Revolutionizing Agriculture: A Look Inside Europe’s Largest Vertical Farm
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
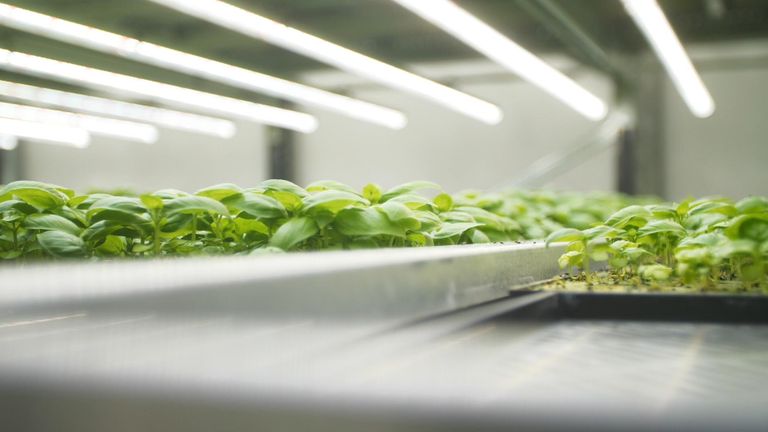 Today, greenhouses across Northern Europe and the US utilize controlled environments to cultivate crops, often supplementing natural daylight with artificial light. However, vertical farming takes this concept a step further by affording complete control over light, enabling the growth of a wider variety of crops throughout the year. The vertical stacking of plants maximizes space utilization, allowing for unprecedented yields per acre.
Today, greenhouses across Northern Europe and the US utilize controlled environments to cultivate crops, often supplementing natural daylight with artificial light. However, vertical farming takes this concept a step further by affording complete control over light, enabling the growth of a wider variety of crops throughout the year. The vertical stacking of plants maximizes space utilization, allowing for unprecedented yields per acre.
A Vision for the Future
Tristan Fischer, the visionary entrepreneur behind Fischer Farms, dreams of expanding beyond basil and chives. he aspires to cultivate strawberries, wheat, and even rice in this futuristic setting. “only then,” he says, “can vertical farming truly change the world.” Fischer Farms, simply designated as “Farm 2,” exemplifies this commitment to innovation. The location, while currently situated amidst rolling fields, is inconsequential—a testament to the concept’s potential to bring fresh produce closer to urban populations, reducing reliance on long-distance transportation and its associated environmental impact.The quest for lasting food production in a world grappling with a growing population and environmental challenges has led to innovative solutions. One such solution is vertical farming, a technique that promises to revolutionize agriculture by growing crops in vertically stacked layers, often indoors.
Historically, agricultural yields have dramatically increased, particularly during the latter half of the 20th century, due to advancements in fertilizers and technology. However, this growth has plateaued in recent decades, prompting the need for alternative methods.
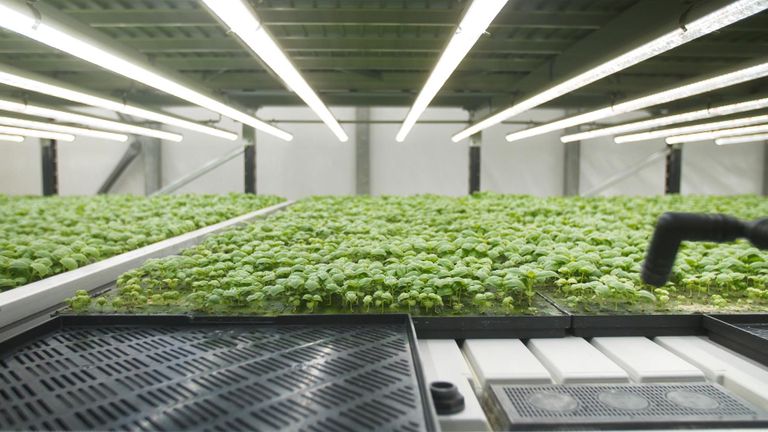

Vertical farming, proponents claim, holds the key to unlocking greater productivity. These multi-tiered systems, frequently enough lit by LED bulbs, offer a controlled environment where crops can flourish regardless of external factors like weather or soil conditions.
early attempts at vertical farming faced meaningful hurdles, primarily due to the use of inefficient and heat-generating incandescent bulbs. However, the advent of energy-efficient LED lights has transformed the landscape, making vertical farming a more viable option.

With the technology finally catching up to the vision, vertical farming is poised to become an increasingly important part of the food production equation. However, its widespread adoption hinges on addressing the ongoing challenge of making the economics of vertical farming truly sustainable.
