Israel Expands Control in Syria, Citing Security Concerns
Table of Contents
- 1. Israel Expands Control in Syria, Citing Security Concerns
- 2. Escalation of Airstrikes and Ground Operations
- 3. Concerns Over Chemical Weapons
- 4. Regional Tensions Intensify
- 5. Israel Expands Control in Golan Heights, Sparking Controversy
- 6. The Golan Heights: A contested Territory
- 7. Israel and syria: Post-Assad Tensions
Table of Contents
- 1. Israel Expands Control in Syria, Citing Security Concerns
- 2. Escalation of Airstrikes and Ground Operations
- 3. Concerns Over Chemical Weapons
- 4. Regional Tensions Intensify
- 5. Israel Expands Control in Golan Heights, Sparking Controversy
- 6. The Golan Heights: A contested Territory
- 7. Israel and syria: Post-Assad Tensions
Tensions have escalated in the region as Israel has widened its military presence within Syria, launching airstrikes against Syrian military bases and deploying troops into the demilitarized buffer zone along the Golan Heights. This intervention marks a significant expansion of Israeli control over Syrian territory. While Israel justifies these actions as necessary measures to protect its citizens, critics argue that it exploits the current political instability in Syria to weaken a longstanding adversary.
Escalation of Airstrikes and Ground Operations
According to the UK-based Syrian Observatory for Human Rights (SOHR), the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) have conducted over 310 attacks since the fall of the Assad regime on December 8. These strikes, stretching from Aleppo in the north to Damascus in the south, have targeted key Syrian army facilities, including weapons depots, ammunition storage, airports, naval bases, and research centers.
rami Abdul Rahman, the founder of SOHR, asserts that these attacks have effectively crippled the Syrian army’s capabilities.Israel maintains that its actions aim to prevent weapons from falling into the hands of extremist groups as Syria enters a post-Assad era.
Concerns Over Chemical Weapons
israel’s intervention is further complicated by concerns over Syria’s stockpile of chemical weapons.While the exact location and quantity of these weapons remain unknown, it is widely believed that former President Bashar al-Assad possessed them.
Adding to the international alarm, the UN chemical watchdog issued a warning to Syrian authorities on December 9, urging them to secure all chemical weapons under their control. Ake Sellstrom, a former UN weapons inspector in Syria and currently an associate professor of histology at Umea University in Sweden, suggests that Israel’s airstrikes were specifically targeting Syria’s chemical weapons infrastructure.

Regional Tensions Intensify
The situation in Syria remains highly volatile, with Israel’s aggressive actions further intensifying regional tensions. As the country navigates a delicate post-conflict transition, the international community faces a complex challenge in ensuring stability and preventing the proliferation of deadly weapons.

BBC news Indonesia present on WhatsApp.
Be the first to get news, investigations and in-depth coverage from BBC News Indonesia, directly on your WhatsApp.
