In a recent review published in the journal Current Opinion in Chemical Biologyresearchers discussed the latest advances in the antimicrobial properties of human milk.
 Revue : Recent advances on the antimicrobial activity of human milk oligosaccharides. Image credit: HTeam / Shutterstock
Revue : Recent advances on the antimicrobial activity of human milk oligosaccharides. Image credit: HTeam / Shutterstock
Wallpaper
HMOs vary in composition
The gut microbiome of non-breastfed newborns is different from that of breastfed infants. Formula-fed infants show greater microbiota diversity, while those who are breastfed have probiotic-dominated microbiota Bifidobacterium. In the later stages of lactation, Bacteroides dominate the microbiome.
Antibacterial activity of HMOs
Streptococcus agalactiaea group B Streptococcus
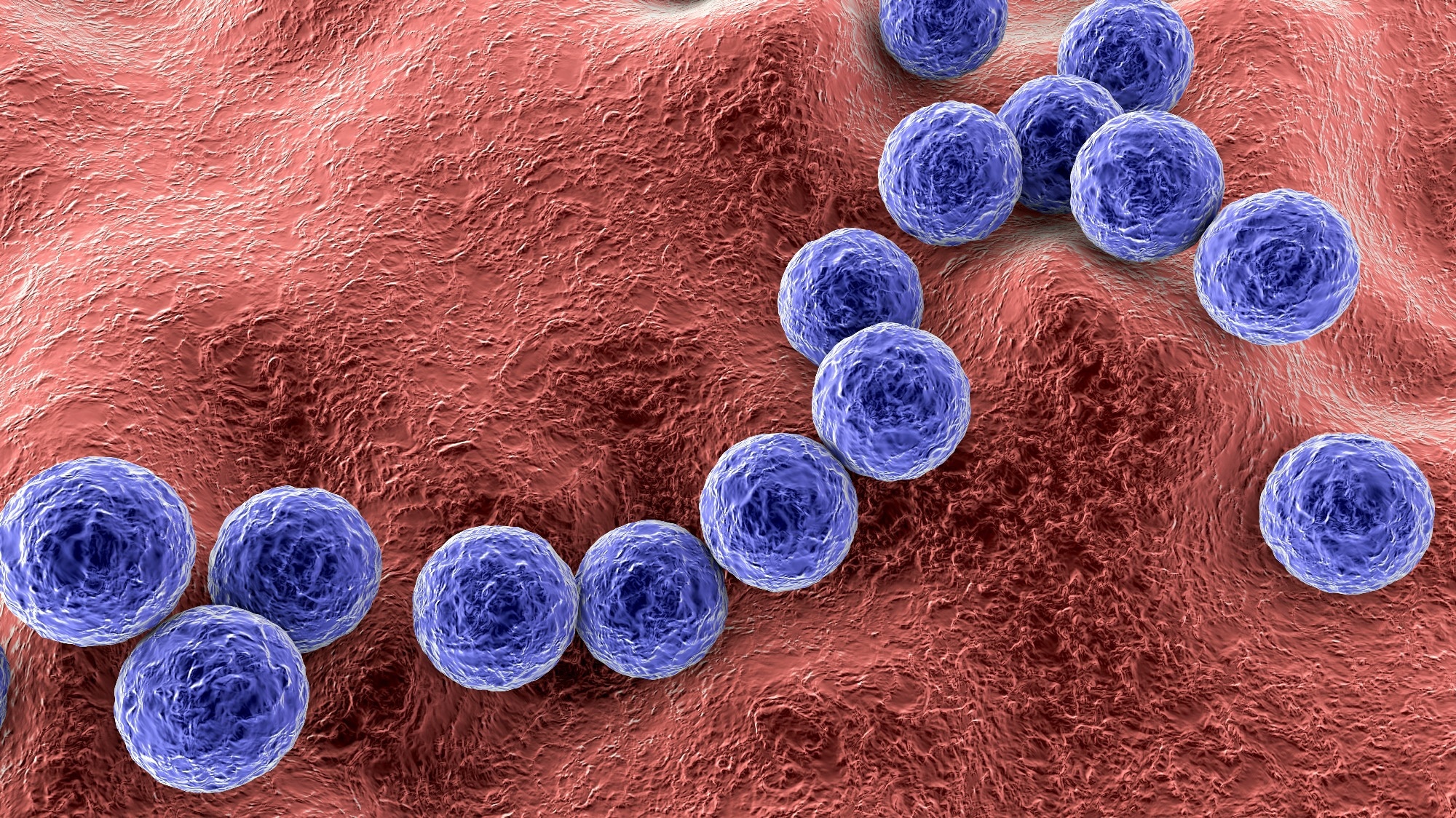
 Gram positive bacteria Streptococcus agalactiae. Image credit: Kateryna Kon / Shutterstock
Gram positive bacteria Streptococcus agalactiae. Image credit: Kateryna Kon / Shutterstock
HMOs inhibit the formation of biofilms
Staphylococcus aureus colonizes the skin and nasopharynx of 30% of the population.
S. aureus biofilms.
Additionally, synthetically modified HMOs demonstrated an enhanced inhibitory effect on biofilm formation. Another study observed a reduction in the viability of bacterial cells within S. aureus biofilms, suggesting cell death. Enteropathogens Escherichia coli (EPEC) is a group of E. coli
in vitro Acinetobacter baumannii, a gram-negative species, is widely known for its multidrug resistance (MDR). A. baumannii occur in intensive care units (ICUs), where patients are immunocompromised.
A. baumanniiA. baumannii and noted significant reductions in biofilm formation for all isolates tested.
Final remarks
A. baumannii et S. aureus.