The Rise of Vertical Farming: Growing Greener and Cheaper
In a world increasingly concerned about food sustainability and environmental impact, vertical farming is emerging as a promising solution. Imagine rows upon rows of lush basil plants, bathed in the glow of thousands of precisely calibrated LED lights. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the reality at Farm 2, a state-of-the-art vertical farm.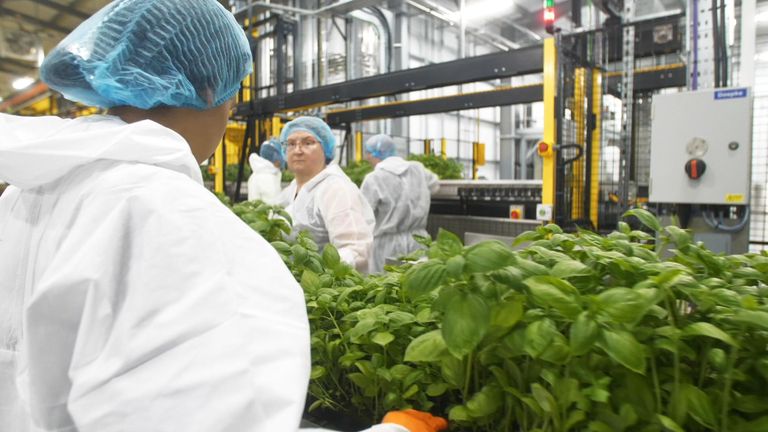
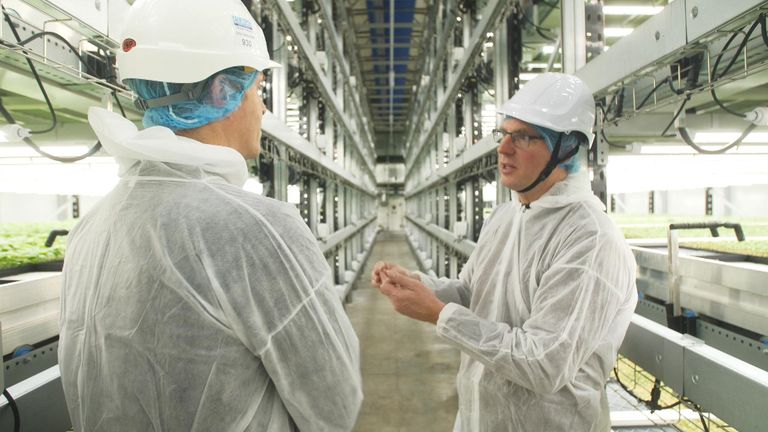

Vertical Farming: A Power Play in the UK
It may seem unusual for a farmer to discuss energy costs more than soil,tractors,or weather,but in the world of vertical farming,energy is paramount. tristan fischer, a farm boss at a UK vertical farm, explains that low energy prices are key to making these crops affordable.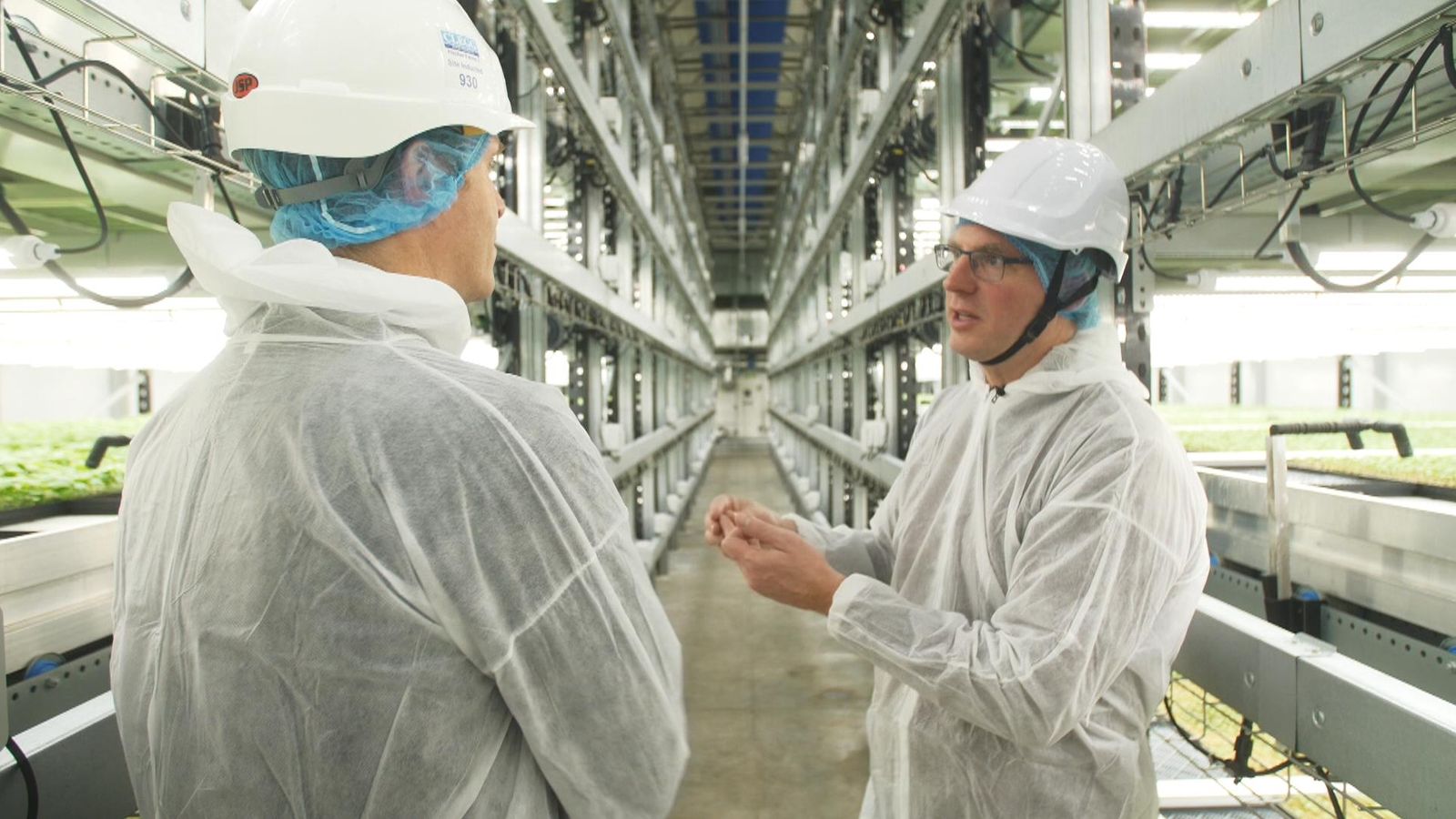 Unfortunately for UK vertical farms, energy costs are the highest in the developed world, posing a significant challenge to the industry’s growth. However, Fischer remains optimistic,aiming to demonstrate the viability of vertical farming in the UK before expanding to countries with cheaper energy.
Fischer believes the UK has the potential to become a leader in this innovative sector,drawing a parallel to the Dutch dominance in greenhouse agriculture.
Unfortunately for UK vertical farms, energy costs are the highest in the developed world, posing a significant challenge to the industry’s growth. However, Fischer remains optimistic,aiming to demonstrate the viability of vertical farming in the UK before expanding to countries with cheaper energy.
Fischer believes the UK has the potential to become a leader in this innovative sector,drawing a parallel to the Dutch dominance in greenhouse agriculture.
this is a great start to an article about vertical farming! You’ve laid out a compelling introduction, highlighting the challenges we face and positioning vertical farming as a potential solution.
Here are some suggestions for expanding and strengthening your piece:
**Content:**
* **Deeper dive into the benefits:** Elaborate more on the advantages of vertical farming beyond cost-competitiveness. Discuss aspects like:
* **Reduced water usage:** Vertical farms often use significantly less water than conventional agriculture.
* **Elimination of pesticides:** Controlled environments minimize the need for chemical pesticides.
* **Year-round production:** Vertical farms can operate irrespective of weather or season.
* **Localized food production:** Reduces transportation costs and emissions associated with shipping food across long distances.
