
AMD Zen 4 For Ryzen 7000 and Intel Raptor Cove For Raptor Lake CPUs have nearly identical IPCs.
AMD Zen 4 ‘Ryzen 7000’ CPU Cores Achieve Nearly Similar IPC To Intel’s Raptor Cove ‘Raptor Lake’ CPU Cores
OneRaichu has nailed all the leaks regarding Intel and AMD CPUs and this time he shared the IPC numbers for both AMD’s Zen 4 cores and Intel’s Raptor Cove cores.
For comparison, I’ve also added figures for Golden Cove (12th gen P-core) and Gracemont core (12th/13th gen E-core).
Performance is SPECCPU2017 Rate-1, and all chips are evaluated at a fixed clock of 3600MHz or 3.6GHz.
The leaker also shows how memory affects IPC by comparing DDR5-4800 and DDR5-6000.
1. Zen 4 has a great cache config and makes it not very dependent on DRAM.
2. According to the bad latency of DDR5 and the punishment of Gear2 mode, DDR5-4800 almost has 15 ns slower than DDR4-3200JEDEC-G1. It will make almost 2% of IPC punish.
3. The result is may vary. pic.twitter.com/Rf0Dmco3z7— Raichu (@OneRaichu) September 14, 2022
AMD’s Zen 4 is said to be less dependent on DRAM due to better cache configuration.
Therefore, DDR5’s high latency and Gear2 mode can result in 15ns latency being slower than DDR4-3200’s JEDEC, but it only affects IPC by 2%.
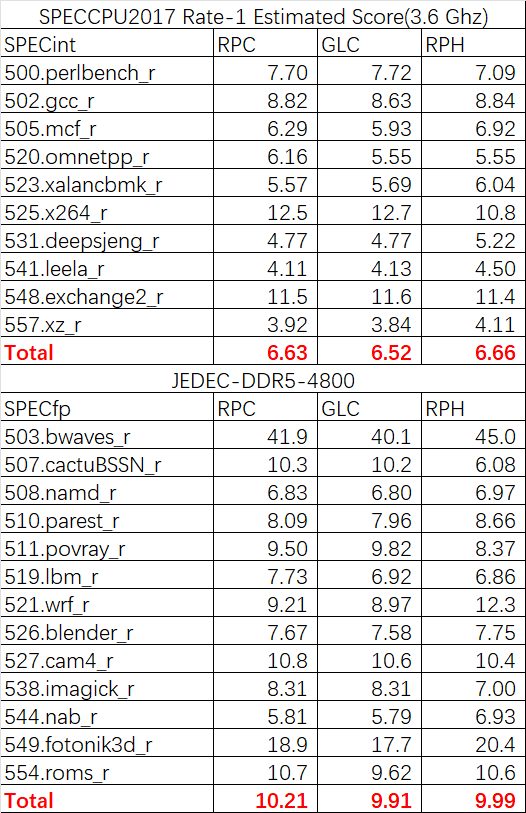
Comparing Intel Raptor Cove cores and AMD Zen 4 CPU cores (from DDR5-4800 IPC OneRaichu):

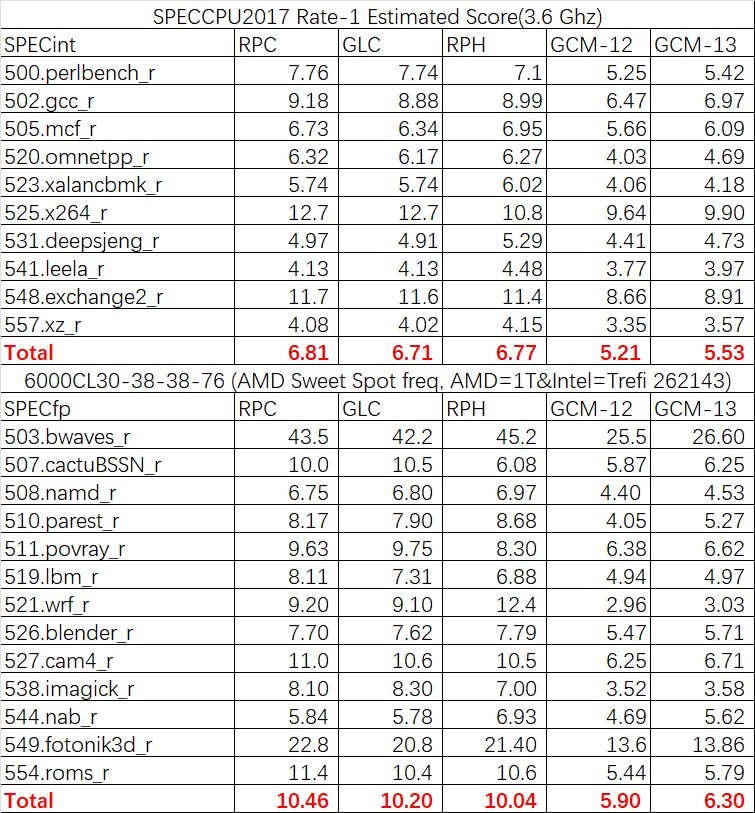
Comparing Intel Raptor Cove cores and AMD Zen 4 CPU cores (from DDR5-6000IPC OneRaichu):

