Amateur astronomers from Germany, who constantly observe through their eyepieces, appear to have made a remarkable discovery. Martin Kabatnik and his friends have found a celestial object that is moving at an astonishing speed—so fast that it is bound to exit our Galaxy.
Twice as Fast as the Sun
Astrophotographs reveal that this small dot shifts position rapidly, indicating an incredible velocity. Calculations suggest that it travels at 1.6 million kilometers per hour, equivalent to 440 kilometers per second.
For comparison, the Sun moves through the Galaxy at a speed of 220 kilometers per second—this new object is traveling at twice that speed.
Observatories face incredible mysteries of the Universe
Calculations indicate that this new “acquaintance” will quickly traverse the Galaxy and depart from it. This realization itself constitutes a scientific discovery, suggesting that the space separating hundreds of billions of galaxies is not empty.
Equally intriguing is the nature of this object. By astronomical standards, it is relatively small and resembles so-called “brown dwarfs.” Scientists define these as substellar objects that are too small to be classified as stars yet too large to be ordinary planets.
Brown Dwarfs in the Vast Universe
These objects lack the mass required to initiate full-fledged nuclear reactions in their cores, which would convert conventional space debris into luminous, heat-emitting stars.
Related to “brown dwarfs” are the gas giant planets. Among the celestial bodies in our Solar System, Jupiter currently most closely resembles the newly discovered “flyer” identified by the German astronomers. Scientists now hypothesize that weak nuclear reactions might occur within Jupiter’s core.