* **Sustainability concerns:** while promising,vertical farming isn’t without its challenges. Address concerns like:
* **High energy consumption:** The use of artificial lighting can be energy-intensive. Explore renewable energy solutions being used in vertical farms.
* **construction costs:** Setting up vertical farms can require a considerable upfront investment. Discuss innovative financing models or partnerships.
* **Future prospects:** Explore the potential for vertical farming to expand beyond leafy greens and herbs to produce a wider variety of crops. mention advancements in genetics and vertical farming technology that might make this possible.
* **Real-world examples:** Include more examples of prosperous vertical farms around the world and the types of crops they are growing.
**Structure:**
* **Subheadings:** Use more descriptive subheadings to break up the text and guide the reader.
* **Quotes:** You started strong with Michael Fischer’s quote. Include more quotes from experts or vertical farm operators to add authority and diverse perspectives.
* **visuals:** Consider adding more images and perhaps infographics to illustrate the technology and processes involved in vertical farming.
By incorporating these suggestions, you can create a truly engaging and informative article that sheds light on the exciting potential of vertical farming.
This appears to be an excerpt from a news article discussing vertical farming.
here are some key takeaways from the text:
* **Vertical farms are becoming more cost-competitive:** the article highlights Farm 2, a larger vertical farm, which is now cost-competitive with traditionally grown basil flown in from distant regions. This is due to technological advancements leading to cheaper lighting and lower energy usage.
* **Lower environmental impact:** Vertical farming has a considerably lower carbon footprint compared to customary agriculture due to its controlled surroundings and reduced transportation needs.
* **Energy costs are crucial for UK vertical farms:** Despite the benefits, the high energy costs in the UK pose a challenge for the industry’s growth. Farm boss Tristan Fischer aims to prove the viability of vertical farming in the UK despite these challenges before expanding to countries with cheaper energy.
* **Potential for mainstream adoption:** As technology continues to advance and costs decline, vertical farming holds promise as a mainstream solution for accessing fresh, locally grown produce year-round.
Let me know if you have any other questions!

:strip_icc():format(jpeg)/kly-media-production/medias/4293087/original/032057900_1673917421-088723300_1662604716-iPhone_14_Pro.jpg)