A new analysis has shown concern that Elon Musk Space Company Space X Launched from California last week by The rocket A hole has probably been created in the Earth’s ionosphere.
The Falcon 9 rocket, launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on July 19, likely punched a hole in the ionosphere, the review said.
The ionosphere, or sphere, is a layer around the fluid Earth that contains the fourth type of plasma of matter, where a sea of electrically charged particles floats at an altitude of about 80 to 650 kilometers.
While reviewing the footage of the rocket launch, Jeff Baumgardner, an astrophysicist at Boston University in the United States, said, “It is quite possible that the launch created a hole in the ionosphere.”
He told US website spaceweather.com: ‘This is a well-studied phenomenon when rockets are releasing heat from their engines 200 to 300 kilometers above the Earth’s surface.’
Previous research has shown that with the increasing number of rocket launches around the world, holes in the ionosphere are becoming more common, making it possible to transmit radio communications to Earth.
The ionosphere is also dynamic and expands and contracts based on solar conditions. It is classified into sub-regions known as D, E and F. This classification is based on a layer’s ability to absorb wavelengths of solar radiation.
Studies show that flares from rockets and their engines can change the process by which charged particles form in this layer around Earth.
Rocket motions can also create large disturbances in the ionosphere that travel faster than the speed of sound and create shock waves in the layers.
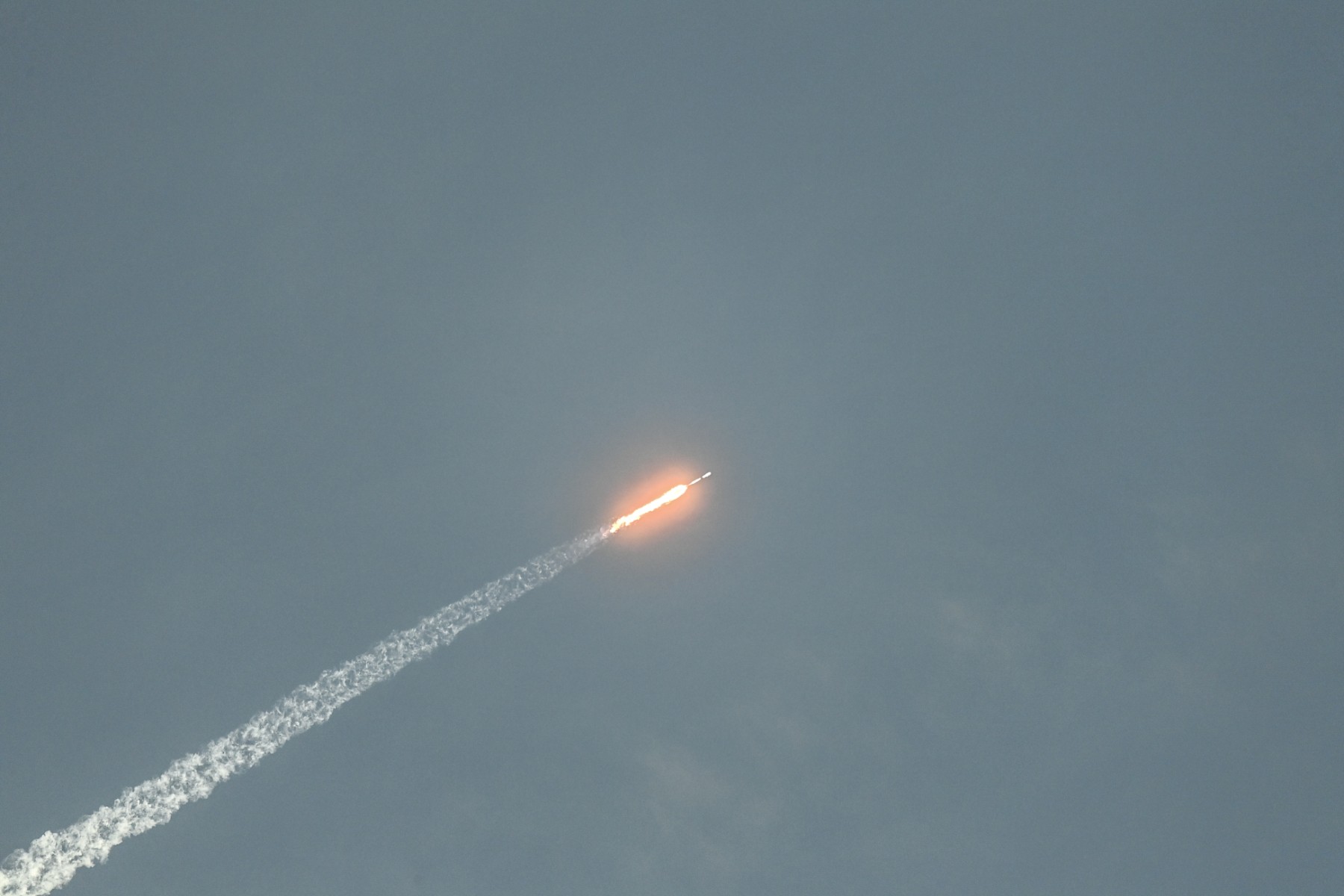

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket was also launched from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on February 27, 2023 (AFP)
Research shows that as fast-moving rockets move toward the edge of space, they release water and carbon dioxide that can reduce the ionization process by two-thirds.
They particularly affect the F layer of the ionosphere, the subregions of which have the highest electron density.
This section contains related reference points (Related Nodes field).
Holes in the ionosphere caused by rockets are identified by their red color because the oxygen ions in this layer react with electrons from the rocket emission.
Experts said it produces light at the same wavelength as the red aurora.
Previous rockets launched by SpaceX also created holes in the ionosphere.
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launched in August 2017 produced massive circular shock acoustic waves in the ionosphere about five minutes after carrying Taiwan’s Formosat 5 satellite.
