Teh brightest comet in nearly 20 years, comet G3 ATLAS (C/2024), is expected to reach its peak brilliance later this week into early next week. The only question is: “Will you actually be able to see it?”
This celestial paradox belongs to Comet 2024 G3 (ATLAS), which was first sighted on April 5 of last year by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) survey,in images obtained with a 0.5-meter (19.7-inch) reflector telescope located in Rio Hurtado,Chile. At the time of revelation, the comet was 407 million miles (655 million km) from Earth and shining at an exceedingly faint magnitude of +19. That’s roughly 158,000 times dimmer than the faintest star visible to the naked eye.
Returning after 160 millennia
Table of Contents
- 1. Returning after 160 millennia
- 2. The Journey of Comet G3 ATLAS: A Southern Sky spectacle
- 3. A Southern Hemisphere Highlight
- 4. The Challenge for Northern Observers
- 5. The Fragile Nature of comets
- 6. G3 ATLAS Comet: A Celestial Mystery Unfolds
- 7. A Sudden Surge in Brightness
- 8. Is Disintegration Imminent?
- 9. How Bright Will G3 ATLAS Become?
- 10. What’s Next for G3 ATLAS?
- 11. Comet G3 ATLAS: A Celestial Spectacle to watch in January
- 12. Key Dates and Distances
- 13. The Challenge of Visibility
- 14. Forward Scattering: A Potential Game-Changer
- 15. When and Where to look
- 16. What Makes this Comet Special?
- 17. Final Thoughts
- 18. How to spot Comet G3 ATLAS: A Rare Celestial Event in January
- 19. When and Where to Look
- 20. tips for Spotting Comet G3 ATLAS
- 21. Why This Comet is Special
- 22. Is Comet G3 ATLAS Visible During Daylight?
- 23. Tips for Observing comet G3 ATLAS
- 24. What Makes G3 ATLAS Unique?
- 25. How to Safely Observe Comet G3 ATLAS as It Nears the Sun
- 26. the Safest Way to Witness the Event
- 27. Why SOHO is your Best Option
- 28. Final Thoughts
- 29. Comet G3 ATLAS: A Impressive Celestial Event Captured by SOHO
- 30. How SOHO Brings comet G3 ATLAS to Life
- 31. SOHO’s Legacy of Comet Discoveries
- 32. Why This Event matters
- 33. Stay Updated
- 34. Space Dialog: Bridging the Gap Between Earth and Beyond
- 35. The Evolution of Space Communication
- 36. The Role of Social Media in Space Communication
- 37. Challenges and Future Prospects
- 38. Conclusion
- 39. How has teh development of technologies like Starlink and the Deep Space network influenced the capabilities of space dialog in the 2000s to the present day?
- 40. Key Milestones in Space Communication
- 41. The Role of Social Media in Space Communication
- 42. Examples of Social Media in Action
- 43. Challenges and Future Directions
- 44. Future Trends in Space Communication
- 45. Conclusion
A preliminary orbit for this comet indicated that it was going to pass exceptionally close — less than 9 million miles (14 million km) from the sun in mid-January 2025; only about one-quarter the distance of Mercury, the closest planet to the sun.However, these initial calculations also suggested that G3 ATLAS was a new comet coming directly from out of the Oort cloud, a vast bubble composed of countless billions of icy objects encircling our solar system, located perhaps 10 trillion miles (16 trillion km) from the sun. Small sun-skirting Mercury, the closest planet to the sun.
The Journey of Comet G3 ATLAS: A Southern Sky spectacle
Comets have long captivated stargazers with their ethereal beauty and unpredictable paths. Among these celestial wanderers, Comet G3 ATLAS has recently drawn attention, particularly for its trajectory favoring the Southern Hemisphere. Originating from the distant Oort Cloud, this comet’s journey has been both captivating and challenging to observe for those in the northern latitudes.
A Southern Hemisphere Highlight
Comet G3 ATLAS has carved a path through the southern constellations, making it a treat for skywatchers below the equator. Over the past month, its route has taken it through the constellations of Lupus and Scorpius, and it now resides in Sagittarius. For those in the Northern Hemisphere, however, the comet has remained frustratingly low on the southeastern horizon, often lost in the glare of morning twilight.