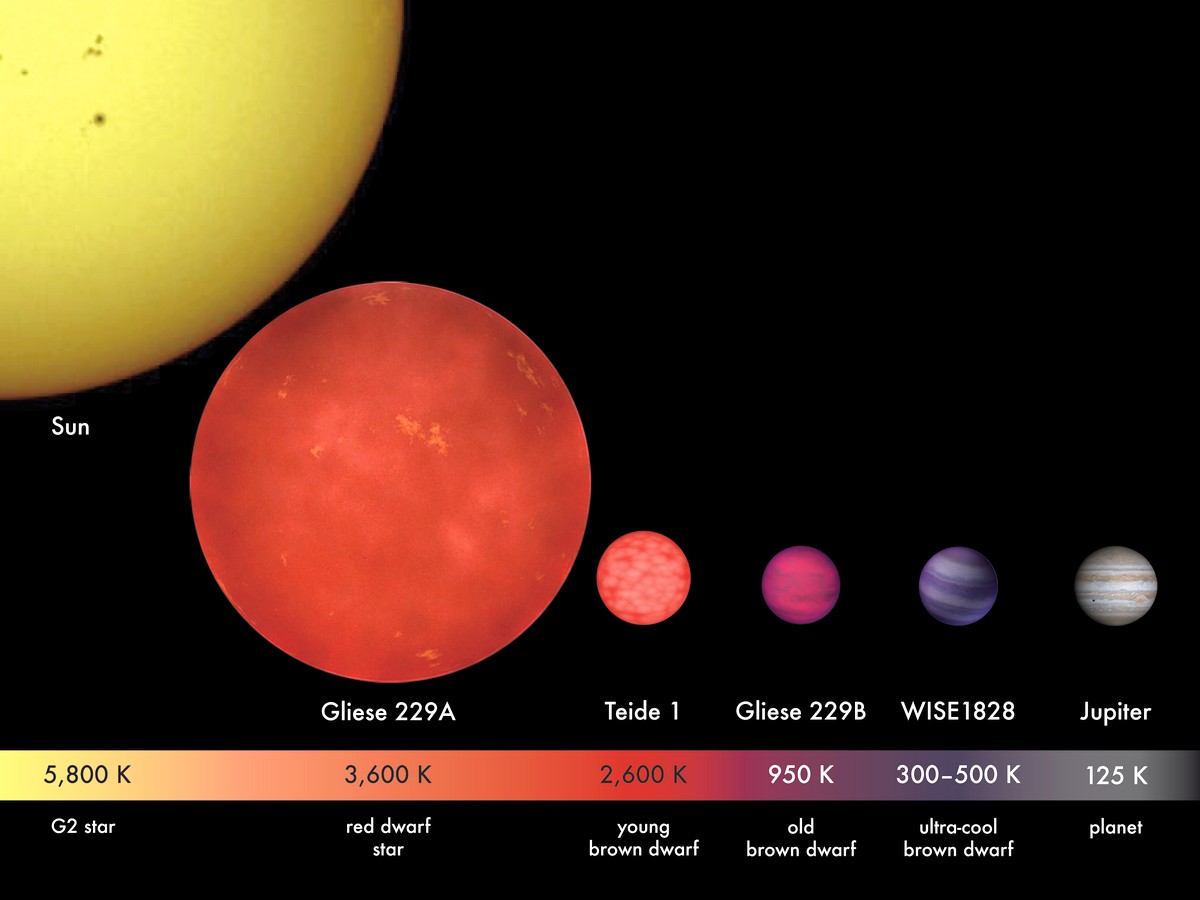 Classic brown dwarfs are the third, fourth, and fifth objects on this diagram. Jupiter is at the end, while the Sun is located in the upper left corner
Classic brown dwarfs are the third, fourth, and fifth objects on this diagram. Jupiter is at the end, while the Sun is located in the upper left corner
This current dwarf, based on its rapid movement, appears to deplete its nuclear fuel quickly and becomes invisible. It remains easily observable, allowing for the hypothesis of its “youth” to be plausible.
However, research indicates that the object contains almost no metals, including iron. This leads to the conclusion that the “galactic wanderer” is quite old, belonging to nearly the first generation of stars in our Galaxy.
Moreover, the Milky Way itself was formed over 13 billion years ago. One can appreciate the scale of this occurrence: the brown dwarf discovered by amateur astronomers “remembers” times that are unimaginably distant.
 A galaxy similar to our Milky Way
A galaxy similar to our Milky Way
Astronomers understand well what they are discussing. All contemporary chemical elements, including those found on Earth, are byproducts of nuclear reactions that have occurred within stars over billions of years.
Old stars are deficient in chemical elements because many of these elements had not yet formed during their existence. This raises another question: how has this object not extinguished yet?
A Sub-Star That Became an Asteroid
Equally significant is the question of what has propelled our new acquaintance to such great speeds. Few forces in the universe could cause an object to move at over 400 kilometers per second.
Currently, scientists are proposing traditional hypotheses. Perhaps this dwarf, larger than Jupiter, was initially traveling at a more moderate pace but encountered a black hole along its path. The object could have executed a gravitational maneuver, which subsequently accelerated its speed.