Israel Expands Control in Golan Heights, Sparking Controversy
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu announced that Israeli forces have taken control of the demilitarized buffer zone in the Golan Heights, effectively expanding Israel’s territorial control in the region. Netanyahu characterized this move as a “temporary defensive position” until a lasting solution is reached. Professor Gilbert Achcar of SOAS University London, however, offered a different outlook. “Israel says that it wants to prevent attacks like the Hamas attack on October 7 from the Syrian side,” he explained.”But this is an possibility to move forward and stop other forces from moving closer to the borders of the occupation zone.”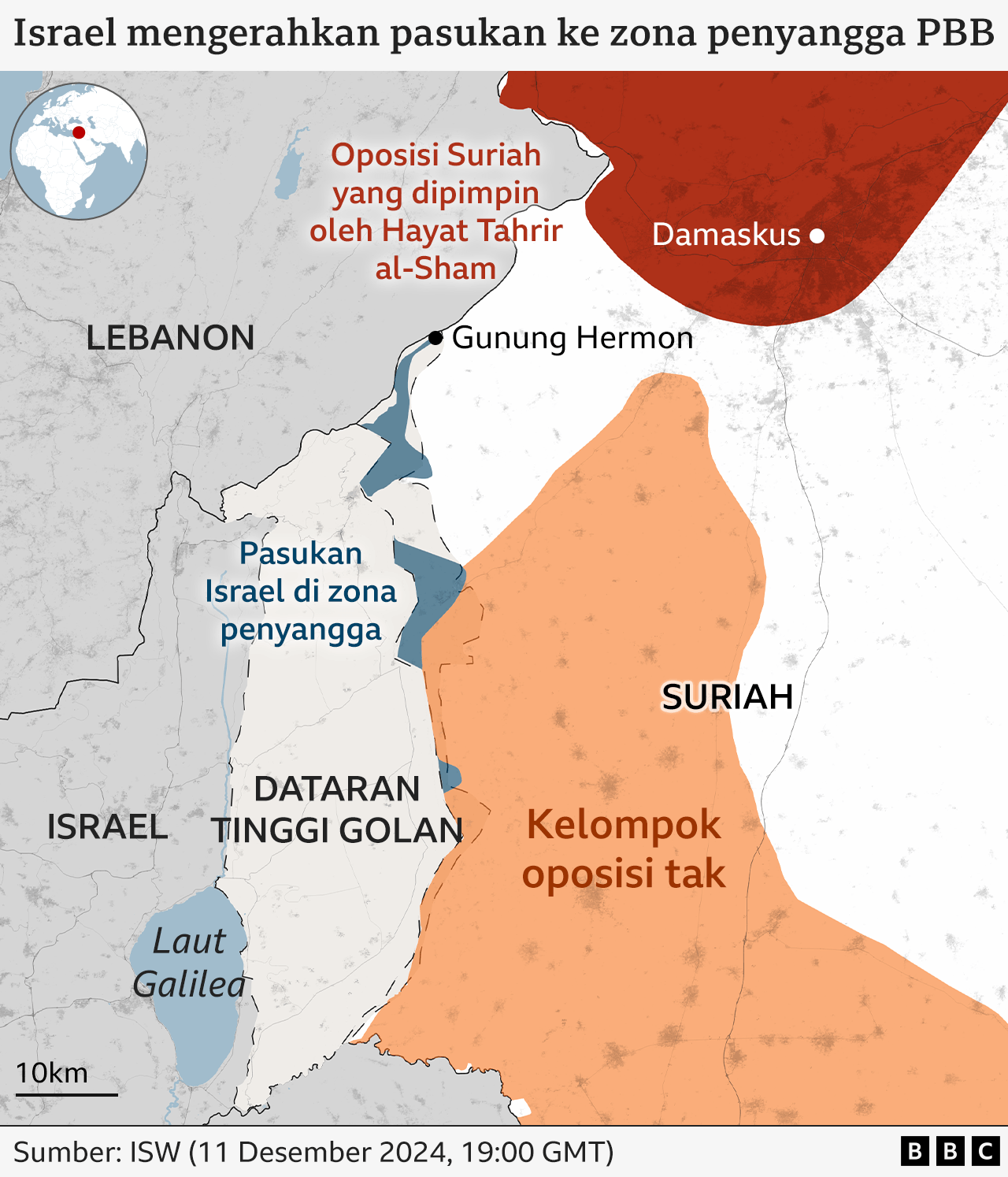 This expansion has drawn strong criticism from Arab countries. Egypt’s foreign Ministry condemned the action as “occupation of Syrian territory and a violation of the 1974 Liberation Agreement.”
Reports circulating within Syria suggest that Israel’s presence extends beyond the buffer zone,possibly reaching within 25 km of Damascus. While Israeli military sources have denied these claims, the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) acknowledged for the first time that their troops are operating outside the demilitarized zone.IDF spokesman Nadav Shoshani insisted, though, that the Israeli offensive had not advanced further.
This expansion has drawn strong criticism from Arab countries. Egypt’s foreign Ministry condemned the action as “occupation of Syrian territory and a violation of the 1974 Liberation Agreement.”
