Psychiatry News | Chong-ki Kim, Specialist in Psychiatry
What is Anxiety? Basically, anxiety is the emergency siren that our body makes.no see. It’s a kind of alarm that strains your body and mind so you can prepare for a dangerous situation. Because Anxiety is an essential instinct for our survival and adaptation.It can be said that If we are not anxious, we are not nervous, and if we are not nervous, we cannot survive in the jungle, and we cannot compete in society. A certain amount of anxiety is certainly the stress we need.
then What is the difference between anxiety and fear? Fear is also an emergency siren and alarm posture for escaping or fighting a dangerous situation.no see. In fact, the area of the brain responsible for fear and the area of the brain responsible for anxiety are very similar. However, the term ‘fear’ is used when the identity of the danger is very clearly imminent.You can. Relatively, ‘anxiety’ is a term used when there is a danger that is a little further away or that has not yet arrived, or when the target is ambiguous. For example, consider walking alone through a dark alleyway in a dangerous neighborhood late at night. Anxiety is the emotion you feel when you are nervous and withdrawn, worrying that someone will suddenly jump out of the alley or a ghost will come out. Then, when a killer with a chainsaw really appears in front of you, the emotion you feel at that time is fear. Of course, in most situations, anxiety and fear are mixed.

Anxiety and fear, as I said, are fundamentally ‘readiness for danger’. Thus, whenever our body is anxious and fearful, it unconsciously prepares to fight (Fight) or flee (Flight) a dangerous target. A Fight or Flight reaction appears.

How would you react if a killer appeared in front of you as in the previous example? To run away or fight back as fast as possible, your muscles need to exert more force than usual. Because of this, the muscles of the body contract and become tense as they prepare to use force. Also, because it has to pump more blood to the muscles, the heart starts pounding in advance and pumping out more blood faster. The pupil dilates to receive and observe as much light as possible. To conserve body temperature and look puffy, the hairs on the skin begin to stand up. The hairless part only shrinks the pores and gives goosebumps like chicken meat. How are you? Can you imagine?
Our body has a system that automatically directs this series of reactions.There is this. Right away autonomic nervous system(Autonomic Nervous System). Autonomic nervous system, as the word ‘autonomy’, is a nervous system that we cannot control ourselvesthat is. Just as we can’t control our heart rate or the size of our pupils at will, our autonomic nervous system controls them.
As in the previous example, the autonomic nervous system has a system that makes us tense – the ‘sympathetic nervous system’, and on the other hand, there is a ‘parasympathetic nervous system’ that relaxes us. In other words, Anxiety is the same as being active in the sympathetic nervous system.no see.
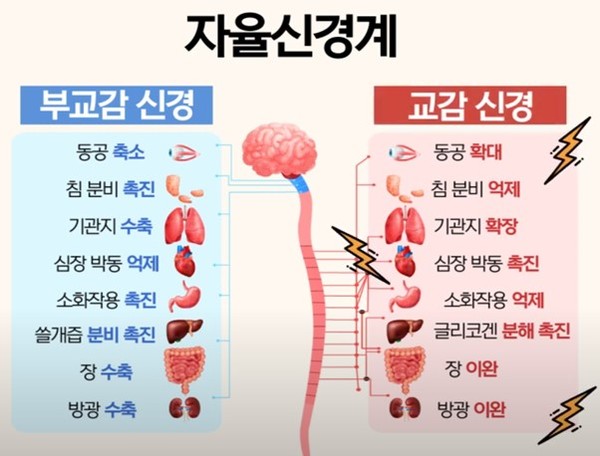
As with all mental disorders, Anxiety disorders also occur when excessive anxiety occurs, or when problems in daily life occur due to excessive anxiety. In other words, when the sympathetic nerve is activated excessively, when the sympathetic nerve is activated inappropriately, we can develop an anxiety disorder. You should only be properly tensed when you are in a really dangerous or tense situation, and if your sympathetic nervous system is ramping up even when you’re comfortably resting, you can get an anxiety disorder.
So, why does it happen? Why is the sympathetic nervous system working unnecessarily? As with most psychiatric disorders, there are many different causes of anxiety disorders.