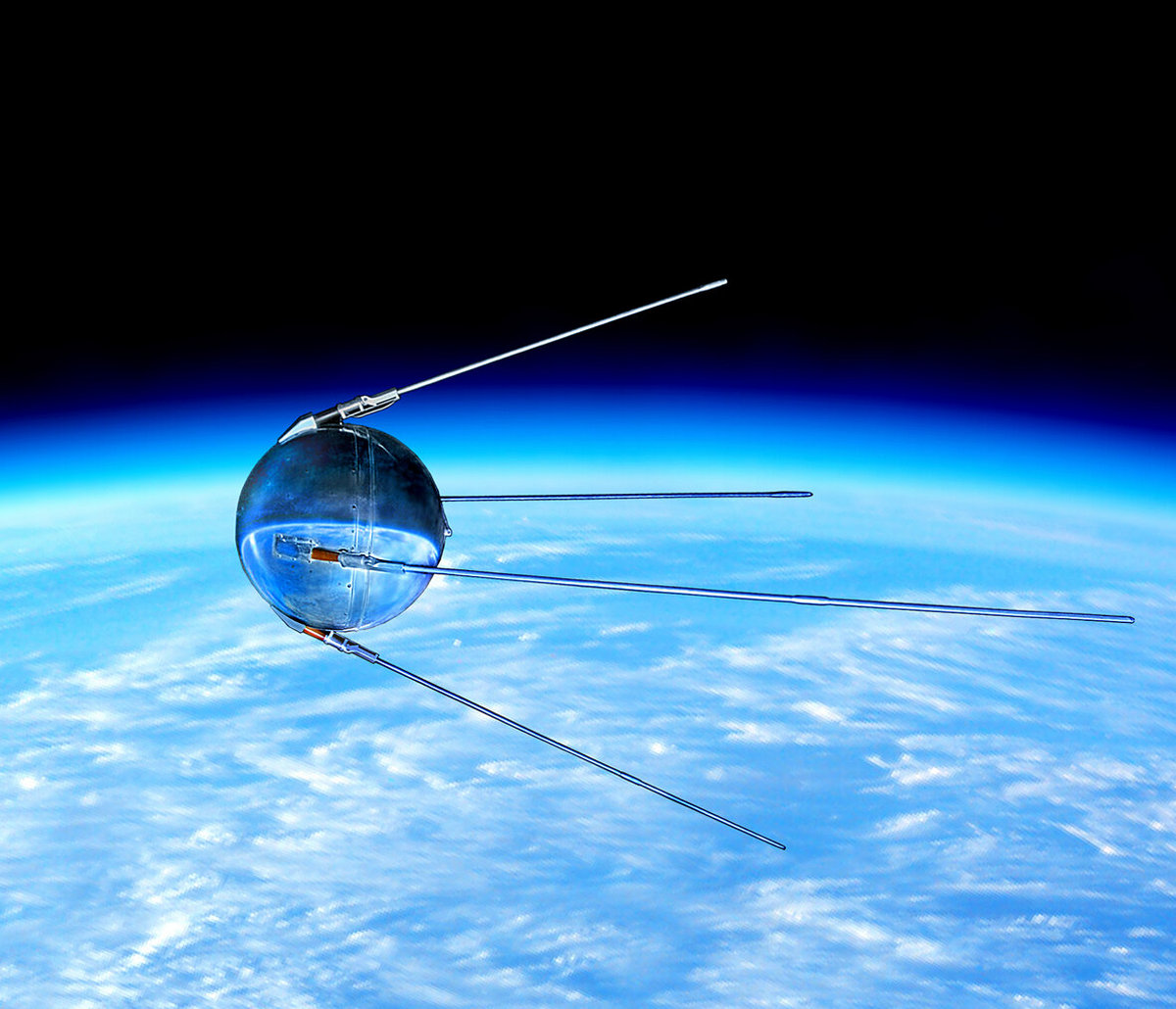 The space age of humanity will turn 67 on October 4. What discoveries still await us? This photo features the first artificial satellite of Earth, created and launched by the USSR
The space age of humanity will turn 67 on October 4. What discoveries still await us? This photo features the first artificial satellite of Earth, created and launched by the USSR
The object might have been part of a binary star system. If its partner star exploded due to mutual atomic reactions, our “acquaintance” could have been expelled by a powerful shockwave.
We live in an age of various speculations based on incomplete data. So let’s consider this theory: what if this is an alien vessel? While no one can definitively rule out the existence of intelligence beyond our planet, the idea remains purely theoretical.

However, the speeds required for interstellar travel are still astonishing and would cause significant distortions in matter. This has been depicted numerous times in both scientific literature and science fiction, though even this possibility cannot be dismissed, despite the scant data supporting it.
Army of Amateurs
Another aspect of this story is how this object was discovered. Fifteen years ago, NASA allowed amateur astronomers worldwide to freely analyze thousands of space images. This work is voluntary, with images transmitted by the Neowise space telescope, launched into Earth orbit in 2009.
Consequently, Kabatnik and his colleagues made their remarkable discovery:
“When I noticed how fast it was flying, I wondered: could it be that only we discovered this object? I can’t express how excited I felt,” Komsomolskaya Pravda quotes him as saying.
