Fraudulent cryptocurrency apps were found from the App Store (iOS) and Play Store (Android). The information came through cybersecurity company Sophos, where it is said that scammers have been encouraging through Facebook and Tinder apps to download malicious cryptocurrency apps to then steal large amounts of money.
Victims of the scams that are taking place are encouraged to download applications aimed at cryptocurrency trading with the promise of making a lot of money by investing in supposed real assets. However, the transferred money is actually going to the scammers’ bank account.
According to Sophos, a large wave of scams is currently taking place in China that is being called “ShaZhuPan”. This operation demonstrates a high organizational level and has several interaction teams to apply blows.
How the scam happens
Scammers target male users of Facebook and Tinder. They use profiles of women with images stolen from other social media accounts. The fake profile usually shows a person with a luxurious life, containing photos in expensive restaurants and stores in beautiful surroundings.

After gaining the victim’s trust, fraudsters say they have an uncle who works for a financial analysis company and invite the person to participate in a cryptocurrency investment through an app on the Play Store or App Store. Obviously the link leads to a fake cryptocurrency buying and selling application.
The victim is instructed to make a deposit on the Binance platform, which actually exists. Then the scammer tells her to transfer the amount to the fake app.
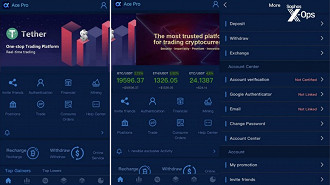
According to Sophos, the fake cryptocurrency apps on the App Store are called “Ace Pro” and “MBM_BitScan”, while on the Play Store there is “BitScan”. These apps allow the victim to withdraw small amounts of cryptocurrency at first. However, soon following, they end up blocking the account when large amounts are being moved.

How does the fraudster organization get into mobile app stores?
Bypassing security checks on the Play Store and App Store is simple. For example, in the App Store, the organization “ShaZhuPan” submits an app signed with a valid certificate issued by Apple. While awaiting approval, the app connects to a trusted server and its behavior is considered legitimate. However, following Apple’s review, the developer changes the domain and the app connects to a malicious server.
When the victim opens the rogue application, a cryptocurrency trading interface provided by the malicious server is displayed. However, everything displayed in the app is fake, except for the deposit made by the user.
According to Sophos researchers, the BiScan apps for Android and iOS have a different developer name. However, both communicate with the same server, where the domain used seems to represent bitFlyer, a real cryptocurrency trading company in Japan.