Reports circulating within Syria suggest that Israel’s presence extends beyond the buffer zone,possibly reaching within 25 km of Damascus. While Israeli military sources have denied these claims, the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) acknowledged for the first time that their troops are operating outside the demilitarized zone.IDF spokesman Nadav Shoshani insisted, though, that the Israeli offensive had not advanced further.
The Golan Heights: A contested Territory
The Golan Heights, a rocky plateau in southwestern syria, has been under Israeli occupation for over five decades. During the 1967 Middle East War, Syria used the Heights to launch attacks against Israel. Israel successfully repelled these attacks, capturing approximately 1,200 square kilometers of territory, which subsequently came under military rule. Syria attempted to reclaim the Golan Heights during the 1973 Yom Kippur War but was unsuccessful. A ceasefire agreement was reached in 1974, with UN observer forces stationed along the demarcation line. Despite international condemnation, Israel annexed the territory in 1981.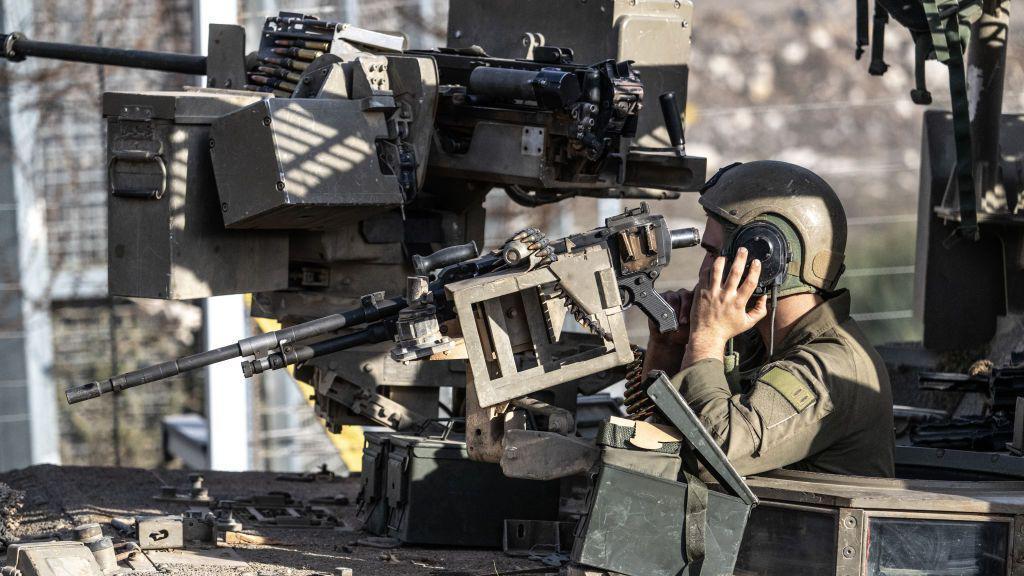 Syria’s future remains uncertain, and Israel’s concerns about its security in the region are deeply rooted in history.
The Golan Heights, captured by Israel from Syria in 1967, has become a flashpoint in the ongoing tensions between the two countries. While israel insists its presence in the region is a necessary security measure, Syria demands its full withdrawal as a prerequisite for peace.
Adding to the complexity, more than 20,000 Israeli settlers now reside in the Golan Heights, living alongside a similar number of Syrian Druze who remained in the area after the 1967 conflict. These settlements, considered illegal under international law by many, further solidify Israel’s presence in the region.
A Delicate Balance
Syria’s future remains uncertain, and Israel’s concerns about its security in the region are deeply rooted in history.
The Golan Heights, captured by Israel from Syria in 1967, has become a flashpoint in the ongoing tensions between the two countries. While israel insists its presence in the region is a necessary security measure, Syria demands its full withdrawal as a prerequisite for peace.
Adding to the complexity, more than 20,000 Israeli settlers now reside in the Golan Heights, living alongside a similar number of Syrian Druze who remained in the area after the 1967 conflict. These settlements, considered illegal under international law by many, further solidify Israel’s presence in the region.
