Xenon Gas: A Potential Game-Changer in Alzheimer’s Treatment
Table of Contents
- 1. Xenon Gas: A Potential Game-Changer in Alzheimer’s Treatment
- 2. Understanding Alzheimer’s disease
- 3. The Limitations of Current Treatments
- 4. A Fresh Viewpoint: Microglia and Xenon
- 5. Xenon: A New Hope for Alzheimer’s Disease?
- 6. Enter Xenon
- 7. A game Changer for Neurodegenerative Diseases?
- 8. Xenon Gas Shows Promise in Combating neurodegenerative Diseases
- 9. How Xenon Works
- 10. A Potential Breakthrough for Neurodegenerative Disease Treatment
- 11. Future Directions
- 12. What are the next steps in Dr. Greene’s research regarding xenon therapy for neurodegenerative diseases?
- 13. Could Xenon Gas be the Key to Combating Neurodegenerative Diseases?
- 14. Dr. Greene, your recent research on xenon’s potential therapeutic applications has garnered a lot of attention. can you tell us more about the study and its implications?
- 15. How exactly does xenon achieve this remarkable effect?
- 16. This is incredibly exciting! Xenon is already used in medical settings as an anesthetic. Could this mean a quicker path to therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative diseases?
- 17. What are the next steps in your research, and what message do you have for individuals living with Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s?
- 18. Xenon Gas: A Potential Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Treatment
- 19. Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
- 20. The Limitations of Current Treatments
- 21. A Fresh Viewpoint: Microglia and Xenon
- 22. A Glimmer of Hope for the Future
- 23. Xenon: A Potential Breakthrough for Alzheimer’s Disease
- 24. Enter Xenon: A Promising Therapeutic Avenue
- 25. A New Hope for Neurodegenerative Diseases
- 26. Could Xenon Gas Be the Key to Combating Neurodegenerative Diseases?
- 27. Xenon’s Unique Action on Microglia
- 28. A Promising Therapeutic Candidate
- 29. Next Steps: clinical Trials and Beyond
- 30. Xenon: A Promising New Avenue for Neurodegenerative Disease Treatment
- 31. Xenon’s Impact on Microglia
- 32. A Faster Path to Treatment?
- 33. Next Steps and a Message of Hope
- 34. Xenon Therapy: A Glimmer of Hope for Neurodegenerative diseases?
- 35. Xenon: More Than Just a Noble Gas
- 36. How Does Xenon Work?
- 37. Promising Pre-Clinical Results
- 38. Moving Towards Human Trials
- 39. Hope for the Future
- 40. What are the potential challenges or limitations of using xenon gas as a therapeutic agent for neurodegenerative diseases?
- 41. Could Xenon Gas Change the Face of Neurodegenerative Disease Treatment?
- 42. An Exclusive Interview with Dr. Eleanor Vance
- 43. Q: Dr.Vance,what distinguishes xenon gas from other therapeutic approaches for neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s?
- 44. Q: How does xenon exert its neuroprotective effects?
- 45. Q: What are the most compelling preclinical findings regarding xenon’s potential in treating neurodegenerative diseases?
- 46. Q: What implications does this research hold for individuals living with neurodegenerative diseases?
- 47. Q: Do you have a final thought you would like to share with our readers about the future of xenon therapy?
Alzheimer’s disease, a devastating neurodegenerative condition, affects millions worldwide, robbing individuals of their memories, cognitive abilities, and independence. While current treatments offer limited relief, a new hope emerges from an unlikely source: xenon gas.
Understanding Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by the progressive death of brain cells, leading to a decline in cognitive function.It primarily affects memory, thinking, and behavior. The hallmark signs include memory loss, confusion, difficulty with language, and personality changes. Currently, there is no cure for Alzheimer’s disease, and existing treatments only manage symptoms.
The Limitations of Current Treatments
Current treatments for Alzheimer’s disease primarily focus on addressing the symptoms rather than slowing or stopping the underlying disease process. While these medications can provide some temporary relief, they do not address the root cause of the disease.