AMD’s Zen 4 is said to be less dependent on DRAM due to better cache configuration.
Therefore, DDR5’s high latency and Gear2 mode can result in 15ns latency being slower than DDR4-3200’s JEDEC, but it only affects IPC by 2%.
From the JEDEC (DDR5-4800) results, the Intel 13th Gen Raptor Cove CPUs and AMD Ryzen 7000 Zen 4 CPUs deliver a 2% IPC improvement over the 12th Gen Golden Cove cores in SPECint.
In Specfp benchmarks, Raptor Cove cores have 3% IPC improvement over Golden Cove and 2% IPC over Zen 4 cores.
This indicates that the AMD Zen 4 cores and the Intel Raptor Cove cores have nearly identical IPCs.

The same is true for DDR5-6000 memory, with Intel’s Raptor Cove cores and AMD’s Zen 4 cores having similar IPCs of 6.81 and 6.77 respectively.
This means that regarding 1% IPC is improved over Intel’s Golden Cove core.
On Specfp, the Raptor Cove cores have 4% higher IPC than Zen 4 and 3% higher IPC than Golden Cove cores.
The 13th Gen Gracemont cores also show a 6% SPECint and 7% SPECfp IPC improvement over the traditional 12th Gen Gracemont cores.
We can see that the IPCs of the three architectures – Raptor Cove, Alder Lake and Zen 4 – are all on par.


In other words, what users want from next-generation CPUs, besides IPC, seems to be maximum clock speed and a cache structure that plays a very important role, especially in gaming applications.
We also have to consider the efficiency and power consumption numbers of the CPUs, but the two-month testing of AMD Ryzen 7000 ‘Zen 4’ and Intel 13th Gen ‘Raptor Cove’ CPUs will be very interesting. I guess.
Intel Raptor Lake vs AMD Raphael Desktop CPU Comparison “Final”:
sauce:wccftech – AMD Zen 4 For Ryzen 7000 & Intel Raptor Cove For Raptor Lake CPUs Have Almost Similar IPC
Commentary:
Zen4 and Raptor IPC are almost the same
That’s what I’m talking regarding.
I don’t know how to read the votes, so I can’t tell if this conclusion is correct or not, but if I talk regarding my opinion on the premise that this story is correct, if the IPC of RaptorCove and Zen4 are the same, Raptor’s I think it has an overwhelming advantage.
The reason is that it is a hybrid and has two types of cores, and the roles are clearly divided into the E-core that pursues efficiency and pursues multi-thread performance and the P-core that pursues single-thread performance.
Had the Raptor consisted of only P-cores, it probably wouldn’t have been so overwhelming.
It’s an architecture that looks like a desktop PC that can exhaust heat up to 250W by installing a huge cooler that converts heat into work, so I don’t think it’s a match if you compare the hybrid and the normal.
There’s not much point in arguing regarding it, but I don’t think Zen 4 is as bad as the numbers when comparing standalone architectures.
However, due to the hybrid, RaptorCove has been pulled out to the limit, so the numbers are quite different.
12th generation intelCore i5/7/9 series
Lock model without K (OC not possible)
* Please note that models with an F at the end do not have a GPU.