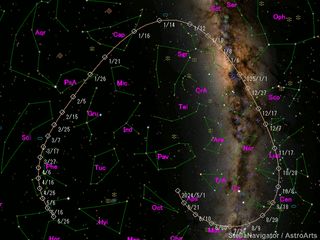
(Image credit: Seiichi Yoshida)
The Challenge for Northern Observers
For astronomers and enthusiasts in the Northern Hemisphere, Comet G3 ATLAS has been a tricky target. Its position low on the horizon, combined with the brightness of dawn, has made it nearly impossible to spot. This is a common challenge for comets on trajectories favoring southern skies, leaving many northern observers waiting for the next celestial visitor.
The Fragile Nature of comets
Comets like G3 ATLAS, which hail from the Oort Cloud, frequently enough face perilous journeys as they approach the sun. Many disintegrate before reaching perihelion,their closest point to the sun.This fragility adds to the rarity and intrigue of these icy travelers, making each successful approach a moment of scientific and visual significance.
As Comet G3 ATLAS continues its journey, its story serves as a reminder of the wonders and challenges of observing the cosmos. Whether visible from the Southern Hemisphere or elusive to northern eyes, it remains a testament to the dynamic nature of our universe.
G3 ATLAS Comet: A Celestial Mystery Unfolds
As the G3 ATLAS comet hurtles toward the sun, its dramatic brightening has captivated astronomers and skywatchers alike.This celestial visitor, now in the final stretch of its journey, has sparked both excitement and uncertainty about its fate. Will it survive its close encounter with the sun, or will it disintegrate under the intense heat? Let’s dive into the latest observations and expert insights.
A Sudden Surge in Brightness
on January 2, 2025, the G3 ATLAS comet experienced a remarkable outburst, with its apparent brightness increasing nearly fourfold. This sudden spike, documented in the Comet Observation Database (COBS), has left experts divided. John Bortle, a renowned comet observer, shared his thoughts in an email:
“the apparent instability exhibited in the recent magnitude increase usually can be interpreted as a bad sign that the comet is showing evidence of breaking up, but some other unusual features that have been reported, such as the ‘shadow of the nucleus,’ are classic features of any large comet near perihelion and not a sign of disruption.”
despite this, Bortle remains cautious, estimating the comet’s chances of survival at “about 50:50.”
Is Disintegration Imminent?
Nick James of the British Astronomical Association also weighed in on the comet’s behavior. He noted that while the brightness surge could indicate early signs of disintegration, the comet continues to brighten, suggesting it may still be intact. In a statement to Spaceweather.com, James said:
“The sudden jump in brightness was notable. This could have been an early sign of disintegration, but since then, the comet is still brightening. It looks as if this outburst has not been fatal.”
This cautious optimism has kept the astronomical community on edge, eagerly awaiting further developments.
How Bright Will G3 ATLAS Become?
One of the most pressing questions is whether G3 ATLAS will become bright enough to be visible against the twilight sky. Predicting the brightness of comets is notoriously difficult, especially for long-period comets like G3 ATLAS, which have no prior observational records. As Daniel Green of the Central Bureau for Astronomical telegrams pointed out, comets are as unique as snowflakes, making it challenging to forecast their behavior with precision.
For now, the comet’s trajectory will curve slightly northward, offering observers north of the equator a fleeting opportunity to catch a glimpse. However, its proximity to the sun means visibility will remain a challenge.
What’s Next for G3 ATLAS?
As G3 ATLAS approaches perihelion—the point in its orbit closest to the sun—its fate hangs in the balance. Will it survive the intense solar radiation and gravitational forces,or will it fragment into smaller pieces? Only time will tell.For now,astronomers continue to monitor its progress,hoping to unravel the mysteries of this enigmatic visitor.
Whether it fades away or puts on a dazzling display,G3 ATLAS serves as a reminder of the unpredictable and awe-inspiring nature of our universe.
Comet G3 ATLAS: A Celestial Spectacle to watch in January
Astronomers and stargazers alike are eagerly anticipating the arrival of Comet G3 ATLAS, which is set to make its closest approach to the sun and Earth in mid-January. according to the latest updates from the Central Bureau for Astronomical Telegrams in Cambridge, Massachusetts, this celestial visitor could become one of the brightest comets of the year, offering a rare opportunity for observation—if conditions align just right.