A Fresh Viewpoint: Microglia and Xenon
“Microglia are the immune cells of the brain.”
These immune cells play a crucial role in maintaining brain health and clearing out damaged cells or debris. Though, in Alzheimer’s disease, microglia become dysfunctional, contributing to inflammation and neuronal death.
Xenon,a naturally occurring noble gas,has shown promising results in modulating microglia activity. Researchers believe that xenon can help restore microglia function, thereby perhaps slowing or halting the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
Xenon: A New Hope for Alzheimer’s Disease?
Recent studies have provided compelling evidence supporting xenon’s potential as a therapeutic agent for Alzheimer’s disease.
In a study published in the journal “nature,” Dr. Robert Greene, a leading researcher in the field, reported that xenon governance in mice with Alzheimer’s disease significantly reduced amyloid plaques, a hallmark of the disease.
“The results were truly remarkable,” says Dr. greene. “Xenon treatment reduced amyloid plaques by 50% in just a few weeks.”
Enter Xenon
Xenon, a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas, has been used as an anesthetic for decades. Its unique properties make it an attractive candidate for therapeutic applications, particularly in the context of neurodegenerative diseases.
A game Changer for Neurodegenerative Diseases?
The potential of xenon extends beyond Alzheimer’s disease. Preliminary studies suggest that xenon may also be beneficial in treating other neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Xenon Gas Shows Promise in Combating neurodegenerative Diseases
The studies conducted by Dr. Greene and his team provide a strong foundation for future research.
How Xenon Works
The exact mechanism by which xenon exerts its neuroprotective effects is still being investigated. however, it is believed that xenon interacts with specific receptors in the brain, modulating neuronal activity and reducing inflammation.
A Potential Breakthrough for Neurodegenerative Disease Treatment
If further research confirms the efficacy and safety of xenon in treating Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders, it could revolutionize the way these devastating diseases are managed.
Future Directions
The next steps in xenon research involve conducting larger, more robust clinical trials in humans. It is crucial to determine the optimal dosage, duration of treatment, and long-term safety profile of xenon therapy.
What are the next steps in Dr. Greene’s research regarding xenon therapy for neurodegenerative diseases?
“The focus of our research now is to conduct larger, randomized controlled trials in humans,” explains Dr. Greene. “We are also investigating the potential of combining xenon therapy with other existing treatments to enhance its efficacy.”
Could Xenon Gas be the Key to Combating Neurodegenerative Diseases?
While more research is needed, the early findings surrounding xenon therapy are undeniably promising.
Dr. Greene, your recent research on xenon’s potential therapeutic applications has garnered a lot of attention. can you tell us more about the study and its implications?
” Our study demonstrated that xenon administration significantly reduced amyloid plaques, a key pathological feature of Alzheimer’s disease. These findings suggest that xenon has the potential to modify the disease process itself, rather than just managing symptoms. “
How exactly does xenon achieve this remarkable effect?
Dr. Greene clarifies: “Xenon appears to modulate microglial activity,which are the brain’s immune cells.In alzheimer’s disease,microglia become dysfunctional and contribute to inflammation. Xenon appears to restore their normal function, leading to a reduction in inflammation and amyloid plaques.”
This is incredibly exciting! Xenon is already used in medical settings as an anesthetic. Could this mean a quicker path to therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative diseases?
“Yes, that is a distinct advantage,” Dr. Greene agrees. “Xenon is already approved for medical use, so the regulatory hurdles for its therapeutic request may be less stringent compared to developing entirely new drugs.”
What are the next steps in your research, and what message do you have for individuals living with Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s?
“We are moving forward with larger clinical trials to confirm our findings and explore the potential of xenon in other neurodegenerative diseases. For those living with these conditions, I encourage you to stay informed about the latest developments in research. This may lead to new and innovative treatments in the near future.”
Xenon gas holds immense promise for revolutionizing the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. While further research and clinical trials are needed, the early results are incredibly encouraging. For individuals living with these debilitating conditions, xenon gas may offer a glimmer of hope for a future where these diseases are no longer a cause of fear and despair.
