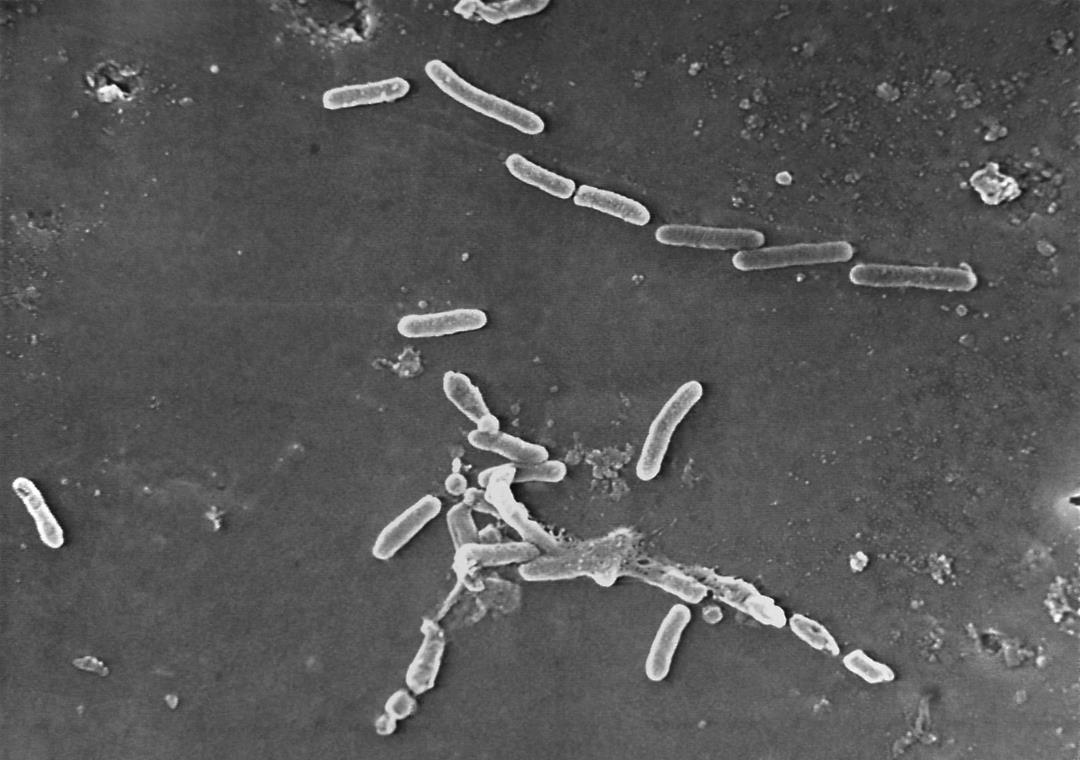
Two dogs in New Jersey have recently tested positive for a drug-resistant strain of bacteria that caused a fatal outbreak linked to eyedrops used by people. The CDC investigator revealed that the bacteria found in the dogs, known as carbapenemase-producing carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, is closely related genetically to the germs responsible for the illnesses of 81 individuals across 18 states last year. Shockingly, 14 patients lost their vision, and four fatalities occurred as a result of this outbreak.
The implications of this discovery are cause for concern among health officials. The germs that produce carbapenemase have the ability to break down carbapenem antibiotics, which are typically reserved for infections resistant to other treatments. The spread of the resistance genes to other pathogens is also a worrisome prospect. Swabs taken from the dogs were sent for further analysis to a laboratory in Pennsylvania. As the laboratory noticed unusual signs of resistance in the germs, they uploaded the strain’s genetic sequence to a national database. This prompted the CDC and state health authorities to initiate an investigation.
These findings led the FDA to issue warnings to consumers regarding the contaminated eyedrops and request recalls. It is a critical reminder of the importance of safety in medical products and the potential dangers when hygiene protocols are not followed thoroughly.
The discovery of a drug-resistant strain of bacteria in dogs raises several questions regarding the potential spread of this resistance. Given the close genetic relation to the strain responsible for last year’s outbreak in humans, there is a genuine concern regarding the bacteria spreading beyond the canine population. The introduction of this bacteria into the United States via artificial tears serves as a stark reminder that resistance can easily spread and become a significant public health threat.
While the focus has been on the connection between the eyedrops and the outbreak, it is imperative to explore broader implications and future trends regarding drug-resistant bacteria. The emergence of such strains highlights the ongoing battle once morest antibiotic resistance and the need for stringent measures to prevent its spread.
In light of these findings, it is crucial for the medical community, government agencies, and pharmaceutical companies to collaborate on research and development efforts. Investment in alternative treatments, such as bacteriophage therapy, may prove to be an effective avenue to combat drug-resistant bacteria. Bacteriophages are viruses that can target and destroy specific bacteria, offering a potential solution to the growing threat of antibiotic resistance.
This recent incident also underscores the significance of public awareness and education on proper hygiene practices. It is vital for individuals to understand the importance of responsible antibiotic use and the potential consequences of improper use. Additionally, healthcare professionals must remain vigilant in adhering to hygiene protocols and promptly identifying drug-resistant infections. This includes implementing robust surveillance systems to detect outbreaks early on, allowing for swift intervention and containment.
Moreover, this discovery raises questions regarding the overall effectiveness of current antibiotics and the need for continued research and development in the field. The era of widespread antibiotic use and its effectiveness may be coming to an end, necessitating the exploration of alternative treatments and the development of new antibiotics targeting drug-resistant strains.
In conclusion, the findings regarding the drug-resistant bacteria in dogs highlight the broader issue of antibiotic resistance and the need for proactive measures to address this growing public health concern. Collaboration between various stakeholders, investment in alternative treatments, and improved public education are necessary to combat the spread of drug-resistant strains. It is crucial to remain vigilant and proactive in mitigating the risks associated with antibiotic resistance, shaping the future of healthcare and the industry.