A Shocking Case of Tapeworm Larvae in the Brain
In a surprising medical discovery, a man in the US was found to have tapeworm larvae in his brain, leading to frequent migraines. This bizarre ailment was likely linked to his consumption of undercooked bacon. The 52-year-old patient sought medical attention when his migraines worsened and his usual medication ceased to have any effect.
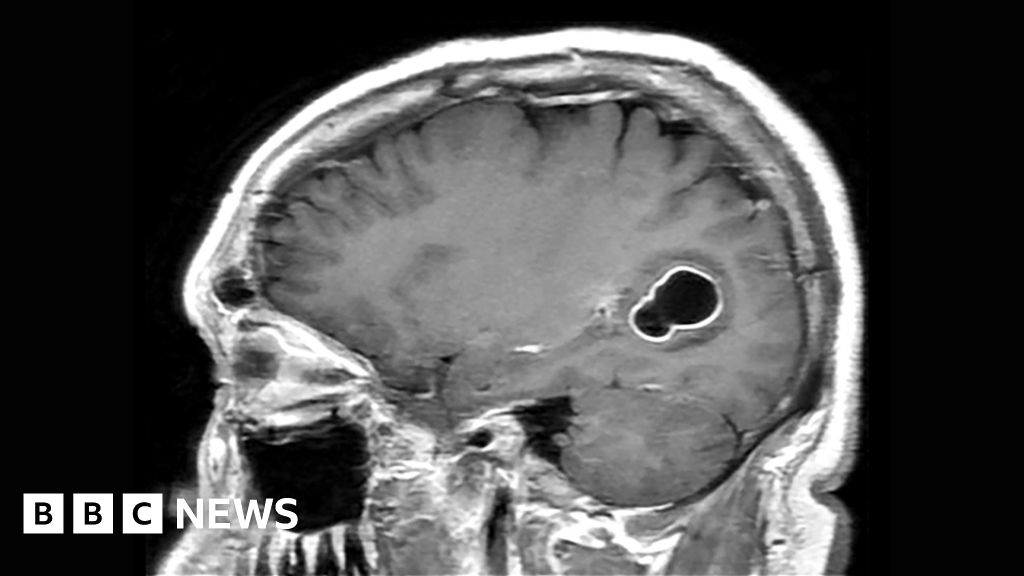
Upon conducting scans, doctors discovered tapeworm larval cysts in his brain, a condition known as cysticercosis. This infection is caused by the larvae of the parasite Taenia solium, commonly referred to as pork tapeworm. The doctors attributed the man’s condition to improper handwashing, speculating that he contracted the tapeworm by consuming undercooked pork.
Cysticercosis manifests as the development of cysts (known as cysticerci) in the brain due to the larvae of T.solium. Interestingly, individuals with tapeworms can infect themselves with tapeworm eggs, a process called autoinfection. These eggs can be excreted in feces and potentially infect others within the same household.
It is important to note that directly consuming undercooked pork cannot lead to cysticercosis. In this particular case, the doctors attributed the infection to the patient’s preference for undercooked pork, reinforcing the link to his eating habits.
Fortunately, the patient responded well to anti-parasitic and anti-inflammatory treatment, making a complete recovery from this rare condition. However, this case highlights the importance of proper handwashing and food safety practices to prevent infections such as cysticercosis.
Analyzing the Implications
The emergence of this unusual case raises several intriguing implications and connections to current trends in healthcare and food safety. Firstly, it underscores the significance of hygiene and proper handwashing practices in preventing the transmission of diseases. In a world grappling with the COVID-19 pandemic, the importance of personal hygiene cannot be emphasized enough. The tapeworm infection serves as a stark reminder that neglecting such practices can have serious health consequences.
Furthermore, this case demonstrates the potential dangers associated with consuming undercooked meat. While public health measures and thorough testing largely prevent cysticercosis in countries like the US and UK, it remains a significant concern in regions with poor food safety practices, particularly in rural areas of Latin America, Asia, and Africa. As global travel and cultural exchange continue to grow, it is crucial for individuals to be aware of the risks associated with consuming undercooked meat and to prioritize safe cooking practices.
Looking ahead, it is important for the medical community to remain vigilant in tracking and managing unusual infections. Though cysticercosis is considered rare outside of classic exposures or travel, this case presents a potential shift in the prevalence of infected pork in the United States. It raises questions regarding the effectiveness of current control measures and the need for further research and understanding of tapeworm infections.
Recommendations for the Industry
In light of this case, it is essential for both healthcare professionals and the food industry to collaborate and educate individuals on the risks associated with undercooked meat consumption. This can be achieved through public awareness campaigns, emphasizing the importance of proper cooking techniques and the potential consequences of neglecting food safety practices.
Additionally, healthcare providers should consider incorporating questions regarding dietary habits and potential exposure to tapeworm infections during routine medical evaluations. Early detection and prompt intervention are vital in managing such conditions effectively.
As for the food industry, continued adherence to rigorous testing and quality control measures is of utmost importance. Regular inspections, stringent hygiene protocols, and comprehensive education for food handlers can help minimize the risks associated with contaminated meat products. This commitment to ensuring food safety not only protects consumers but also supports the industry’s reputation and the overall well-being of society.
In conclusion, the alarming case of tapeworm larvae in the brain serves as a cautionary tale of the potential consequences of neglecting proper handwashing and safe cooking practices. It highlights the importance of personal hygiene, rigorous food safety standards, and continuous research to safeguard public health. By remaining vigilant and taking proactive measures, both individuals and the food industry can contribute to a safer and healthier future.