As a rocket carrying a payload launches directly above the ionosphere, it creates a circular shock wave on the crust.
A study of the phenomenon, published in the journal Space Weather, found that a large hole formed in the ionosphere about 10 minutes into the flight.
The scientists wrote in the study: ‘The rocket plume later produced an ionospheric plasma hole of mass 900 km in diameter with a TET reduction of 10 to 70 percent compared to reference days.’
#hole #Earths #ionosphere #feared #SpaceX #rocket
What are the potential consequences of rocket launches puncturing the ionosphere?
## SpaceX Rocket Punching Holes in Earth’s Ionosphere?
**(News Anchor)** Welcome back. SpaceX, the company behind revolutionary rockets like the Falcon 9, is in the headlines again, this time not for its ambitious space exploration goals, but for potentially causing disruptions to Earth’s atmosphere. Joining us to shed light on this unusual phenomenon is Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in astrophysics. Dr. Carter, thank you for joining us.
**(Dr. Carter)** It’s a pleasure to be here.
**(News Anchor)** So, this news about SpaceX rockets and the ionosphere, can you explain what exactly is happening?
**(Dr. Carter)** Sure. The ionosphere is this vital layer in Earth’s upper atmosphere, filled with charged particles.
**(News Anchor)** Right, and it plays a role in radio communications, right?
**(Dr. Carter)** Exactly. Now, when a rocket like the Falcon 9 launches and blasts through this layer, the intense heat from its engines can temporarily disrupt the delicate balance of charged particles, creating what some scientists call a “hole.”
**(News Anchor)** A hole? Doesn’t sound very good.
**(Dr. Carter)** Well, it’s a temporary disruption. Think of it like a ripple spreading through a pond when you throw a stone in. The ionosphere is dynamic and recovers, but these disturbances are becoming more frequent with increasing rocket launches.
**(News Anchor)**
So, what are the potential implications? Could this affect our communication systems?
**(Dr. Carter)** There is a potential for interference with radio communications, especially long-distance ones. However, the extent of the impact is still being studied. What’s crucial is that we understand the long-term consequences of this phenomenon as space exploration intensifies.
**(News Anchor)** Dr. Carter, thank you for clarifying this complex issue for us. It certainly highlights the unseen impacts of our growing spacefaring endeavours.