An international team of scientists led by researchers from the Institute of Astrophysics of the Canary Islands (IAC) near us discovered two exoplanets with masses close to the mass of the Earth. Both exoplanets were found around the star GJ 1002, a red dwarf at a distance of 16 light-years from the solar system. The most amazing thing is that both exoplanets are in the habitable zone of a local star, which means the possibility of the development of biological life.
Image Source: Alejandro Suárez Mascareño and Inés Bonet (IAC)
The discovery of exoplanets around GJ 1002 was preceded by years of observations. The light of a star is extremely weak, so the spectral information regarding its characteristics was collected for quite a long time, but the result was worth it. For the discovery, scientists combined observational data from the CARMENES instrument, which is installed on the 3.5-m telescope at the Calar Alto Observatory in Spain, and data from the spectrograph ESPRESSOconnected to four 8.2-m telescopes of the complex VLT (Very Large Telescope) European Southern Observatory (ESO) in the Atacama Desert in Chile. GJ 1002 was observed by CARMENES from 2017 to 2019 and by ESPRESSO from 2019 to 2021.
After analyzing the data, astronomers concluded that the planet GJ 1002b – closest to its star – rotates with a period of just over 10 days, and the second planet – GJ 1002c – has an orbital period of just over 21 days. Since the star GJ 1002 has a mass of regarding 1/8 of the Sun, such a close location of the planets to the star does not pose a threat to them to burn out all living (biological) there, if any. The figure below shows where these exoplanets would be in our system in relation to the star.
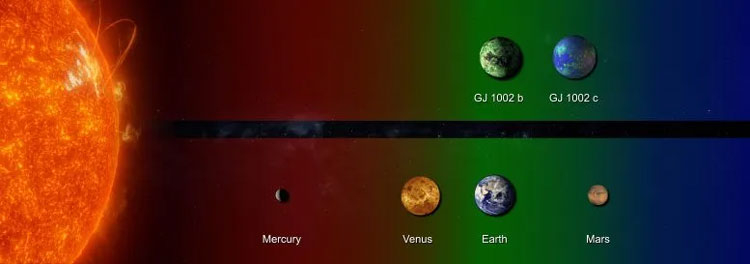
Together with previously discovered exoplanets of approximately Earth mass, we now have seven candidates for habitable alien worlds, potentially similar to Earth. Future studies will reveal the composition of the atmosphere of the recently discovered exoplanets of the GJ 1002 system, but this will not happen until the Extremely Large Telescope comes into operation (ELT) with the 40th mirror. He will receive a more sensitive ANDES spectrograph and this will not happen until 2030.
If you notice an error, select it with the mouse and press CTRL + ENTER.



/img/9238500.jpg?v=0&st=AkYS32jRvmmRqj4IdLOO17_wfDfb8JksVNBef1iYCHk&ts=1600812000&e=0)