Key Dates and Distances
Comet G3 ATLAS is expected to reach perihelion—the point in its orbit closest to the sun—on January 13 at 10:17 Universal Time (UT). At this moment, it will be approximately 8.7 million miles (13.99 million km) from the sun.Later that same day, the comet will make its closest approach to Earth, coming within 87.1 million miles (140.1 million km) of our planet.
Astronomer Daniel green predicts that the comet could achieve a maximum magnitude of -3.2, making it brighter than Jupiter and nearly as luminous as Venus. “The comet will be close to the sun when brightest, but it’s becoming difficult now even for Southern Hemisphere observers to see,” Green told Space.com. “It’s really hard to call these comets when close to the sun like this, in terms of visibility.”
The Challenge of Visibility
While the comet’s predicted brightness is impressive, its proximity to the sun poses a significant challenge for casual observers. The bright twilight sky may obscure the comet, making it difficult to spot without specialized equipment.However,if the comet experiences a phenomenon known as forward scattering,its visibility could improve dramatically.
Forward Scattering: A Potential Game-Changer
Forward scattering occurs when sunlight reflects off the comet’s dust particles, creating a “dusty windshield effect” that can substantially enhance its brightness. For Comet G3 ATLAS, the phase angle—the angle between the sun, the comet, and the observer—is expected to reach a maximum of 115 degrees on January 13. This could amplify the comet’s luminosity, perhaps pushing its magnitude to -4, rivaling venus in brightness.
Some predictions are even more optimistic. Dutch amateur astronomer Gideon van Buitenen forecasts a peak magnitude of -6, which would make the comet nearly three times brighter than Venus. However, such extreme brightening is considered unlikely by most experts.
When and Where to look
For those hoping to catch a glimpse of Comet G3 ATLAS, timing and location are crucial. The best viewing opportunities will occur shortly after sunset on January 13, when the comet will be positioned low in the western sky. Observers in the Southern Hemisphere may have a slight advantage, as the comet will be higher above the horizon. However, even in ideal conditions, spotting the comet will require clear skies and minimal light pollution.

What Makes this Comet Special?
comet G3 ATLAS is not just another icy visitor from the outer solar system. Its potential brightness and the timing of its approach make it a standout event for astronomers and skywatchers. While its visibility remains uncertain, the possibility of witnessing a comet as bright as Venus is a rare and exciting prospect.
As Green aptly noted, “It’s really hard to call these comets when close to the sun like this, in terms of visibility.” But for those willing to brave the challenges, Comet G3 ATLAS could offer a once-in-a-lifetime celestial show.
Final Thoughts
Whether you’re an experienced astronomer or a casual stargazer, Comet G3 ATLAS is worth keeping an eye on this January. While its brilliance is not guaranteed, the chance to witness such a luminous comet is a reminder of the wonders that await us in the night sky. So mark your calendars, prepare your telescopes, and keep your fingers crossed for clear skies on January 13.
How to spot Comet G3 ATLAS: A Rare Celestial Event in January
Published on: January 10, 2024

Stargazers in the Northern Hemisphere are in for a treat this January as Comet G3 ATLAS makes its appearance. This celestial visitor offers a rare opportunity to witness a cosmic spectacle, but you’ll need to act quickly.The comet will be visible for just three days, from January 12 to 14, and spotting it will require some readiness and patience.
When and Where to Look
Your first chance to catch a glimpse of Comet G3 ATLAS comes early on January 12. For observers in mid-northern latitudes, the comet will rise approximately 35 minutes before sunrise. It will be positioned just 5 degrees above the sun at local sunrise.To maximize your chances of seeing it, start scanning the east-southeast horizon with binoculars about 25 minutes before sunrise. A slow, steady sweep of the area should help you locate the comet.
on the evening of january 14, the comet will set 35 minutes after the sun. At sunset, it will be situated about 7 degrees above the west-southwest horizon. Begin your search about 10 minutes after sunset, using binoculars to scan the area carefully. A flat horizon, such as a shoreline or open field, will significantly improve your chances of spotting this elusive object.
tips for Spotting Comet G3 ATLAS
- Find a Clear View: Ensure you have an unobstructed view of the east-southeast and west-southwest horizons. The comet will be very low in the sky, so any obstacles like trees or buildings could block your view.