A wide variety of factors, such as genetic factors, growth environment, external factors, and biological conditions, disturb the activity of the autonomic nervous system.You can do it. Because the autonomic nervous system is controlled through a series of systems that run from the adrenal gland (the tiny little thing attached to our kidneys) to the pituitary gland and then the hypothalamus, it can be disrupted when this system is broken. Disruption of this system means that many of the hormones that regulate it are either over-secreted or under-secreted.
First of all, before the biological cause of anxiety was discovered, Freud thought that the cause of this anxiety was a conflict in our subconscious. We all have biological and primordial instincts and needs. Our subconscious desires, sexual and destructive and love needs, are so animalistic that they have no time, no time, no direction, just like animals do. Although we may not be conscious of it. However, as they evolve into social animals, and grow up through nurture, they are unable to act according to their original desires. Freud called the superego, the identity that speaks in our subconscious once morest these desires, the identity that says, “You must not do that.”
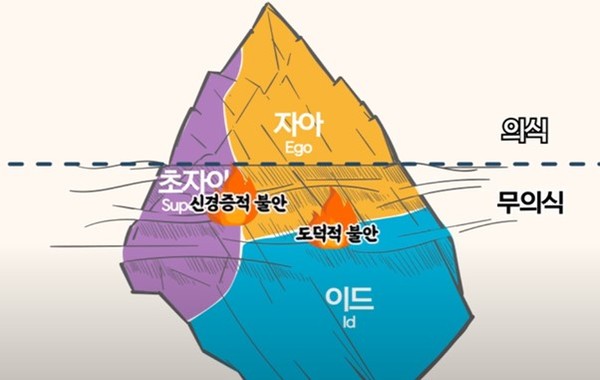
Because of this superego, or even if it’s not within the superego, realistic circumstances make most of our desires unfulfilled. Freud thought that the psychological conflict that occurred in this process was ‘anxiety’. We also said that because this ‘anxiety’ is painful, we ‘repress’ emotions such as desire, anxiety and anger.
Brain imaging studies have shown that the most active area during anxiety is the amygdala in the center of the brain. And in fact, it has been shown that the amygdala can be activated by unconscious stimuli without the influence of external stimuli or conscious memory. Most patients with anxiety disorder have excessive activation of the amygdala.can be observed.

or Anxiety disorders can be explained by behavioral medicine do. The fear response we experience in a threatening situation is learned by our body and conditioned as a kind of reflex.no see. You may be familiar with the conditioned reflex experiment, in which a dog salivated by ringing a bell and feeding it, and then salivating the dog just by ringing the bell without food. Similarly, the fear response experienced in a particular situation is subconsciously conditioned with something else in the situation, and later, when another stimulus similar to the situation is received without a dangerous object, the fear and anxiety responses are reflexively produced.
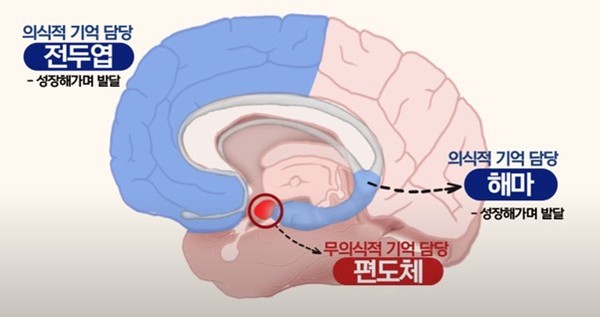
In fact, the amygdala, which stores our unconscious anxiety memories, is fully developed from the time we are born. But our conscious memory, the memory systems we can recall, the frontal lobe and hippocampus, are still underdeveloped at birth. The reason we don’t remember events in newborns isn’t because we’re too old, but because our brains aren’t developed enough to store events in the first place. However Since the amygdala is fully developed, the memory conditioned by the anxiety response is stored.This might be In that case, In childhood, when we encounter a conditioned object, we suddenly and subconsciously become anxious, but we cannot recall the memory, so we may not know what makes us anxious. Being unnecessary and excessively anxiousno see.
Because the factors that cause anxiety are so diverse, anxiety disorders can appear in many different forms. The form and course of anxiety disorders will vary from person to person and from situation to situation. DSM generally classifies anxiety disorders as follows:are doing

However, even if you suffer from the same anxiety disorder, as mentioned above, the origin and mechanism may be different, so the approach and direction to treat the anxiety disorder must be tailored accordingly.
Onan Mental Health Clinic | Director Kim Chong-ki