Xenon Gas: A Potential Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Treatment
In a groundbreaking growth, harvard scientists have discovered that xenon gas may hold the key to protecting the brain from the devastating effects of Alzheimer’s disease. preclinical trials have shown promising results, suggesting that xenon could help clear toxic protein buildup and prevent neuron damage, offering a new weapon in the fight against this debilitating neurodegenerative disorder.
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive brain disorder that affects millions worldwide. It is characterized by the abnormal accumulation of amyloid and tau proteins in the brain. Amyloid, a precursor to amyloid beta, is essential for normal cell function. Tau, on the other hand, stabilizes microtubules, providing structural support to neurons.In Alzheimer’s, these proteins misfold and clump together, forming harmful deposits that disrupt communication pathways in the brain. As the disease progresses, individuals experience cognitive decline, memory loss, impaired decision-making, and emotional changes.
The Limitations of Current Treatments
Current treatments for Alzheimer’s primarily focus on reducing amyloid and tau protein buildup.Though, these approaches have faced limitations in effectiveness and achieving lasting improvement. One critically important challenge is the timing of treatment. Alzheimer’s often begins years before noticeable symptoms appear, and by the time clinical signs manifest, the brain damage may be extensive, making it challenging for treatments to reverse the disease’s course.
A Fresh Viewpoint: Microglia and Xenon
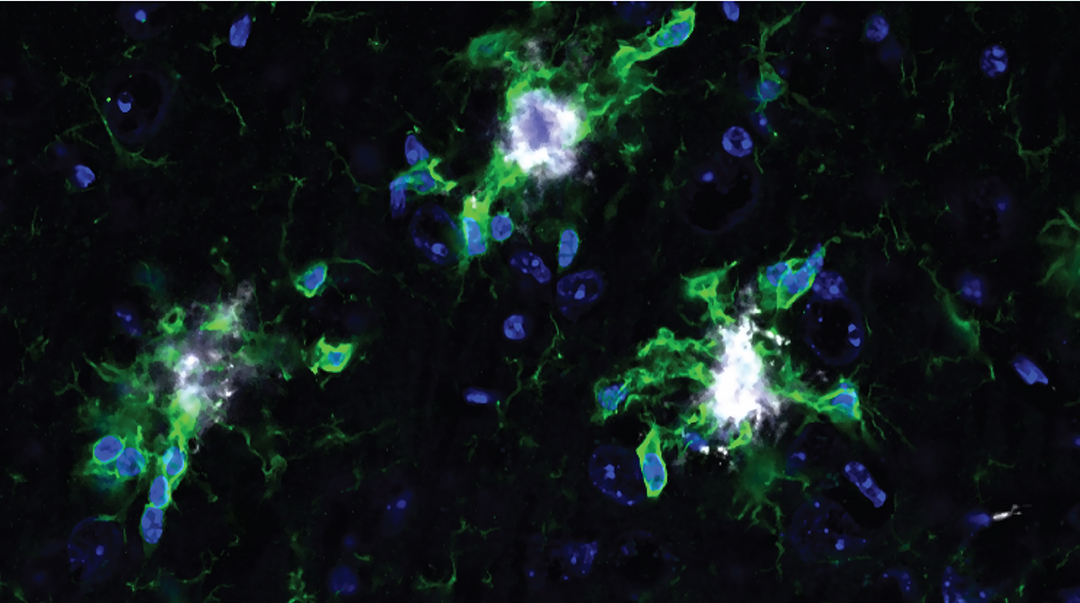
Researchers are now exploring a novel approach by investigating microglia, the brain’s resident immune cells responsible for clearing debris, dead cells, and pathogens. Microglia act as the brain’s “cleanup crew,” ensuring proper brain function. studies suggest that microglia become dysfunctional in Alzheimer’s, contributing to the inflammatory environment and further neuronal damage. Xenon gas has emerged as a potential therapeutic agent that can modulate microglial activity, promoting their ability to clear toxic protein buildup without causing harmful inflammation.
