1 in 10 people over the age of 65 have dementia Causes and management methods
Person A in her 30s feels that her 70-year-old mother’s forgetfulness has worsened recently. I don’t remember what I was told an hour ago, and I don’t ask once more or often shut off the gas valve. She sometimes forgets her promises, and gets nervous even when she tells them that she has an appointment. Ms. A guessed that it might be the effect of not being able to exercise for more than two years due to the Corona 19 epidemic, and the reduced interaction with her friends. Mr. A, who thought that there were no major problems in her daily life, started to worry that her mother might have dementia.
It is easy to find people around you who complain of difficulties in coming up with words, difficulty in calculating, and missing items one by one following going out. Most of them don’t take it seriously in situations where there are no major problems in daily life and communication is possible. However, experts say that the early stage of dementia should be suspected if symptoms appear repeatedly and short-term memory is significantly lower than before.
If you know first what you forgot, you become forgetful.
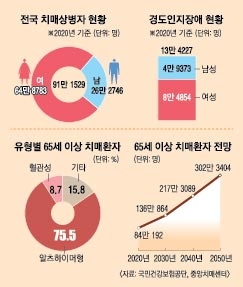
Dementia refers to a condition in which it is difficult to maintain daily life due to cognitive impairment such as memory impairment, concentration, language ability, and calculation ability. According to the ‘Dementia Status in Korea 2021’ published by the Central Dementia Center in April, in 2020, 830,000 out of 8.13 million people aged 65 and over were diagnosed with dementia. That is, 1 in 10 elderly people suffer from dementia. As the elderly population increases, it is predicted that 1.36 million people over 65 will have dementia in 2030 and 2.17 million in 2040.
Dementia has slightly different symptoms depending on the cause. Alzheimer’s disease, a typical disease that causes dementia, is a degenerative neurological disease in which abnormal proteins such as tau protein accumulate in the brain and brain neurons die. Symptoms such as memory loss or language disorder gradually worsen over a long period of time, so it is difficult for you or your family to notice the symptoms in the early stages.
On the other hand, vascular dementia, another cause of dementia, occurs when large and small cerebral blood vessels are repeatedly blocked and brain tissue is damaged, and the symptoms worsen relatively rapidly or in steps. 30% of Alzheimer’s disease patients show mixed dementia with vascular dementia.
Professor Kim Eo-soo of the Department of Psychiatry at Severance Hospital said, “In frontal lobe dementia or vascular dementia, where dysfunction occurs first in the frontal lobe, the front part of the brain, personality changes or depression or language disorders appear first. The memory may deteriorate first.”
For this reason, mild cognitive impairment, in which memory is markedly lowered, is not dementia and should be carefully considered. According to several studies, 10% of patients diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment are diagnosed with dementia one year later, and 80% progress to dementia within six years. In some cases, the condition improves, so it is important to receive an accurate diagnosis and to make active efforts to prevent the progression to dementia.
Avoid sugary foods and eat plenty of vegetables and protein
So, how do we differentiate between forgetfulness and mild cognitive impairment? Forgetfulness, a symptom of aging, refers to temporary forgetting due to insufficient capacity when you have to remember several things at once. It is different from dementia, in which the symptoms of forgetting memory appear suddenly and then recover. Kim Hee-jin, a professor of neurology at Hanyang University Hospital, said, “If you know what you have forgotten first, you are forgetful, and if others find out first, you should suspect dementia or mild cognitive impairment.” In the early stages of mild cognitive impairment, he does not know or deny that his memory deteriorates.”
To prevent dementia, it is helpful to follow basic health rules such as regular exercise, smoking cessation, and abstinence from alcohol. It is better to exercise for 40 minutes a day, slightly sweating, than to exercise vigorously for a long time at once. Both obesity and underweight can adversely affect cognitive function. It is recommended to avoid sugary foods and eat vegetables and foods high in protein.
●Chopsticks and chewing food are good for brain stimulation
It is also good to increase social and leisure activities. It has been reported that seeing friends, family, or relatives once a month lowers the risk of dementia by 15%, and seeing them every day reduces the risk of dementia by 40%. Activities such as reading, reading newspapers, and learning new languages can also be effective in maintaining cognitive function. Just chewing with chopsticks and chewing food can give good stimulation to the brain.
But the most important thing is a positive attitude to life, experts advise. Depression reduces memory, and people who are stressed or worried are more likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease. The brain also needs adequate rest.
If you have been diagnosed with dementia, drug treatment is important. In mild dementia, the goal is to maintain cognitive function as much as possible and to delay late-stage dementia. In Korea, many vascular dementia symptoms can be improved with drug treatment, and depression, which 40% of dementia patients suffer from, can also be controlled with drug treatment. It is also important not to stop taking cognitive function improvement drugs as soon as possible. Even if you don’t feel the effect right away, if you stop taking the drug, your cognitive function will drop significantly following 1 year, and even if you use the drug once more, the effect of the drug will decrease.
Recently, there are many non-drug treatments to improve cognitive function.
Jinsan Lee, a professor of neurology at Kyunghee University Hospital, said, “Pharmaceutical treatment is meaningful in relieving the course of the disease and maintaining daily life for a long time. There are not a few patients who give up following being diagnosed with dementia, but dementia is a manageable disease.”
Dementia is not limited to people over the age of 65. Early-onset dementia occurs between the ages of 45 and 65, and symptoms worsen a little faster than senile dementia. If a parent or sibling has dementia or has various adult diseases, the risk of developing dementia in early childhood is relatively high. Habitual excessive drinking can destroy brain cells and lead to alcoholic dementia.
Reporter Kim Joo-yeon