Flashes of Light and Clicks of Sound: A Potential Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Treatment
In a groundbreaking study, scientists have made incredible strides in understanding the underlying causes of Alzheimer’s disease and potential methods of treatment. Recent experiments conducted by researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have shown that stimulating high-frequency brain waves, known as gamma waves, can effectively clear out amyloid protein clumps in the brains of mice – a finding that holds immense promise for future treatments.
Alzheimer’s disease is a devastating neurodegenerative condition, characterized by the accumulation of amyloid proteins, also known as amyloid plaques, in the brain. These protein clumps disrupt normal brain function, leading to cognitive decline and memory loss. While the exact role of amyloid plaques in the development of Alzheimer’s is still not fully understood, they are widely believed to play a critical role in the disease.
The Glymphatic System: A ‘Plumbing’ Network
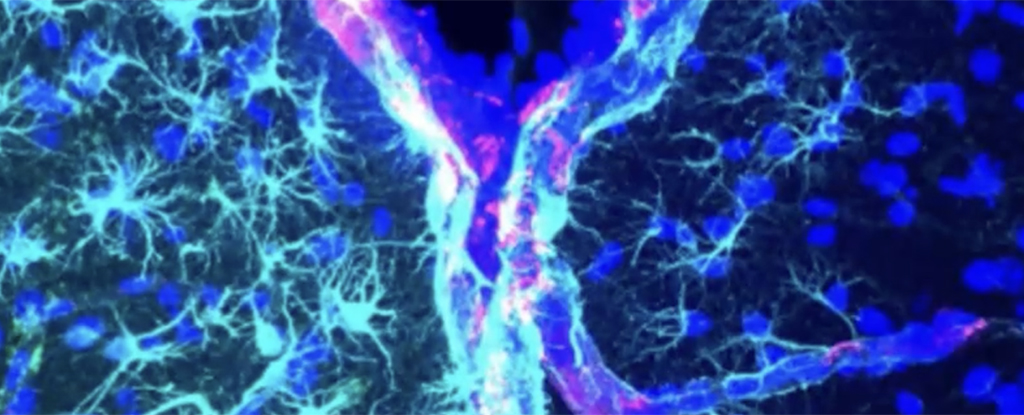
Central to the recent study’s findings is the brain’s glymphatic system, a fascinating self-cleaning mechanism that removes harmful substances from the brain. This network of vessels acts as a plumbing system, effectively flushing out waste and maintaining brain health. Researchers discovered that flashing light and sound at a frequency of 40 hertz stimulated this glymphatic system in mice, resulting in the removal of amyloid proteins.
The team observed a notable increase in the brain’s protective cerebrospinal fluid when the mice were subjected to the gamma wave stimulation. Furthermore, they noticed heightened pulsations in neighboring arteries, further enhancing the brain’s ability to clear out biological waste. Additionally, an increase in interstitial fluid leaving the brain was observed, confirming the boosted efficiency of waste removal.
Promising Pathways for Future Research
While the study’s focus was on the stimulation of gamma waves to clear amyloid proteins, it also shed light on other critical elements related to Alzheimer’s disease. Researchers uncovered the significance of aquaporin-4 (AQP4) channels in astrocyte cells, which are central nervous system cells responsible for supporting and protecting the brain. Blocking these channels resulted in a return to normal amyloid protein buildup, indicating that AQP4 channels may be a potential target for future therapeutic interventions.
Furthermore, the researchers found an increase in the production of a peptide associated with combating Alzheimer’s. These findings imply the potential for developing new therapies that might target this specific peptide or the subset of neurons responsible for its production.
An Optimistic Outlook for Alzheimer’s Treatment
The implications of this study are vast and exciting. By deepening our understanding of how gamma wave stimulation can enhance the brain’s waste removal system, we may be one step closer to developing effective treatments for Alzheimer’s disease. Although many questions remain unanswered, the study presents a compelling case for further exploration in this field.
The findings also underline the importance of continuously investing in research and development to tackle the growing prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease worldwide. With an aging population and an increasing number of individuals affected by the disease, Alzheimer’s presents a significant public health challenge that demands urgent attention.
Looking Ahead: Future Trends and Recommendations
The potential future trends arising from this study open up a plethora of possibilities for Alzheimer’s research and treatment. The development of innovative therapies utilizing gamma wave stimulation might revolutionize the field and offer much-needed hope to millions of individuals currently suffering from this debilitating disease.
Furthermore, the study’s findings highlight the importance of early detection and intervention. Identifying individuals at high risk for Alzheimer’s disease and implementing preventive measures might potentially delay or even halt the progression of the disease.
Additionally, investment in further research is crucial to unraveling the complexities of Alzheimer’s and developing more targeted therapies. Collaborative efforts between academia, industry, and healthcare institutions will be pivotal in driving progress and translating scientific discoveries into tangible treatment options.
As we move forward, it is essential to prioritize the development of personalized medicine approaches. Tailoring treatments to individuals based on their unique genetic profile, lifestyle, and other factors might significantly improve outcomes and enhance the efficacy of therapeutic interventions.
The Path Ahead
The recent study unlocking the potential of gamma wave stimulation to clear amyloid protein clumps in the brain provides a glimmer of hope for the future of Alzheimer’s treatment. By delving into the fascinating world of the brain’s glymphatic system and unveiling its responsive capabilities, researchers have opened up new avenues for exploration and innovation.
As we stand on the precipice of a new era in Alzheimer’s research, it is vital to maintain momentum and continue pushing the boundaries of our knowledge. The discoveries made today lay the foundation for future breakthroughs and, ultimately, the development of effective treatments that can transform the lives of those affected by this devastating disease.
References:
– “Could Alzheimer’s Disease One Day be Treated by Flashes of Light and Clicks of Sound?” ScienceAlert
– “Previous Research” Nature
– “How Sensory Gamma Rhythm Stimulation Clears Amyloid in Alzheimer’s Mice” MIT News