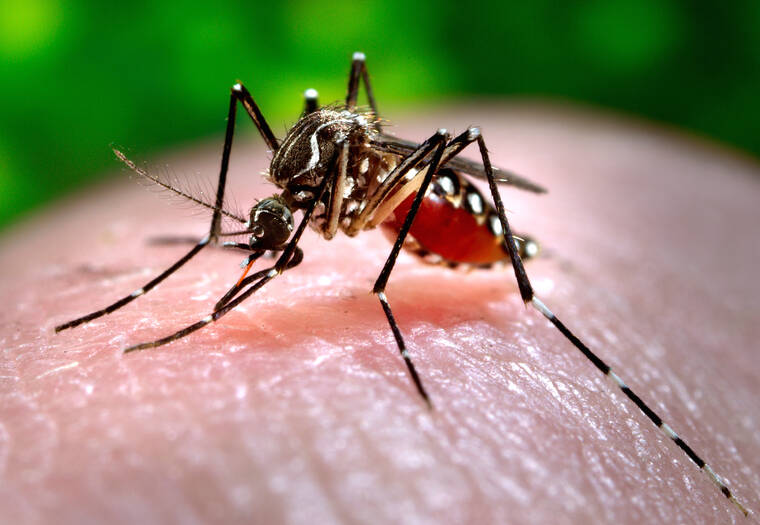
Haleiwa Reports Another Case of Travel-Related Dengue
Yet another case of travel-related dengue has been confirmed in Haleiwa, according to the state Health Department. This follows a similar case reported on Oahu earlier this week. While the exact location of the first case was not disclosed, the Health Department has voiced concerns regarding the high number of visitors in Haleiwa Harbor and the presence of the Aedes albopictus mosquito, a known carrier of the dengue virus.
The Department of Health has already taken steps to address this issue, with vector control teams treating the affected area and monitoring it closely. As part of their efforts, they are also urging the public, especially those in Haleiwa, to take extra precautions in protecting themselves from mosquito bites by using repellent or wearing protective clothing. Moreover, they are requesting residents to help prevent mosquitoes from breeding by getting rid of standing water in containers and other possible breeding grounds.
Matt Kurano, the head of the Department of Health’s vector control branch, emphasized the importance of cooperation from the public in tackling this issue. During a news briefing, he stated, “The smallest things that people can do, like getting rid of standing water in buckets and boat covers, can make a significant difference in preventing the spread of dengue.”
Dengue is a viral infection that spreads through the bite of infected mosquitoes. While Hawaii is home to mosquitoes capable of carrying the dengue virus, the disease itself is not endemic in the state. The symptoms of dengue include fever, nausea, vomiting, rash, and body aches, which typically last for regarding a week.
As of now, there have been a total of ten travel-related dengue cases reported in Hawaii since January 2023. Out of these cases, five individuals had traveled to Central or South America, while the remaining five had visited Asia.
To learn more regarding preventing mosquito-borne diseases, you can visit the Department of Health’s website.
Analysis: Examining the Implications
The recent cases of travel-related dengue in Haleiwa and Oahu serve as a reminder of the ongoing battle once morest insect-borne diseases. With the increasing interconnectedness of our world through travel and trade, infectious diseases, such as dengue, can quickly spread to new areas. The presence of highly dense populations of the Aedes albopictus mosquito in Haleiwa only compounds the risk of dengue transmission.
These cases highlight the importance of timely and focused vector control efforts to mitigate the spread of mosquito-borne diseases. It is encouraging to see the Department of Health taking swift action by treating the affected areas and engaging with the local community. However, it is crucial for individuals to take personal responsibility and adopt preventive measures, such as using mosquito repellents and eliminating mosquito breeding sites, in order to effectively combat the spread of dengue.
While dengue is not currently endemic in Hawaii, the presence of the disease-carrying mosquitoes reminds us of the potential threats posed by climate change and increased global travel. As temperatures rise and suitable habitats expand, these mosquitoes might establish breeding populations, leading to the sustained transmission of dengue and other mosquito-borne illnesses in the future.
As we analyze the potential future trends related to dengue and other similar diseases, it is important to consider emerging technologies and strategies that can aid in their prevention and control. Novel approaches, such as genetically modified mosquitoes or innovative vector control methods, may play a significant role in reducing the impact of these diseases. Additionally, ongoing research into vaccines and antiviral treatments for dengue might contribute to better management and mitigation efforts.
To ensure effective control and prevention of mosquito-borne diseases, it is essential for governments, healthcare organizations, and communities to collaborate and share information. Rapid response protocols and robust surveillance systems should be in place to detect and contain outbreaks swiftly. Education and public awareness campaigns also play a critical role in ensuring individuals have the necessary knowledge to protect themselves and their communities.
As we continue to navigate a world affected by infectious diseases, it is imperative that individuals, society, and industries remain vigilant. By understanding the implications of these outbreaks and actively working towards prevention and control, we can strive for a healthier and safer future for generations to come.