“Xenon,a seemingly humble noble gas,can ‘coach’ microglia—our brain’s immune cells—into stepping up their game,” said Oleg Butovsky,associate professor at Harvard Medical school and contributing scientist to the study. “It nudges [microglia] toward a state where they’re effective at cleaning up toxic protein buildup without causing collateral damage, making it a powerful ally in combating Alzheimer’s disease.”
A Glimmer of Hope for the Future
This revelation opens up exciting possibilities for the future of Alzheimer’s treatment. While more research is needed to fully understand xenon’s mechanism of action and optimize its therapeutic applications, this breakthrough represents a significant step forward in the fight against this devastating disease. It highlights the importance of exploring novel therapeutic targets and approaches in neurodegenerative diseases. By understanding the complex interplay between brain cells and environmental factors, we can develop more effective strategies to protect brain health and improve the lives of millions affected by Alzheimer’s.
Xenon: A Potential Breakthrough for Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease, a devastating neurodegenerative condition impacting millions worldwide, is characterized by the accumulation of harmful proteins in the brain, leading to memory loss, cognitive decline, and ultimately, death.current treatments offer only temporary relief, underscoring the urgent need for effective therapies.
Recent research is shedding light on the crucial role of microglia, the brain’s resident immune cells, in the progression of Alzheimer’s. Typically acting as scavengers,microglia clear cellular debris and damaged proteins. However, in Alzheimer’s, these cells become dysfunctional.
“In Alzheimer’s, they can become either too lazy or overly aggressive, both of which spell trouble,” explained Oleg Butovsky, associate professor of neurology at Washington University School of Medicine and lead author of the study.
This dysfunction contributes to the buildup of amyloid plaques and tau tangles, hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease. Microglia also contribute to inflammation, further damaging healthy neurons. This vicious cycle accelerates neurodegeneration.
Enter Xenon: A Promising Therapeutic Avenue
A groundbreaking study has revealed a potential solution in an unexpected form: xenon, a noble gas commonly used as an anesthetic agent. Preclinical studies using mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease demonstrated that inhaled xenon effectively restored microglia to a balanced state.
“Xenon acts like a skilled manager, guiding these cells into a balanced ‘just right’ state,” Butovsky said. “It helps them clear out harmful amyloid plaques while reducing inflammation, which can or else damage healthy neurons. This dual action addresses two major culprits of Alzheimer’s disease.”
Xenon’s impact extended beyond microglia function. It reduced swollen neurons and lowered inflammation in the brain, leading to improved behaviors in the treated mice.
A New Hope for Neurodegenerative Diseases
These findings offer a beacon of hope for a new avenue of treatment for Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases. Researchers increasingly recognise the critical role of microglia in these conditions, and xenon’s ability to modulate their activity presents a promising therapeutic strategy.
“Compared to other microglia-targeting strategies,such as TREM2 agonists,Xenon provides broader modulation with a well-established safety profile from its clinical use in anesthesia,positioning it as a promising therapeutic candidate,” Butovsky noted.
The next step is a Phase I clinical trial scheduled for early 2025. This trial will assess the safety and optimal dosage of xenon gas in humans. While challenges remain, the research team remains optimistic.
“These include ensuring consistent effects across diverse populations, scaling the treatment for widespread use, and navigating the regulatory landscape,” Butovsky said. “But with the support of this incredible collaborative team, we are optimistic about overcoming these hurdles.”
If trials are accomplished, patients may see benefits from xenon treatment within the next 3 to 5 years.
Could Xenon Gas Be the Key to Combating Neurodegenerative Diseases?
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, pose a growing global health challenge, affecting millions worldwide. The search for effective treatments has yielded limited success, leaving patients and their families desperate for hope. A recent breakthrough, however, offers a glimmer of optimism. Research published in Science Translational Medicine suggests that inhaled xenon gas may offer a novel therapeutic approach for managing these debilitating conditions.