- Use Binoculars: While the comet might potentially be visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions,binoculars will greatly enhance your chances of spotting it.They’ll help you pick out the faint glow against the twilight sky.
- Check the Weather: Clear skies are essential for comet hunting. Cloud cover or poor visibility can make it nearly impossible to see the comet, so plan your observation sessions accordingly.
- Be Patient: Spotting a comet requires time and persistence. Take your time to scan the horizon slowly and methodically.
Why This Comet is Special
Comet G3 ATLAS is a rare visitor to our skies, and its appearance is a reminder of the dynamic and ever-changing nature of our solar system. While it may not be as bright or dramatic as some of its predecessors,its fleeting presence offers a unique opportunity to connect with the cosmos. As one astronomer aptly put it, “Comets are like cosmic postcards, reminding us of the vastness and beauty of the universe.”
Whether you’re an experienced stargazer or a casual observer, don’t miss this chance to witness comet G3 ATLAS. With a little preparation and a lot of patience, you might just catch a glimpse of this celestial wanderer before it disappears from view.

(Image credit: Nicolas Lefaudeux)
Is Comet G3 ATLAS Visible During Daylight?
On Monday,January 13,Comet G3 ATLAS is expected to reach its peak brightness. Predictions for its magnitude vary widely, ranging from -3 to -6. If the comet achieves a magnitude of -4 or brighter, it could potentially be visible during the day, though this remains speculative.
Significant Safety Note: observing the comet during daylight hours is extremely risky, as it will pass just 5 degrees above the sun.Directly viewing the sun or its immediate surroundings without proper protection can cause permanent eye damage. Always use solar filters or indirect viewing methods if attempting to observe the comet near the sun.
Tips for Observing comet G3 ATLAS
- Choose the Right Location: Find a high vantage point, such as a hill, to avoid obstructions like trees or buildings. Clear skies and minimal low-lying clouds near the horizon are essential for a successful sighting.
- Use Binoculars: A pair of 7×50 binoculars is recommended for optimal viewing. For larger binoculars,such as 11×80 models,mount them on a sturdy tripod to stabilize your view.
- identify the comet: G3 ATLAS may appear as a bright, whitish or golden star. If visible, its tail will likely be short and point almost straight up, possibly tilting slightly to the right. After locating it with binoculars, try spotting it with your naked eye.
To estimate distances in the sky,remember that your clenched fist held at arm’s length spans approximately 10 degrees. Therefore, 5 degrees would be about half that width.
What Makes G3 ATLAS Unique?
Comet G3 ATLAS has captured the attention of astronomers and stargazers alike due to its unpredictable brightness and proximity to the sun. Its dynamic tails, composed of gas and dust, create a mesmerizing visual spectacle as it orbits. The comet’s behavior offers valuable insights into the composition and structure of these celestial wanderers.
Whether you’re an amateur astronomer or simply curious about the cosmos, G3 ATLAS provides a rare opportunity to witness the beauty and mystery of comets. However, always prioritize safety and use appropriate equipment to enhance your viewing experience.
How to Safely Observe Comet G3 ATLAS as It Nears the Sun
Comet G3 ATLAS is making headlines as it approaches the sun, offering a rare celestial spectacle.Though, observing this event requires caution. Directly staring at the sun, even for a moment, can cause irreversible retinal damage, leading to permanent vision loss. This risk is heightened when attempting to spot the comet during daylight hours. Under no circumstances should you use binoculars or telescopes to scan for the comet near the sun.
the Safest Way to Witness the Event

(Image credit: Comet plot by Joe Rao.SOHO image courtesy of NASA and ESA.)
The most secure method to observe Comet G3 ATLAS’s close encounter with the sun is through the SOHO spacecraft’s live feed. This approach eliminates the risks associated with direct observation and provides a clear, real-time view of the comet’s journey. The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) offers a unique vantage point, capturing the comet’s path as it traverses the sun’s vicinity.