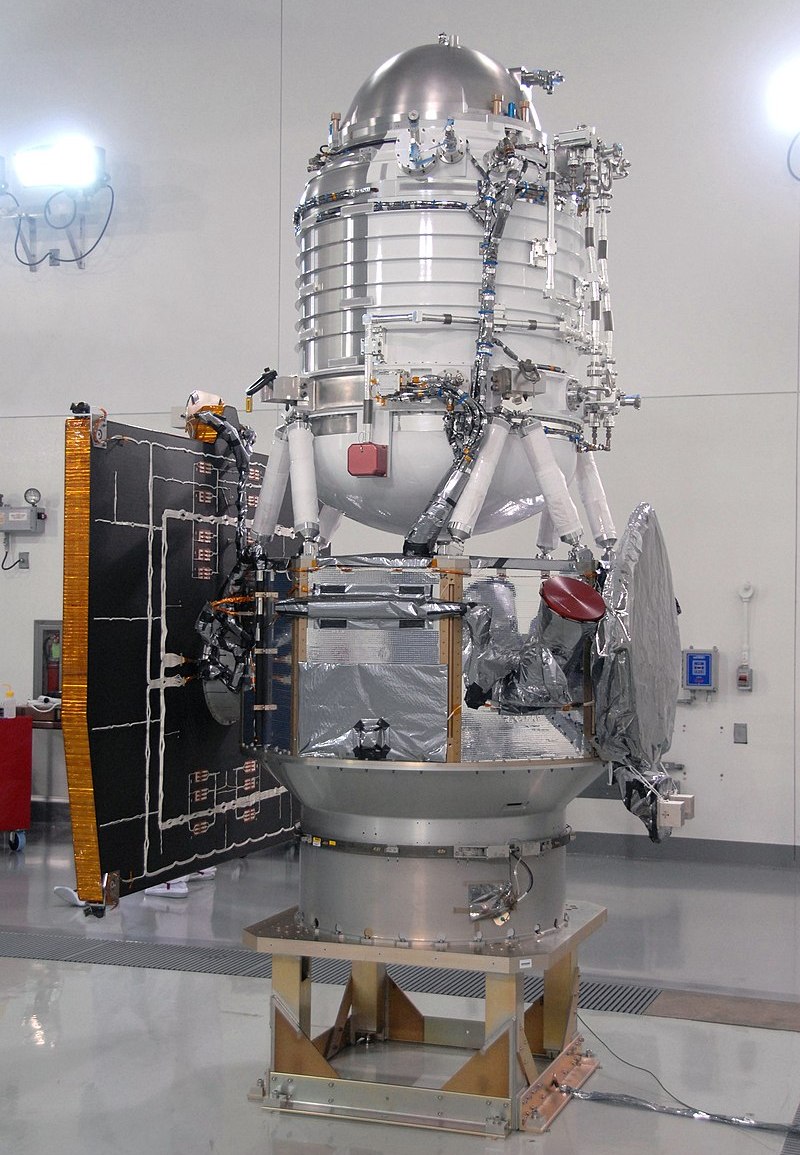 The same satellite telescope after assembly
The same satellite telescope after assembly
In the future, the army of amateurs may be overshadowed by neural networks, but this discovery is undoubtedly remarkable! We hope that our scientists will play a significant role in studying the mysterious objects of the Universe, despite all the challenges posed by sanctions.
In the Hustle and Bustle of Our Days
Moreover, we note that in addition to the baffling dwarfs, NASA has detected five asteroids within our Solar System that measure 150 meters in diameter and are heading toward Earth. Humanity will have to unite and put aside all conflicts to study the mysteries of the Universe and to defend against threats such as asteroids.
Indeed, one of the clear objectives for this century is to commence extensive exploration of the Moon and Mars, alongside addressing issues here on Earth.
 Love and the Milky Way
Love and the Milky Way
For those inspired by such matters, here is a quote from Nikola Tesla:
“If you want to understand the secrets of the universe, think in terms of energy, frequency, and vibration.”
Let us return to where we began: the starry sky above us helps cleanse the soul of anger. And when, dear readers, you take a moment to unwind, look at the stars to your heart’s content, and embrace someone close to you. It will certainly improve your mood, and the rush of daily life will remain with us.
Author: Alexander Kaminsky
Amateur Astronomers Discover Galactic Wanderer: A New Fast-Moving Celestial Object
Amateur astronomers in Germany have made an exciting discovery that has the scientific community buzzing. Martin Kabatnik and his team have identified a celestial object that is moving at an astonishing speed—so fast that it will soon leave our Galaxy altogether. This find not only underscores the capabilities of amateur astronomers but also enriches our understanding of the cosmos.