A Delicate Balance
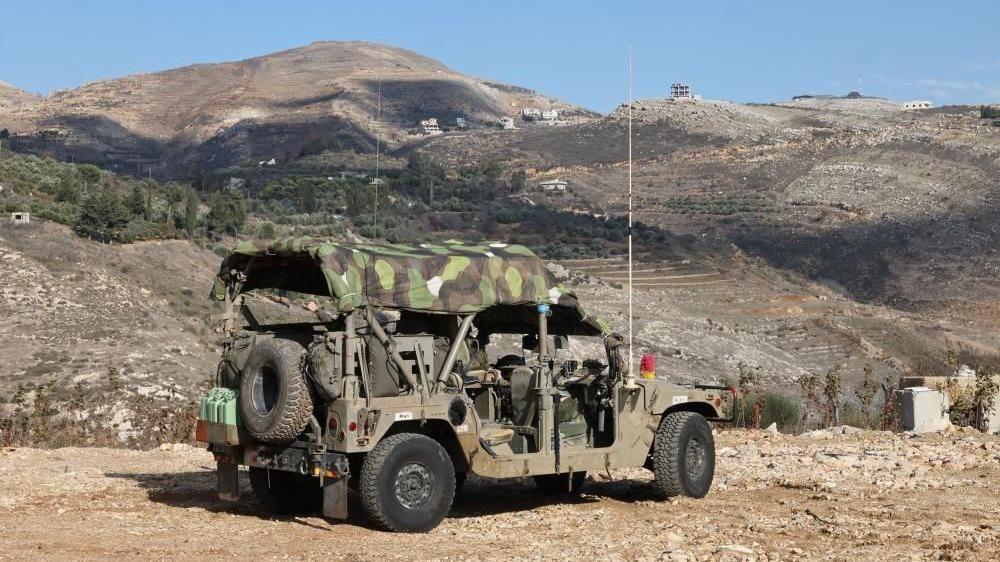 Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu acknowledges the sensitive nature of the situation, stating that Israel’s presence in the Golan Heights buffer zone is temporary. He expressed a desire for peaceful relations with a future Syrian government, but also emphasized Israel’s commitment to defending its borders if needed.
“If we can build neighborly relations and peaceful relations with the new powers that are emerging in Syria, that is our wish,” Netanyahu said. “But if not, we will do whatever it takes to defend the State of Israel and Israel’s borders.”
A History of Occupation and Airstrikes
Dr. HA Hellyer, a Middle East expert at the Royal United services Institute, noted that Israel’s approach is not unprecedented.
“What Israel has in mind is the possibility of an attack on the Golan by forces in Syria and to ensure that there is no such possibility, Israel has gone further,” Hellyer said. He added, “However, Israel previously occupied territory in the Golan Heights as a security measure and then fortified it. Israel may do so again.”
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu acknowledges the sensitive nature of the situation, stating that Israel’s presence in the Golan Heights buffer zone is temporary. He expressed a desire for peaceful relations with a future Syrian government, but also emphasized Israel’s commitment to defending its borders if needed.
“If we can build neighborly relations and peaceful relations with the new powers that are emerging in Syria, that is our wish,” Netanyahu said. “But if not, we will do whatever it takes to defend the State of Israel and Israel’s borders.”
A History of Occupation and Airstrikes
Dr. HA Hellyer, a Middle East expert at the Royal United services Institute, noted that Israel’s approach is not unprecedented.
“What Israel has in mind is the possibility of an attack on the Golan by forces in Syria and to ensure that there is no such possibility, Israel has gone further,” Hellyer said. He added, “However, Israel previously occupied territory in the Golan Heights as a security measure and then fortified it. Israel may do so again.”