Why SOHO is your Best Option
SOHO’s LASCO C3 camera is specifically designed to monitor solar activity and celestial objects near the sun. From January 11 to 14, the spacecraft will document Comet G3 ATLAS’s trajectory, allowing enthusiasts to witness this event safely from their devices. The images and data provided by SOHO are not only visually stunning but also scientifically valuable, offering insights into the comet’s behavior and composition.
As Joe Rao, a renowned comet observer, notes, “The SOHO spacecraft provides an unparalleled opportunity to study comets in close proximity to the sun without the dangers of direct observation.” This makes it an indispensable tool for both amateur stargazers and professional astronomers alike.
Final Thoughts
While the temptation to view Comet G3 ATLAS with the naked eye or optical instruments may be strong, the risks far outweigh the rewards. by leveraging the SOHO spacecraft’s live feed, you can enjoy this astronomical event safely and in stunning detail. Remember, protecting your vision is paramount, and technology offers a safe alternative to experience the wonders of the cosmos.
Comet G3 ATLAS: A Impressive Celestial Event Captured by SOHO
Stargazers and astronomy enthusiasts are in for a treat as Comet G3 ATLAS makes its journey through the solar system, offering a breathtaking celestial display. Thanks to the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO),this cosmic event is being captured in stunning detail,providing a rare opportunity to witness the comet’s close encounter with the sun.
How SOHO Brings comet G3 ATLAS to Life
Launched in 1995, SOHO has been a cornerstone in solar observation, and its Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronagraph Experiment (LASCO) C3 camera is at the heart of this mission. The LASCO C3 camera is designed to block the sun’s bright light, allowing astronomers to study the faint structures around it, including comets. For comet G3 ATLAS, SOHO’s LASCO C3 imagery will be active from January 11 at 20:00 UT (3:00 p.m. EST) through January 15 at 03:00 UT (10:00 p.m. EST on January 14).
During this period,the comet will appear closest to the sun on January 13 at 13:00 UT (8:00 a.m. EST), passing a mere 4.9 degrees from its center.This proximity makes it a prime target for observation, and SOHO’s near-live images and 24-hour time-lapse videos will allow viewers to follow the comet’s journey in real-time. You can access these visuals directly through SOHO’s near-live image feed or NOAA’s LASCO Coronagraph page.
SOHO’s Legacy of Comet Discoveries
SOHO has a remarkable track record when it comes to comet discoveries.As its launch, it has identified over 5,000 comets using its LASCO C3 imagery. One of its most notable captures was Comet Tsuchinshan-ATLAS in October, which captivated the public as it swept close to the sun.This latest observation of Comet G3 ATLAS adds to SOHO’s impressive legacy, further cementing its role as a vital tool for solar and comet research.
Why This Event matters
Comet G3 ATLAS is more than just a celestial spectacle; it provides valuable insights into the composition and behavior of comets. By studying its trajectory and interaction with the sun’s corona, scientists can better understand the dynamics of these icy visitors from the outer solar system. For amateur astronomers and space enthusiasts, it’s a chance to witness a rare event that highlights the beauty and complexity of our universe.
Stay Updated
As Comet G3 ATLAS continues its journey, any significant updates will be shared promptly. whether you’re a seasoned astronomer or simply curious about the cosmos, this event is a reminder of the wonders that lie beyond our planet. Keep an eye on the skies—and on SOHO’s live feeds—for a front-row seat to this extraordinary celestial show.
“SOHO has revolutionized our understanding of the sun and its surroundings, and its ability to capture comets like G3 ATLAS is a testament to its enduring value.”
For more updates on celestial events and space exploration, follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom.
Space Dialog: Bridging the Gap Between Earth and Beyond
In an era where technology is advancing at an unprecedented pace, space communication has emerged as a cornerstone of global connectivity. From enabling real-time data transmission to fostering international collaboration, the role of space communication in modern society cannot be overstated. Platforms like Facebook are at the forefront of this revolution, leveraging cutting-edge technology to bridge the gap between Earth and the cosmos.
The Evolution of Space Communication
Space communication has come a long way since the launch of the first artificial satellite,Sputnik,in 1957. Early systems relied on rudimentary technology, but today, we have complex networks of satellites that facilitate seamless communication across the globe. These advancements have not only transformed how we interact but have also opened up new possibilities for scientific research and exploration.
