Mr. Vuong is a programmer in a company, often working overtime because the program is not completed. Recently, he has always felt severe pain in the chest area, the pain is worse following taking a deep breath or sneezing. Mr. Vuong checked the symptoms on the Internet and all he found was serious heart disease.
He was very scared and rushed to the hospital’s cardiology department for an examination but the electrocardiogram showed everything as normal. The doctor asked him to go to the thoracic surgery department. After asking regarding Mr. Vuong’s medical history and examining chest images, it was diagnosed that he had intercostal neuritis.
For most people, heart problems are the first thing they think of when they have chest pain. But in addition to the heart, there are many tissues and organs in the chest cavity, so chest pain doesn’t necessarily mean “heart attack“.
Chest pain is not necessarily a “heart attack”, need to be careful of 4 diseases
The first disease: Gastroesophageal reflux disease
In daily life, many people may feel a burning pain in the chest area following eating, the pain will increase when lying down. This often occurs in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease.
After eating, food enters the stomach through the esophagus. The esophagus has an anti-reflux barrier so it can prevent the occurrence of acid reflux. However, when your anti-reflux function is impaired, the esophageal clearance function decreases, the anti-reflux balance is disrupted, at this time the contents of the stomach will back up, causing irritation to the inner wall of the esophagus. .
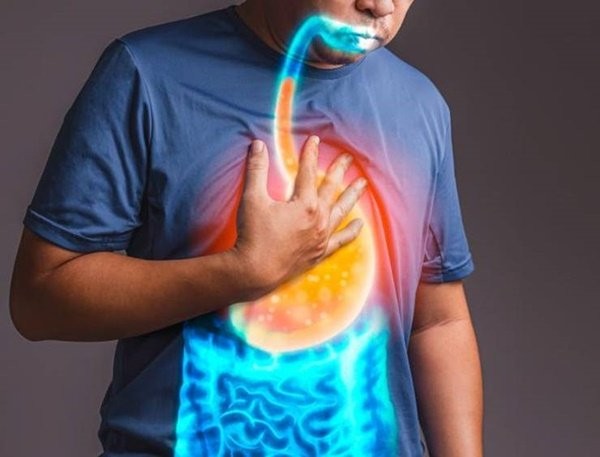
After the esophagus is irritated, there may be chest pain behind the breastbone, similar to angina. Therefore, in clinical practice, many people believe that chest pain is caused by heart disease, but was later found to be caused by gastroesophageal reflux. However, the typical symptoms of GERD are not chest pain but heartburn and regurgitation that causes you to feel a burning sensation behind your breastbone.
Second disease: intercostal neuritis
Mr. Vuong at the beginning of the article suffering from ankylosing spondylitis due to sedentary work will continue to compress the patient’s intercostal nerves, leading to an inflammatory reaction of the intercostal nerves.
Most patients with intercostal neuritis are infected with the herpes zoster virus, which causes an inflammatory reaction in the intercostal nerve, thereby causing pain in the area supplied by the intercostal nerve. It can also be caused by diseases such as thoracic spondylosis, meningitis, etc., causing the intercostal nerves to be pinched, causing pain and discomfort.
After the disease, the patient will feel tightness and burning pain in the chest area. When the patient coughs, takes a deep breath, or sneezes, the pain may worsen. In addition, most of the patient’s pain occurs on one side of the intercostal nerve, presenting specifically as pain in one or two ribs.

Clinically, intercostal neuritis is often secondary to other diseases, so the treatment is usually aimed at the cause such as antiviral therapy, anti-tumor therapy, etc. In addition, analgesic therapy will be performed. depending on the severity of the patient’s pain, the commonly used methods are: drug therapy, physical therapy, blockade therapy, etc. I need to remind everyone that when severe chest pain occurs, should prioritize rest and avoid strenuous exercise as much as possible, so as not to aggravate your discomfort.
Third disease: Pulmonary embolism
When the patient’s venous blood flow is stagnant, the risk of thrombosis increases. When the pulmonary artery is blocked by a thrombus, the patient’s pulmonary artery pressure increases, which in severe cases can lead to ventricular hypertrophy, heart failure, and even death. There are many risk factors for venous thromboembolism, such as tumor, smoking, obesity, and high blood pressure.
Pulmonary embolism lacks specific symptoms and is therefore often overlooked. After a pulmonary embolism, the patient will have episodes of shortness of breath and shortness of breath, the specific level depends on the extent of the arterial embolism. In addition, the patient will also have chest pain, but the pain area is usually small and may worsen following exercise. In addition, regarding 30% of patients may have hemoptysis but not much bleeding.

