healthy. The recommended daily intake is 1.2 to 1.6 mg. Very rare side effects of overdose include polyuria and diarrhea.
Vitamin B3 (niacin) has the effect of maintaining skin moisture and lowering blood cholesterol levels, and the recommended daily intake is 12 to 16 mg. If you consume more than 60 times more, you may experience jaundice, liver function problems, digestive problems, etc.
Vitamin B6 helps strengthen immunity, vascular health, and recover from fatigue. The recommended daily intake is 1.6 to 2.0 mg, but the maximum intake is 100 mg. If you look at the high content products on the market, it is 50 ~ 100mg. One tablet a day may not be a problem, but long-term intake of more than 100 mg can cause nerve damage and numbness in the feet and legs, so special attention is required.
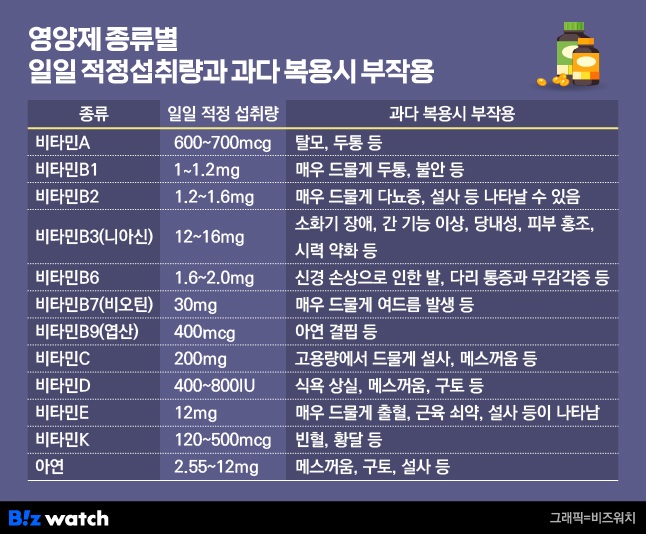
Vitamin B7 is also called biotin, and you may have heard of it in commercials for hair products. Biotin promotes protein metabolism, which supports healthy hair and nails. The recommended daily intake is 30 mg. In case of overdose, there are few side effects, but acne may occur in rare cases.
Vitamin B9 is better known as folic acid. It is also considered an essential nutrient for pregnant women. The reason is that it promotes the production of hemoglobin and red blood cells, which helps in blood formation and prevents congenital malformations in the fetus. I mentioned earlier that most B vitamins have no side effects, but you should be very careful regarding overdosing on folic acid.
The recommended daily intake of folic acid is 400 mcg. Exceeding the maximum safe dose of 1000 mcg (1 mg) may block zinc absorption and lead to zinc deficiency. A lack of zinc in the body can cause hair loss, sexual dysfunction, and growth failure in children.
200mg of vitamin C is the recommended daily intake, but taking up to 2000mg is not a big problem. If you take more than that, diarrhea and nausea may occur in rare cases.
Vitamin D, a nutrient obtained through sunlight, is known to be deficient in 80-90% of Koreans. It has the effect of strengthening bones like calcium, and the recommended daily intake is 400~800IU (0.01~0.02mg). However, if you take an overdose even though it is good, be careful as it can cause not only minor side effects such as vomiting and loss of appetite, but also hypercalcemia and kidney damage.
Vitamin E prevents cell aging and helps strengthen immunity. The recommended intake per day is 12mg, and the maximum intake is 540mg. However, there are 270 to 540 mg of vitamin E supplements on the market, so there is a risk of exceeding the maximum intake. Side effects of vitamin E overdose may rarely include bleeding and muscle weakness.
Vitamin K makes bones strong. The daily appropriate dose is 120-550mcg, and if you take a large dose, red blood cells are destroyed, which can cause anemia and jaundice. In addition, it is recommended to consume 1.55 to 12 mg of zinc per day, which helps with skin health and wound healing and strengthens the immune system.
As the saying goes, too much food can be harmful to the body if it is too much. Sometimes I see people around me eating 3-4 days at a time because they forgot to take nutritional supplements for a few days. Nutritional supplements have a low risk of side effects, but if you overdo it at once, you may experience abnormal symptoms, so please be careful.