One of the most significant milestones in this field was the development of the Deep Space Network (DSN), which allows for communication with spacecraft millions of miles away.This network has been instrumental in missions to Mars, Jupiter, and beyond, providing scientists with invaluable data and insights.
The Role of Social Media in Space Communication
social media platforms like Facebook have played a pivotal role in democratizing access to space communication.By sharing updates, live streams, and educational content, these platforms have made space exploration more accessible to the general public. For instance, Facebook’s dedicated page for space communication serves as a hub for enthusiasts and professionals alike, fostering a sense of community and shared curiosity.
“Space communication is not just about technology; it’s about connecting people and ideas,” says a spokesperson from the space communication community. This sentiment is echoed by millions of users who engage with space-related content on social media, proving that the interest with the cosmos transcends borders and cultures.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the remarkable progress, space communication faces several challenges. Signal delays, data loss, and the high cost of maintaining satellite networks are just a few of the hurdles that need to be addressed. However, with the advent of quantum communication and artificial intelligence, the future looks promising.
Experts predict that the next decade will witness groundbreaking advancements in space communication, including the deployment of mega-constellations of satellites and the development of interplanetary internet. These innovations will not only enhance global connectivity but also pave the way for human colonization of other planets.
Conclusion
Space communication is more than just a technological marvel; it is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of knowlege. As we continue to explore the vast expanse of the universe, platforms like Facebook will play a crucial role in keeping us connected, informed, and inspired. The journey to the stars is just beginning, and the possibilities are truly limitless.
How has teh development of technologies like Starlink and the Deep Space network influenced the capabilities of space dialog in the 2000s to the present day?
F satellites and ground stations that enable seamless communication across vast distances. These advancements have not only enhanced our ability to explore space but have also revolutionized how we communicate on Earth.
Key Milestones in Space Communication
- 1957: Launch of Sputnik, the first artificial satellite, marking the beginning of space communication.
- 1962: Telstar 1, the first active communications satellite, enables the first live transatlantic television broadcast.
- 1969: Apollo 11 mission uses advanced communication systems to broadcast the first moon landing live to millions worldwide.
- 1980s-1990s: Development of geostationary satellites and the Global Positioning System (GPS), revolutionizing navigation and communication.
- 2000s-Present: Emergence of high-speed internet satellites (e.g., Starlink) and deep-space communication networks (e.g., NASA’s Deep Space Network).
These milestones highlight the rapid evolution of space communication, driven by technological innovation and the growing demand for global connectivity.
The Role of Social Media in Space Communication
Social media platforms like Facebook have become integral to space communication, providing a bridge between space agencies, scientists, and the public. These platforms enable real-time updates, live broadcasts of space missions, and interactive discussions, fostering greater public engagement with space exploration.
Examples of Social Media in Action
- Live Broadcasts: Platforms like Facebook and YouTube have hosted live streams of historic events, such as rocket launches, spacewalks, and planetary landings.
- Public Engagement: Space agencies use social media to share updates, images, and videos, making space exploration accessible to a global audience.
- Educational outreach: Social media campaigns and interactive content help educate the public about space science and technology.
By leveraging the power of social media, space communication has become more inclusive and interactive, inspiring a new generation of space enthusiasts.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its advancements,space communication faces several challenges,including signal delays,data transmission limitations,and the need for robust infrastructure. Addressing these challenges requires continued innovation and collaboration among space agencies, private companies, and researchers.
Future Trends in Space Communication
- Quantum Communication: Leveraging quantum mechanics to enable secure and faster data transmission over long distances.
- Laser Communication: Using laser beams to transmit data at higher speeds and with greater efficiency then traditional radio waves.
- Interplanetary Internet: Developing communication networks that can support future missions to mars and beyond.
As we look to the future, space communication will continue to play a pivotal role in advancing our understanding of the universe and connecting humanity across the cosmos.
Conclusion
Space communication is a testament to human ingenuity and our desire to explore the unknown. From the early days of Sputnik to the cutting-edge technologies of today, it has transformed how we connect with each other and the universe. As we continue to push the boundaries of space exploration, platforms like Facebook will remain essential in bridging the gap between Earth and beyond, inspiring curiosity and fostering global collaboration.