Fourth disease: Syphilis
Everyone knows that syphilis is a relatively “common” venereal disease, who would have thought that syphilis might be associated with chest pain? For many people, syphilis and chest pain seem like “a tale of two worlds”. As everyone knows, chest pain caused by syphilis should not be underestimated.
When syphilis causes acute aortic inflammation, it will cause discomfort at the top of the heart, in addition, it will spread to the left shoulder and left neck, easily mistaken for a heart attack. If the site of inflammation of the aorta is very close to the opening of the coronary artery, it will cause coronary insufficiency, so angina will also occur.
When the aorta is dissected by syphilis, it can cause chest pain that resembles a heart attack. Moreover, the scope of influence is wider and the level will be deeper. Not only the chest, but the back, neck… will also feel intense pain.
Therefore, when chest paindo not rush to think that it is a heart disease, but be alert for early warning of the above diseases.
How to tell if chest pain is a “heart attack”?
Under normal circumstances, when chest pain occurs, it is first suspected that it is caused by a heart disease such as coronary artery disease, which is correct. But not all chest pain is a heart attack. There may be other factors, such as excessive anxiety, cervical spondylosis, etc.
1. Distinguish from chest pain details
Attention should be paid to the patient’s time of onset, if angina, which usually occurs when myocardial oxygen consumption increases during work, exertion, and emotional agitation.
On the other hand, we should pay attention to the duration of the pain, the nature of the chest pain. Angina usually lasts no more than 15 minutes, while chest pain due to other illnesses often lasts for hours or even days. Furthermore, non-angina chest pain often presents with sharp, thunderous, tingling pain…

2. Pay attention to see if there are any other symptoms
If you experience chest tightness and pain with no apparent cause and your symptoms do not improve following taking nitroglycerin as directed by your doctor, especially following dinner, the discomfort is aggravated, often accompanied by heartburn and pantothenic acid, you should be alert to the possibility of gastroesophageal reflux, and should do a gastroscopy to rule this out.
In addition, although the main symptom of patients with intercostal neuritis is chest pain, the pain is aggravated by activities such as coughing and sneezing. However, chest pain due to heart disease will not affected by these factors and the pain may subside following a certain period of rest.
When a heart attack occurs, in addition to the pain in the center of the chest, it can spread to other parts of the body, such as the back and shoulders. However, chest pain from other causes often has a specific location of pain.
Of course, the most accurate way to tell the difference is to promptly go to the hospital for an electrocardiogram, a color echocardiogram, and other tests. In general, if there is damage to the heart, the patient’s electrocardiogram will be abnormal. If the chest pain is caused by other diseases, the patient’s electrocardiogram shows no abnormalities, at this time, other tests are being conducted to clarify the specific cause and treat the symptoms.
Now say symptoms can be used to judge whether chest pain is caused by heart disease or not, so when a heart attack occurs, besides chest pain, what other symptoms will appear?
3. When having a heart attack, there are usually the following symptoms:
First of all, if you have problems like ventricular hypertrophy, arrhythmia, heart failure, you may feel your heart beat irregularly, or feel nervous. This is mainly because following a heart problem occurs, the heart’s blood supply and nerve function are not normal, leading to the heart beating too fast and causing the uncomfortable feeling of palpitations.
Secondly, when the patient is active and tired, he may feel a dull pain, tingling in the pre-cardiac area, which will usually subside following a short period of rest. But there are also more serious cases, such as chest pain accompanied by a persistent burning sensation that does not go away, even a feeling of near death.
If the patient has heart failure problems, they may experience shortness of breath following exercise or fatigue, and may even wake up following falling asleep because of shortness of breath. In addition, the patient’s ankles and calves may develop pitting edema, i.e. the skin cannot recover following finger pressing and release.
Finally, many patients with heart failure may develop cyanosis of the lips, fingernails, and other organs. This phenomenon appears to be related to the impaired pumping function of the heart, leading to a decrease in oxygen levels in the blood. In the case of heart failure, the patient’s heart cannot complete the activities of contraction and relaxation, resulting in insufficient pumping volume.
If there is a problem with the heart function, the normal function of other organs in the body will be affected, and the body will also show the above unpleasant symptoms, seriously reducing the quality of life. of the patient. Therefore, in daily life, we should do a good job of nourishing the heart, maintaining the normal functioning of the organs in the body.
4. What to do to protect your heart?
For people with bad heart should limit eating a lot of fatty foods, because when eating too much fat will accumulate in blood vessels, thereby affecting blood circulation, at this time cardiac output will decrease. increased, the disease also worsened. the workload of the heart. Over time, heart function may gradually decline and the risk of heart disease may increase. In addition, you should also reduce the amount of salt you eat. Eating too much salt will lead to water and sodium retention, at which time the pressure on the heart and blood vessels will increase, which is not good for heart health. Therefore, you should eat plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables and whole grains at normal times, which will help your heart health.
You should also stick to exercise in your daily life. Exercise can improve the body’s metabolism, thereby helping the body eliminate waste in the blood vessels, reduce the risk of arteriosclerosis, and reduce the burden on the heart. However, we need to remind people that when choosing sports, it is best to choose lighter sports to avoid cardiovascular events caused by overexertion.

In addition, it is necessary to ensure adequate rest, especially not staying up late, the reason we sleep in is because the organs in the body need rest. If you often stay up late, it will change the heart’s rhythm, increase the risk of arrhythmias, thereby reducing heart function and the incidence of heart disease will increase.
The last thing is to fix the smoking habit. Tobacco contains many harmful substances, if the human body ingests in large quantities, it can make the heart beat faster, increase oxygen consumption, constrict blood vessels, thereby increasing the risk of heart disease.
After lighting a cigarette, a large amount of carbon monoxide is produced, which reduces the oxygen content in the blood. When other organs in the body are not supplied with enough oxygen, the heart needs to speed up blood circulation to ensure the normal functioning of other organs in the body. Therefore, this habit for a long time will increase the workload for the heart and affect the health of the heart.