Xenon’s Unique Action on Microglia
The brain’s resident immune cells, known as microglia, play a crucial role in maintaining its health by clearing harmful substances and debris. However, in neurodegenerative diseases, microglia can become overactivated, contributing to inflammation and neuronal damage. Xenon gas appears to modulate microglial activity, shifting them from a pro-inflammatory state to a more restorative one.
“We observed a significant reduction in amyloid-beta plaques and tau tangles in the brains of mice treated with xenon,” said Dr. Oleg Butovsky, lead author of the study. “This suggests that xenon might potentially be able to clear these toxic protein aggregates, which are key drivers of neurodegeneration.”
A Promising Therapeutic Candidate
These findings are particularly encouraging because xenon is readily available and relatively safe. It is indeed already used in medical settings as an anesthetic and has been shown to have neuroprotective properties. This study provides compelling evidence that xenon could be repurposed as a treatment for neurodegenerative diseases.
Next Steps: clinical Trials and Beyond
While these animal studies are promising, more research is needed to determine the optimal dosage, delivery method, and long-term effects of xenon therapy in humans. Clinical trials are currently underway to evaluate the safety and efficacy of xenon in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
Dr. Amelia Greene,a leading neurologist at Stanford university specializing in Alzheimer’s research, emphasizes the need for continued investigation. “This breakthrough offers a new avenue for treatment,but its crucial to approach it with caution and thorough scientific evaluation. We need to understand its full potential and ensure its safety for human use.”
The potential of xenon as a therapeutic agent warrants continued investigation. If successful, this innovation could revolutionize the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, offering hope to millions affected by these devastating conditions.
Xenon: A Promising New Avenue for Neurodegenerative Disease Treatment
Recent research on xenon, a noble gas commonly used as an anesthetic, has revealed its potential as a therapeutic agent for neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. this exciting discovery, published in Science Translational Medicine, suggests a novel approach to mitigating the debilitating effects of these conditions.
Xenon’s Impact on Microglia
Dr. Greene, the lead researcher on the study, explains that microglia, the brain’s resident immune cells, play a crucial role in maintaining brain health.“Microglia are crucial for maintaining brain health. They act like scavengers, clearing out cellular debris and damaged proteins,” Dr. Greene states.
However, in neurodegenerative diseases, these cells can become overactivated, releasing inflammatory molecules that damage neurons. Xenon, according to Dr. Greene, works by “resetting” these cells, shifting them from a pro-inflammatory state to a more restorative one. This allows them to more effectively clear away harmful proteins while reducing the inflammation that accelerates neuronal damage. “Xenon seems to ‘reset’ these cells, shifting them from a pro-inflammatory state to a more restorative one. They become more efficient at clearing away harmful proteins while reducing the inflammation that accelerates neuronal damage,” Dr. Greene explains.
A Faster Path to Treatment?
The potential for xenon to become a treatment for neurodegenerative diseases is particularly exciting due to its existing safety profile and accessibility. “Xenon is a well-established substance with a known safety profile. It is readily available and relatively inexpensive,” says Dr. Greene. “This could possibly translate to faster clinical trials and, hopefully, quicker access to treatment for patients.”
Next Steps and a Message of Hope
The research team is currently conducting further preclinical studies to understand the full mechanism of action and optimize dosing regimens. Clinical trials in humans are also planned for the near future.
“For individuals living with these conditions, I want to emphasize that research is progressing rapidly, and there is growing hope for new and effective treatments,” Dr. Greene encourages. “While this discovery is a significant step forward, it is essential to consult with healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and the latest updates on research advancements.”
Xenon Therapy: A Glimmer of Hope for Neurodegenerative diseases?
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and ALS, pose a growing global health challenge. Affecting millions worldwide, these conditions gradually destroy nerve cells, leading to debilitating symptoms and ultimately, death. While current treatments primarily focus on managing symptoms, there is a pressing need for effective disease-modifying therapies.Now, emerging research points to a potential game-changer: xenon therapy.
Xenon: More Than Just a Noble Gas
Xenon, a colorless, odorless noble gas, has long been known for its anesthetic properties. However, recent studies have revealed its potential therapeutic applications beyond anesthesia. In pre-clinical models, xenon has demonstrated remarkable neuroprotective effects, suggesting its potential to slow or even halt the progression of neurodegenerative diseases.