Twice as Fast as the Sun: The Speed of Discovery
Astrophotographs taken by Kabatnik and his peers have revealed a small dot that consistently changes its position across the night sky. Calculations indicate that this object travels at a staggering speed of 1.6 million kilometers per hour—equivalent to approximately 440 kilometers per second. In comparison, our Sun is moving through the Galaxy at about 220 kilometers per second, making this new object twice as fast.

Observatories confront incredible mysteries of the Universe
At this extraordinary speed, the newly discovered object will traverse the Galaxy in a relatively short time, presenting both a scientific enigma and an opportunity to deepen our understanding of cosmic phenomena. This discovery highlights the fact that the universe is far from empty; instead, it is teeming with dynamic objects moving through vast expanses of space.
What Exactly Is This Celestial Object?
This object is categorized as a brown dwarf—a type of substellar object that straddles the line between the smallest stars and the largest planets. Brown dwarfs do not possess enough mass to sustain nuclear fusion at their cores, which is critical for traditional star formation and sustenance. Instead, they exhibit characteristics similar to gas giant planets, with Jupiter being the most well-known example.
Brown Dwarfs: The Cosmic Misfits
Brown dwarfs have masses insufficient for complete nuclear reactions but can experience minimal fusion at their centers. Jupiter, for instance, has been theorized to undergo very weak nuclear reactions, hinting at a potentially dynamic interior, even though it lacks the intensity of a true star.

Classic brown dwarfs are the third, fourth, and fifth objects on this diagram. Jupiter is at the end, while the Sun resides in the upper left corner.
Interestingly, while this newly identified brown dwarf seems to be exhausting its nuclear fuel rapidly, making it observable, it contains almost no metals. This discovery suggests that the object is ancient, possibly belonging to the galaxy’s very first generation of stars formed over 13 billion years ago. As these primordial stars lacked the diversity of elements we observe today, the mystery of this object’s continued visibility poses many questions for researchers.
Why Is It Moving So Fast?
The object’s incredible speed begs the question: what factors influenced its acceleration? Scientists begin with several hypotheses:
- Gravitational Slingshot: It’s possible that the brown dwarf encountered a black hole. Instead of being consumed, it could have gained speed through a gravitational maneuver.
- Binary Star Dynamics: If the brown dwarf was once part of a binary star system, its partner might have exploded, unleashing enough force to propel our celestial wanderer at this remarkable velocity.

The space age of humanity will turn 67 on October 4. What discoveries still await us?
Of course, speculative theories abound, including the possibility of extraterrestrial technology. While such ideas belong more to the realm of science fiction, they can’t be entirely discounted without further data. The exploration of such hypotheses showcases both the wonder and the vast unknowns of our universe.
The Role of Amateur Astronomers
This celestial discovery raises questions about the role of amateur astronomers in modern astronomy. Fifteen years ago, NASA provided a revolutionary opportunity for non-professionals to analyze thousands of space images collected by the Neowise space telescope. This initiative enabled countless amateur astronomers—like Martin Kabatnik—to contribute meaningfully to astronomical research.
“When I noticed how fast it was flying, I thought: was it really only us who discovered this object? I can’t even describe the level of my excitement,” Kabatnik expressed.

The Neowise space telescope, which has enabled amateur astronomers to contribute to significant discoveries.
While advancements in artificial intelligence may soon alter how astronomical data analysis is performed, this exciting breakthrough demonstrates the potential of collective human observation and passion for science. It serves as a reminder of the power and possibility inherent in every skyward gaze.
Implications for Future Exploration
This discovery also highlights the pressing need for humanity to unite in pursuit of understanding celestial bodies that could pose threats, such as asteroids that might impact Earth. NASA has detected several near-Earth asteroids, some as large as 150 meters in diameter, which further emphasizes the importance of studies like these.

Scientists and enthusiasts alike must collaborate to explore the cosmos and protect our planet.
Reflection on Our Place in the Universe
As we continue to explore the wonders of space, it’s essential to remember that every discovery contributes to our understanding of the universe and our place within it. Insights derived from these celestial occurrences will drive future exploration of the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
As Nikola Tesla once said, “If you want to understand the secrets of the universe, think in terms of energy, frequency, and vibration.” Let us embrace this spirit of inquiry as we illuminate the mysteries of the cosmos and foster connections with one another.