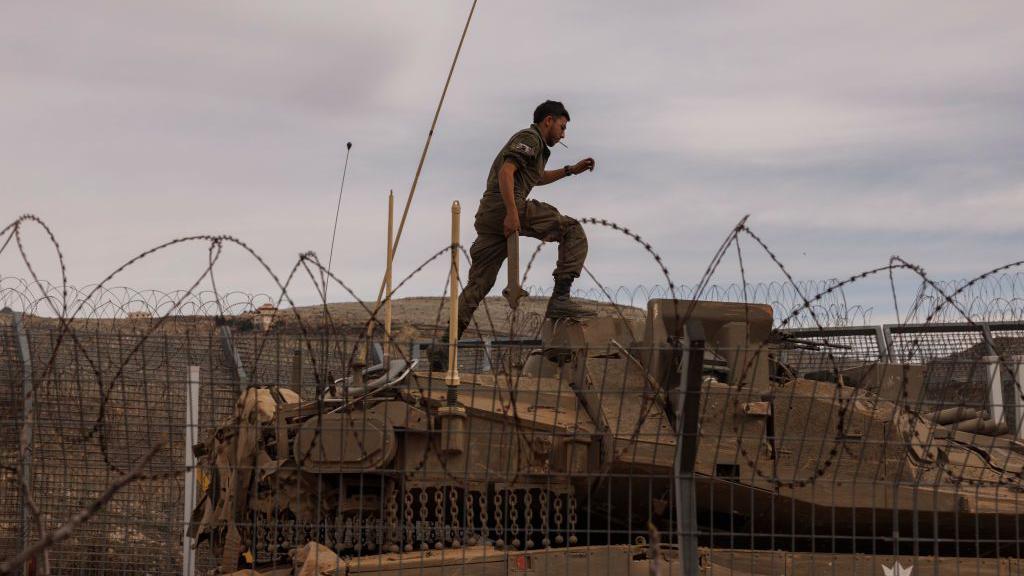 Israel has also carried out hundreds of airstrikes on Syrian territory, citing the need to prevent advanced weaponry from falling into the hands of groups hostile to Israel.
“That is why we attack strategic weapons systems such as, for example, remaining chemical weapons or long-range missiles and rockets so that they do not fall into the hands of extremists,” stated israeli Foreign Minister Gideon Saar.
However, Professor Achcar criticizes the broad scope of these strikes.
“Chemical weapons are not widespread in Syria. they are only present in two or three places. But with more than 300 airstrikes, you are trying to make the country much weaker,” Achcar said.
He added that Israel views the current Syrian government as the “devil they know” and is wary of potential power vacuums that could lead to the rise of factions hostile to Israel’s interests.
“They expect Syria to be divided between warring factions, like Libya, and fear the emergence of factions hostile to Israel.They want to prevent such factions from using the Syrian army’s weapons against them.”
Israel has also carried out hundreds of airstrikes on Syrian territory, citing the need to prevent advanced weaponry from falling into the hands of groups hostile to Israel.
“That is why we attack strategic weapons systems such as, for example, remaining chemical weapons or long-range missiles and rockets so that they do not fall into the hands of extremists,” stated israeli Foreign Minister Gideon Saar.
However, Professor Achcar criticizes the broad scope of these strikes.
“Chemical weapons are not widespread in Syria. they are only present in two or three places. But with more than 300 airstrikes, you are trying to make the country much weaker,” Achcar said.
He added that Israel views the current Syrian government as the “devil they know” and is wary of potential power vacuums that could lead to the rise of factions hostile to Israel’s interests.
“They expect Syria to be divided between warring factions, like Libya, and fear the emergence of factions hostile to Israel.They want to prevent such factions from using the Syrian army’s weapons against them.”
Israel and syria: Post-Assad Tensions
The geopolitical landscape of the Middle east has been in a constant state of flux. The fall of Bashar al-Assad’s regime in Syria has created a power vacuum, leading to increased tensions and instability in the region. In particular, Israel’s actions towards syria have garnered international attention, raising questions about the motivations behind these maneuvers.
Israel has long viewed Syria as a potential threat due to its alliance with Iran and the presence of Hezbollah within its borders. These factors have contributed to a history of conflict and mistrust between the two nations. While Assad’s rule presented a familiar adversary, his potential downfall created uncertainty and new challenges for Israel’s security calculus.