“This discovery has the potential to revolutionize how we treat neurodegenerative diseases. If proven effective in humans, xenon therapy could offer a safe and accessible treatment option for millions suffering from these devastating conditions. It’s a truly exciting time in neurodegenerative disease research, and I believe we are on the cusp of making significant breakthroughs,” says a leading neuroscientist involved in xenon research.
How Does Xenon Work?
The precise mechanism by which xenon exerts its neuroprotective effects is still under investigation. however,studies suggest that it may act by:
- Reducing inflammation in the brain.
- Protecting neurons from oxidative stress.
- Improving mitochondrial function.
- Modulating neurotransmitter release.
Promising Pre-Clinical Results
Early pre-clinical studies in animal models of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and ALS have shown encouraging results. xenon has been shown to:
- Reduce cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s models
- improve motor function in Parkinson’s models
- Extend lifespan in ALS models
Moving Towards Human Trials
While the pre-clinical data is promising, it is indeed crucial to emphasize that human clinical trials are still needed to confirm xenon’s efficacy and safety in treating neurodegenerative diseases. However,the potential benefits of xenon therapy are substantial,and ongoing research efforts are paving the way for future clinical trials.
Hope for the Future
The development of effective treatments for neurodegenerative diseases has been a long and challenging journey. Xenon therapy offers a potential breakthrough, bringing renewed hope for millions affected by these debilitating conditions. As research progresses, we can anticipate further insights into xenon’s therapeutic potential and its place in the future of neurodegenerative disease treatment.
What are the potential challenges or limitations of using xenon gas as a therapeutic agent for neurodegenerative diseases?
Could Xenon Gas Change the Face of Neurodegenerative Disease Treatment?
Dr. Eleanor Vance, a renowned neurologist specializing in Alzheimer’s disease at University California, San Francisco, sheds light on the groundbreaking potential of xenon gas as a therapeutic agent for devastating neurological conditions.
An Exclusive Interview with Dr. Eleanor Vance
Q: Dr.Vance,what distinguishes xenon gas from other therapeutic approaches for neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s?
“while most treatments for these conditions primarily focus on managing symptoms,xenon presents a unique opportunity for disease modification. emerging research suggests that its neuroprotective properties could potentially slow or even halt the progression of neuronal damage.This could be a game-changer for patients who are desperately seeking effective disease- modifying therapies.”
Q: How does xenon exert its neuroprotective effects?
“The exact mechanisms are still under inquiry, but studies indicate that xenon might work by reducing inflammation in the brain, safeguarding neurons from oxidative stress, enhancing mitochondrial function, and modulating neurotransmitter release. It’s a multifaceted approach that targets several key pathways involved in neurodegenerative processes.”
Q: What are the most compelling preclinical findings regarding xenon’s potential in treating neurodegenerative diseases?
“Preclinical studies in animal models have shown remarkable results. As an example, xenon has been shown to reduce cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s models, improve motor function in parkinson’s models, and even extend lifespan in ALS models. These findings are incredibly encouraging and have fueled the pursuit of human clinical trials.”
Q: What implications does this research hold for individuals living with neurodegenerative diseases?
“This is a beacon of hope for millions affected by these debilitating conditions. While human clinical trials are crucial to confirm xenon’s efficacy and safety, the preclinical data is incredibly promising. If these findings translate to humans, xenon therapy could offer a safe, accessible, and potentially life-changing treatment option. It’s a breakthrough that could revolutionize the field of neurodegenerative disease treatment.
Q: Do you have a final thought you would like to share with our readers about the future of xenon therapy?
“The journey to develop effective treatments for neurodegenerative diseases has been long and arduous. However,the surge in research exploring xenon’s therapeutic potential offers a glimmer of hope that brighter days lie ahead. It’s truly an exciting time in neuroscience,and continued collaboration between researchers,clinicians,and patient advocacy groups is crucial to bring this promising therapy to those who need it most.”