With the Syrian government weakened, Israel has intensified its military operations against targets within Syrian territory. These strikes, often targeting Iranian-backed militias and suspected weapons shipments, highlight Israel’s determination to prevent any perceived threat to its national security.
The international community has expressed concerns over the escalating violence in Syria, calling for restraint and dialog. However, the complexities of the Syrian conflict and the competing interests of regional powers make finding a peaceful solution a daunting task.
As the situation in Syria continues to evolve, the international community must prioritize diplomacy and seek solutions that address the underlying issues driving the conflict. The future of the region hangs in the balance, and finding a path towards stability is crucial for the well-being of all involved.
This appears too be the beginning of a news article about Israel’s military presence in the Golan Heights. Here’s a breakdown of the key points and some potential directions the article might take:
**Key Points:**
* **Expansion of Israeli Military Presence:** Israel has moved troops further into Syria, beyond the established buffer zone, reportedly within 25 km of Damascus.
* **Arab criticism:** Arab countries, especially Egypt, have strongly condemned the move as a violation of Syrian sovereignty and the 1974 Liberation Agreement.
* **Golan Heights Dispute:** The article highlights the Golan Heights, captured by Israel from Syria in 1967, as a central point of contention.
* **Israeli Justification:** Israel asserts that its actions are necessary for security,citing potential threats from Syria. Prime Minister Netanyahu expresses a desire for peace but emphasizes israel’s right to defend itself.
* **Ancient Context:** The article mentions past israeli occupation of the Golan Heights and the establishment of settlements there, further complicating the situation.
**Possible Directions:**
* **In-Depth Analysis of Security Concerns:** Exploring israel’s specific security concerns. What threats does it perceive from Syria? Are thes threats credible?
* **Reactions from Syria and International Community:** How has Syria officially responded to the Israeli incursion? What are the reactions of other world powers? Is there any international condemnation or pressure on Israel?
* **Future Outlook:** How might this situation escalate? What are the prospects for a peaceful resolution?
* **impact on Settlers and Syrian Population:** How are Israeli settlers in the Golan Heights reacting? What are the implications for the Syrian Druze population living in the region?
* **Legal Implications:** The article mentions the illegality of settlements under international law. Coudl this latest move further complicate any potential peace agreement?
* **Analysis of Political Dynamics:** How do domestic politics in Israel, syria, and other regional players influence the situation?
Let me know if you have any specific aspects of the article you’d like to explore further.
This is a great start to an informative article about the complex relationship between Israel and Syria. The piece effectively highlights key points of tension, including:
* **Territorial Disputes:** The annexation of the Golan Heights and the presence of Israeli settlements are major sticking points.
* **Security Concerns:** Israel’s perception of threats from Syria,Iran,and Hezbollah drives its actions.
* **Airstrikes and Military Intervention:** israel’s use of force within Syrian territory is controversial and raises questions about its motives and impact.
* **Uncertainty about Syria’s Future:** The potential collapse of the Assad regime and the rise of new power structures raise further concerns for Israel.
Here are some suggestions to enhance the article:
**1.Expand on Ancient context:**
* Provide more background on the history of conflict between Israel and Syria, including significant events like the 1967 Six-Day War and the 1973 Yom Kippur War.
* Mention past peace negotiations and attempts at dialog.
**2.Explore Multiple Perspectives:**
* Include more voices and perspectives from:
* Syrian citizens and refugees
* experts on international law and human rights
* Representatives from other regional players like Iran, Lebanon, and Russia
**3. Address International implications:**
* Discuss the role of international organizations like the United Nations in mediating the conflict.
* Analyse how the situation in Syria affects regional stability and the global balance of power.
**4.Analyze Potential Scenarios:**
* Explore different possible outcomes for the Syrian conflict and their implications for Israel. For example:
* A fragmented Syria with multiple power centers
* The rise of extremist groups
* A restored Assad regime
**5. Conclude with a Thought-Provoking Statement:** Leave the reader with something to think about regarding the challenges and potential pathways to peace in the region.
By incorporating these suggestions, you can create a extensive and insightful article that sheds light on the multifaceted Israel-Syria dynamic.


